Node.js is quite a powerful and popular tool for both server and application usages. Throughout this blog, we will go through Node.js’ installation process and set it up and have it ready to run on your system.
The tutorials will go through the installation process for different Linux distros like CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, and Fedora.
What is Node.js?
Node.js is a JavaScript platform as the ‘js’ suggests which is used for general-purpose programming. It is designed for users to build scalable network applications quickly and efficiently. Node.js used JavaScript in both the front-end and back-end, making the development more consistent and providing designs within the same system.
If you're ready to experience the power of VPS hosting, check out our range of Cheap VPS plans tailored for performance and affordability. You can also explore our Trial VPS to test our services before committing. For those needing flexible and scalable solutions, our VPS Rental options and diverse VPS Locations ensure your server is perfectly aligned with your project requirements.
To explain how Node.js works, let me walk you through a simple situation: Open a file on a server and return it to the client.
In PHP or ASP, the process is as follows:
- Sends the task to the computer’s file system
- Waits while the file system opens and reads the file
- Returns the content to the client
- Ready for the next request
However, in Node.js, it eliminates the waiting time and continues to the next request.
- Sends the task to the computer’s file system
- Ready to cater to the next request
- When the file system has opened and read the file, the server sends the content to the client
HTTP is the best usage of Node.js, which is designed with low-latency and streaming in mind.
For a deeper understanding of the Linux operating system, which serves as the foundation for many VPS setups, check out our guide on What is Linux.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Node.js
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
A single programming language: JavaScript |
No basic libraries or tools |
|
Runs single-threaded processes |
Multithreading is not supported. |
|
Uses asynchronous non-blocking programming |
Not suitable for heavy processing |
|
Uses a microservices architecture |
Inadequate for relational data access |
|
Free Node package manager |
|
Prerequisites
Throughout this article, we will go through the installation guide for CentOS, RHEL, Fedora, Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint. You will need to buy linux vps with root privileges or a non-root user account with Sudo privileges.
How to install Node.js in CentOS, RHEL, and Fedora
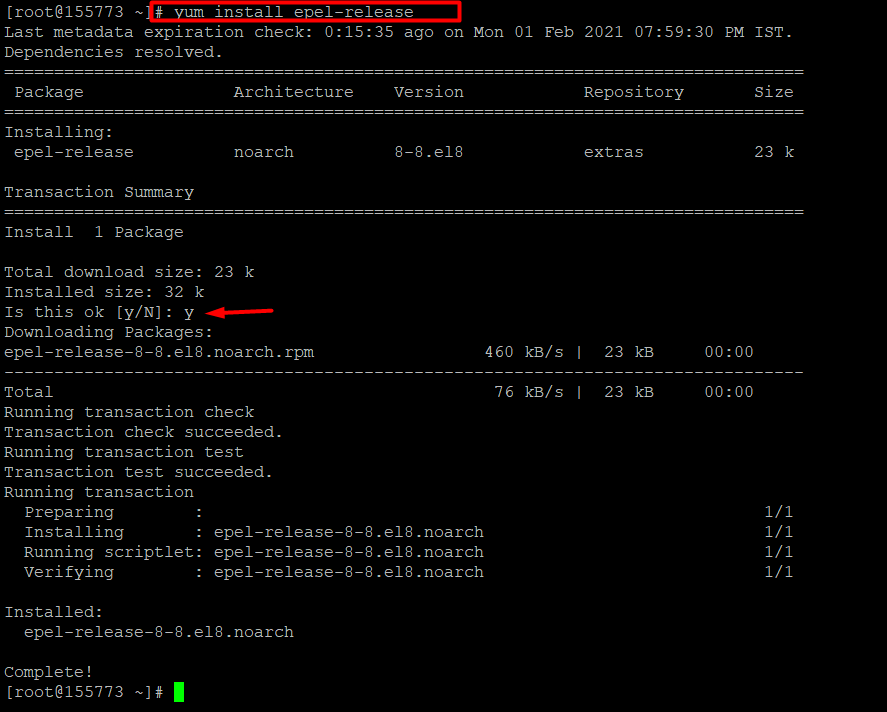
Step 1: Install epel-release on the server
To install Node.js on CentOS or RHEL, the easiest is to install it through the EPEL repositories. For that, let’s install the epel-release first:
# yum install epel-release
When prompted, enter ‘y’ to continue.
