Have you ever took a look at your Ubuntu system and wondered what programs are installed? Perhaps you installed something a while ago and can't remember the name, or you're clearing away unused software. Fear not, Ubuntu user! This blog post will share the secrets behind Linux Ubuntu List Installed Packages command line on your system. We'll look at simple ways to view exactly what software is taking up space on your laptop, allowing you to fully control your Ubuntu environment.
Ubuntu list installed packages by date and time
To Ubuntu list installed packages by date and time, you can use the `dpkg` command along with some additional utilities. Here's a step-by-step guide:
-
Open a terminal window.
-
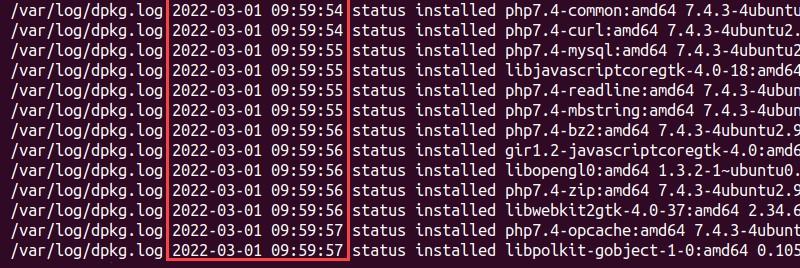
Run the following command to list all installed packages along with their installation dates:
grep " install " /var/log/dpkg.log /var/log/dpkg.log.* | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n | awk '{print $1, $2, $4}'
This option will retrieve and sort the lines providing installation information from the 'dpkg.log' files based on date and time. The output will show the package names, installation dates, and times.
If you want to display the package names only, you can modify the command slightly:
grep " install " /var/log/dpkg.log /var/log/dpkg.log.* | sort -k1,1 -k2,2n | awk '{print $4}'
This will list only the package names sorted by date and time.
Ubuntu list installed packages by size
To Ubuntu list installed packages by size you need to do the following steps:
-
Open a terminal window.
-
Run the following command to list installed packages along with their sizes:
dpkg-query -Wf '${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -n
This command will show a list of ubuntu list installed packages sorted by size in ascending order. Each line indicates the size of the package, followed by its name.
If you want to display the list in descending order (largest packages first), you can add the `r` flag to the `sort` command like this:
dpkg-query -Wf '${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -nr
This will list the largest packages first.
For those looking to deploy a web server, consider following the guide on how to install Apache Tomcat 10 on Ubuntu to get your server up and running.
Ubuntu list installed packages apt
To Ubuntu list installed packages apt package management system, follow these steps:
-
Open the Terminal on your local system or connect to your VPS using SSH via PuTTY or Terminal.
-
Once connected, you need to Ubuntu list all available packages command line. Execute the following command to list all available Ubuntu 22.04 packages:
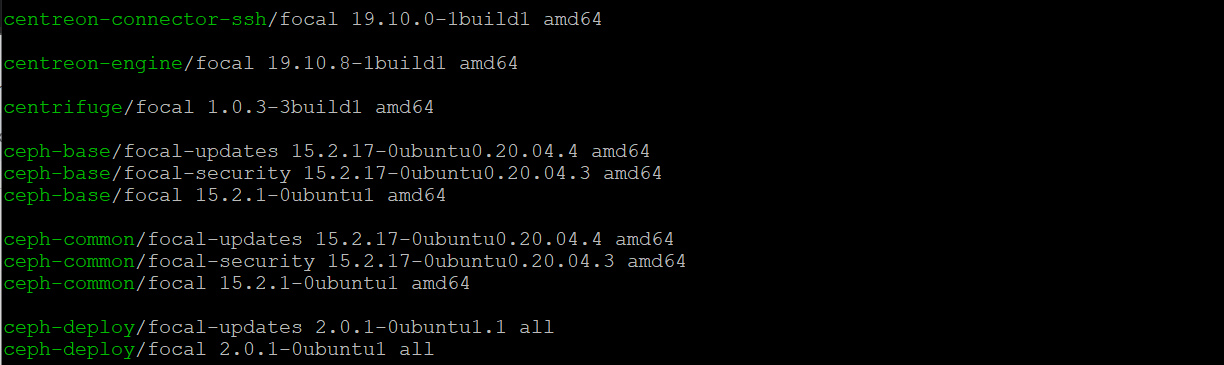
sudo apt list
Now, ubuntu list all available package versions is possible using this command.