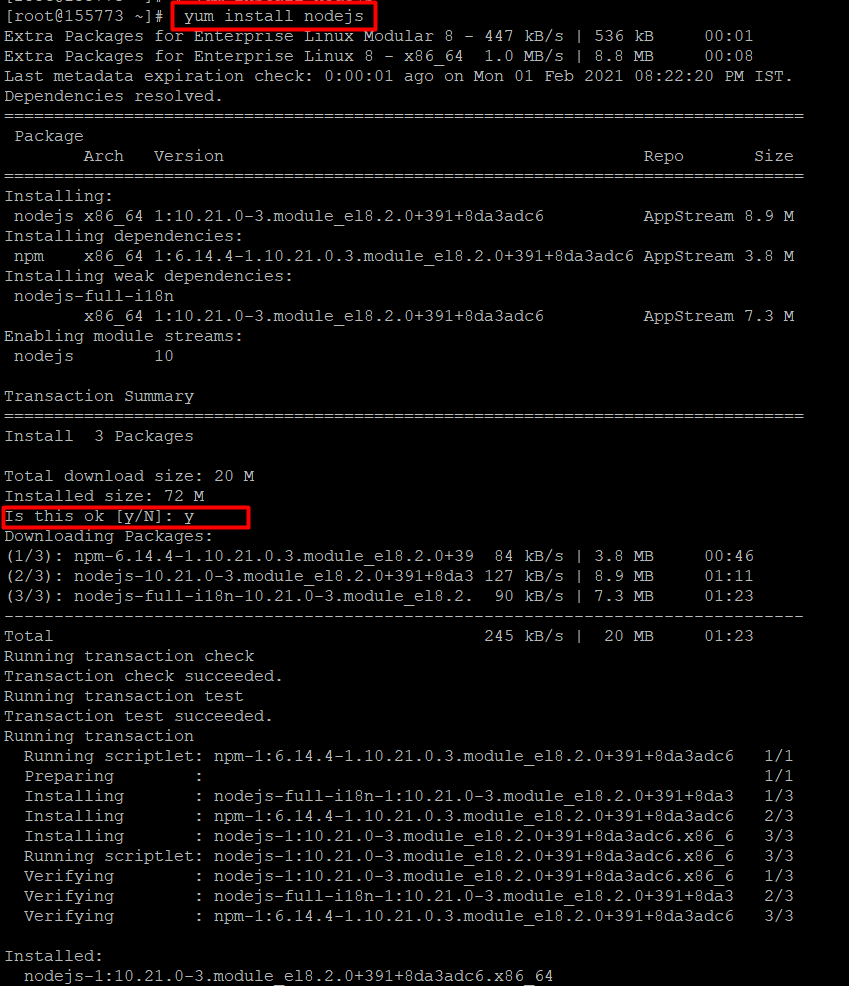
Step 2: Install Node.js on the server
Now let’s install Mode.js package on your system. For this tutorial, I will be using CentOS 8 Linux server. When prompted, don’t forget to enter ‘y’.
# yum install nodejs
It will take a few seconds to complete the installation.
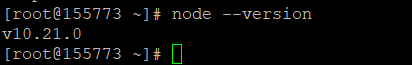
Step 3: Check the Node.js installed version
Now to check if the installed version is correct, enter the following command.
# node --version
How to install Node.js in Ubuntu, Debian, and Linux Mint
For this tutorial, we will be using Ubuntu 18.04. The process is similar when installing on Debian and Linux Mint.
There are two ways to install Node.js on Ubuntu.
- Installing from Ubuntu official repository
- Installing from NodeSource repository
Step 1: Ubuntu official repository
Node.js is available in Ubuntu’s repositories and it’s relatively easy to get it up and running with a few Linux commands.
- Open the terminal
- Use the following command to install node.js
sudo apt install nodejs
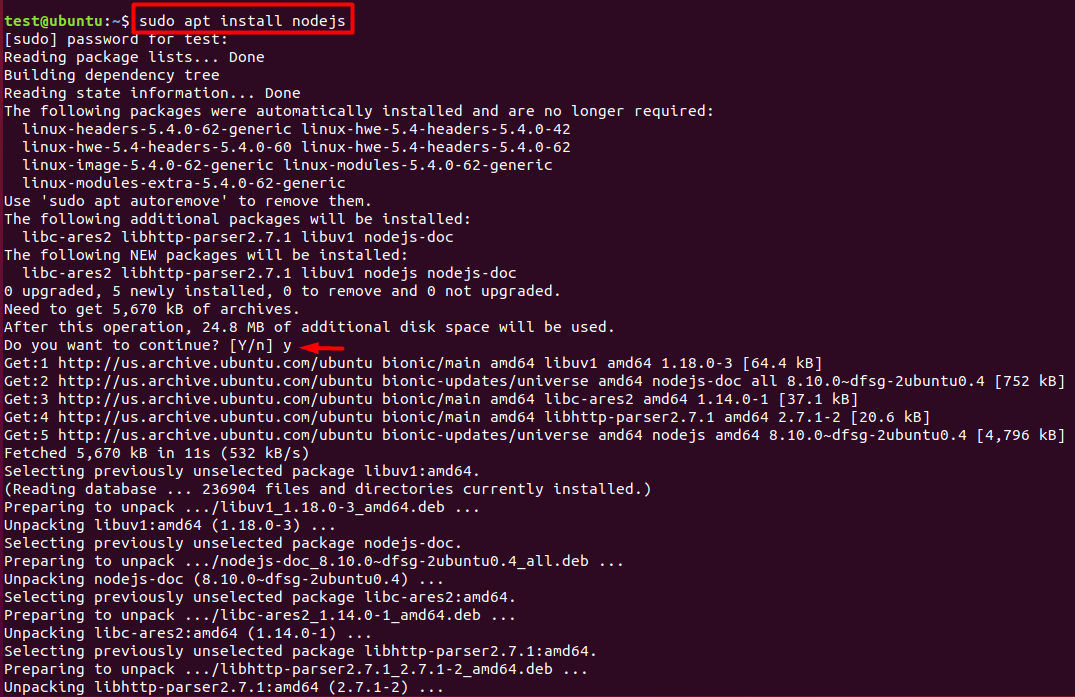
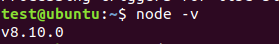
- Once installed let’s verify it by checking the version installed.
node –v
- It is highly recommended to install the Node Package Manager (NPM) together with Node.js. NPM is an open-source library that contains Node.js packages.
sudo apt install npm
npm –v

Congratulations! You have successfully installed and set-up Node.js on your Ubuntu server.
Looking to practice Linux commands online? Check out our guide on the best online Linux terminal for a convenient way to sharpen your skills.
Step 2: NodeSource repository
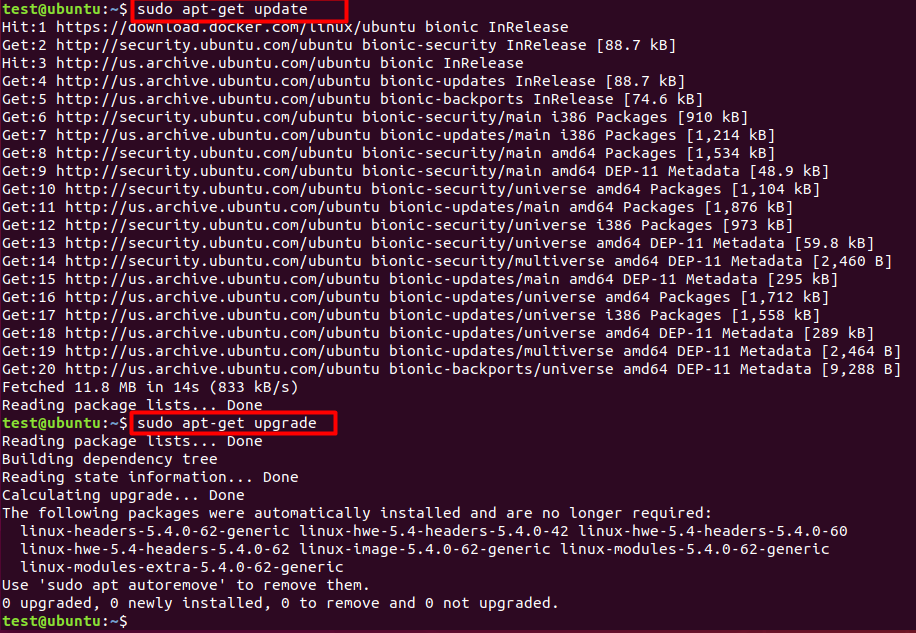
- Update and upgrade the package manager
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
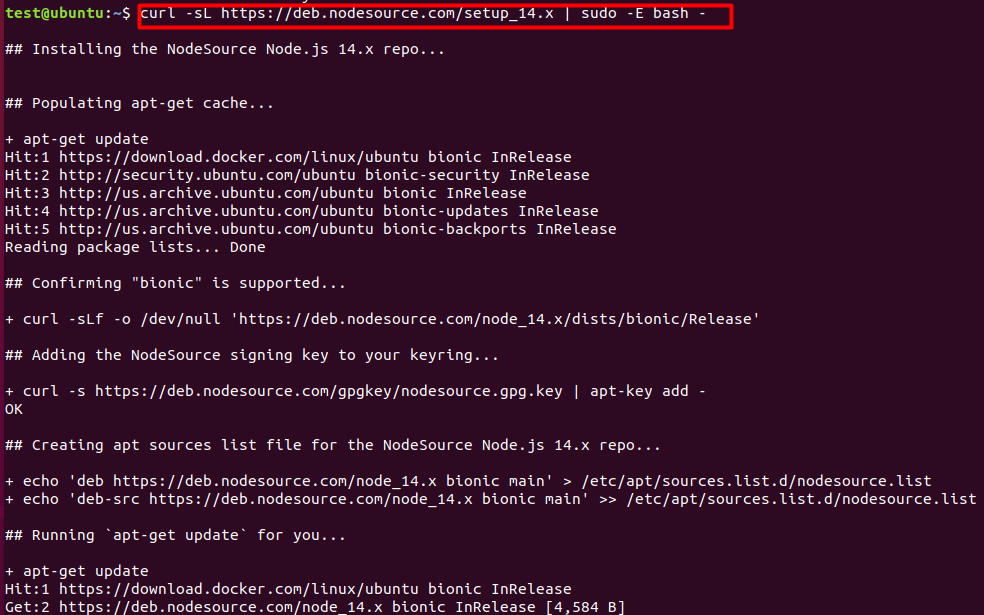
- Add the Node.js PPA to the system
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | sudo -E bash –
- To install Node.js and NPM, use the following command
sudo apt-get install nodejs
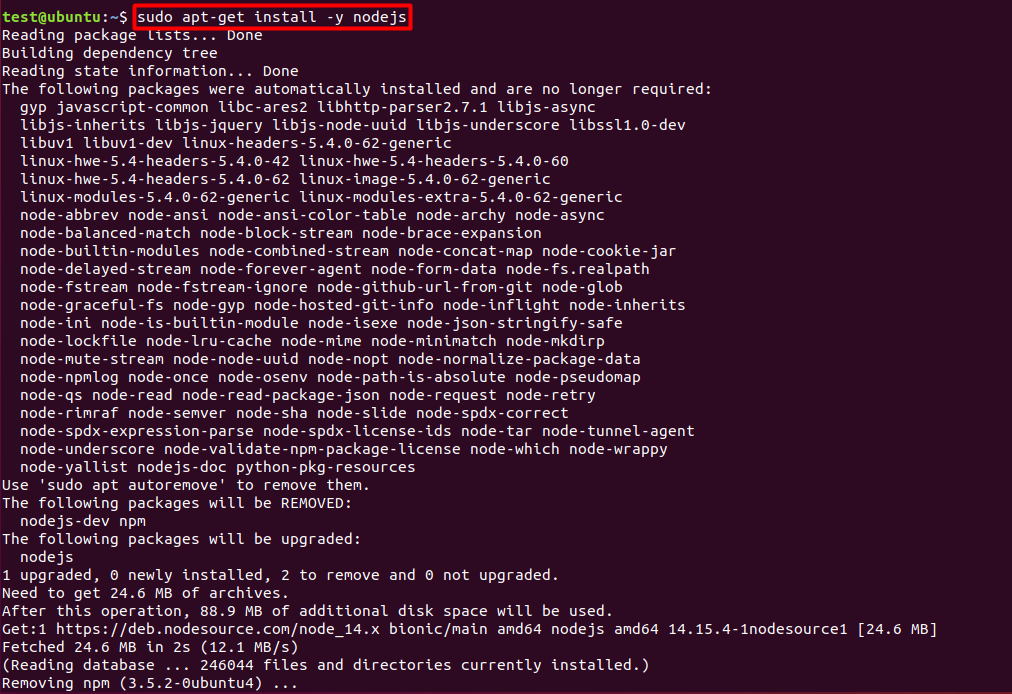
- Once it’s installed, verify it by checking the installed versions
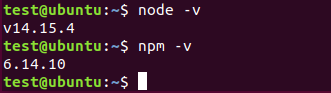
node –v
npm –v
Conclusion
It wasn’t as hard as you thought, right? Relatively simple steps to get Node.js installed successfully on your system. If you come across some errors or problems by any chance, let us know in the comments below, and we will get back to you.
If you’re interested in exploring other options, consider setting up a powerful and versatile Ubuntu VPS server. Ubuntu VPS offers a stable and flexible environment for hosting Node.js and other applications seamlessly.
We hope that this tutorial helped you and we welcome all questions, comments, and any additional information regarding this article. Your comments might take some time to appear, and if the comments are off-topic, we will disregard them.
Installing Node.js on CentOS is a breeze! Update your system and use the yum package manager to get started. For those who need a server environment, consider purchasing a VPS [buy VPS server] to deploy your Node.js applications.
People also read:





![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)