-
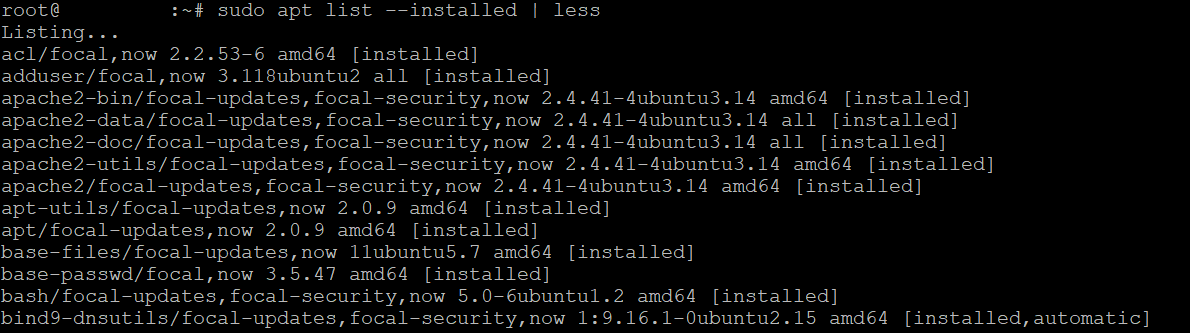
To list only installed packages, use the `--installed` option:
sudo apt list --installed
-
To display a more manageable output, add the `less` argument to compress the output:
sudo apt list --installed | less
-
If you want to check if a specific package is installed, use the `grep` command with the package name:
sudo apt list --installed | grep packagename
Replace `packagename` with the name of the package you're interested in. For example, to list Vim-related packages:
sudo apt list --installed | grep vim
-
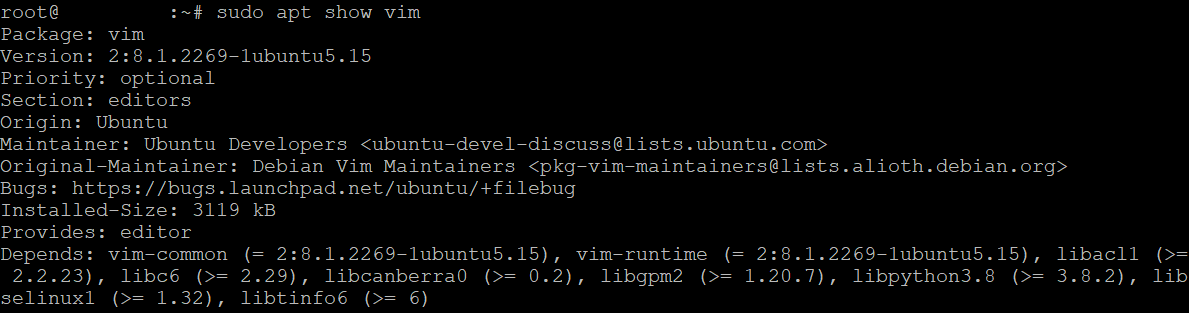
To view detailed information about a particular installed package, use the `apt show` command:
sudo apt show packagename
Replace `packagename` with the name of the package you want to inspect. For example, to view details about the Vim package:
sudo apt show vim
Remember to replace placeholders like `packagename` with the actual names of the packages you're interested in. These commands will help you manage and inspect installed packages on your Ubuntu system.
People also read How to Fix Ubuntu Broken Packages.
Ubuntu list installed packages with version
You can utilize Ubuntu's `apt` commands to ubuntu list installed packages and versions. To begin, run the following command:
sudo apt list --all-versions
This command displays a comprehensive list of all package versions directly in your Terminal window.
To specifically query the installed version of a particular package, append its name to the command. For instance, to check the version of PHP installed, use a command similar to the one depicted below:
sudo apt list --installed php
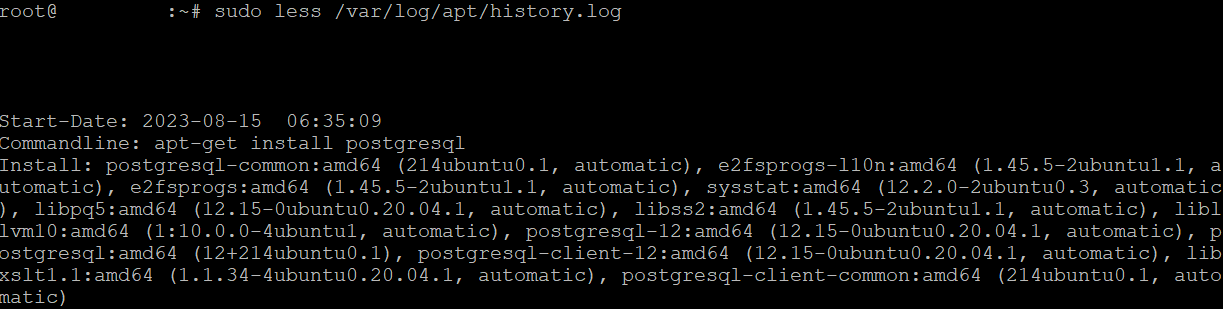
Additionally, users can review log files stored within the `/var/log/apt` directory to track package operations such as removals, updates, or deletions. To access these logs, employ the `less` command:
sudo less /var/log/apt/history.log
This version offers a clearer sequence of steps and explanations, ensuring a smoother understanding of the commands provided.
To further enhance your understanding of system configuration, you may find it helpful to explore how to install BIND on Ubuntu. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to setting up a DNS server, which complements your knowledge of package management on Ubuntu.
Ubuntu list installed packages from repository
Ubuntu list installed packages by repository is also possible. To do that, use the 'apt' command with a few arguments to filter the results. Here's how you can accomplish it:
Open a terminal window and run the following command to list all installed packages from the repository:
apt list --installed
This command will display a list of all installed packages on your system, regardless of their repository origin.
If you want to filter the list to only show packages from a specific repository, you can use the `apt-cache` command in combination with `grep`. Here's how to do it:
First, find the repository of the package you're interested in. You can do this by inspecting the `apt-cache policy` output for a specific package. For example, to find the repository for the `nginx` package:
apt-cache policy nginx
Once you've identified the repository, you can use `apt list --installed` with `grep` to filter the list based on the repository. For example, if `nginx` is from the `main` repository, you can use:
apt list --installed | grep "/main"
Replace `"/main"` with the repository you're interested in. This command will display a list of installed packages that belong to the specified repository.
Ubuntu list installed packages by user manually
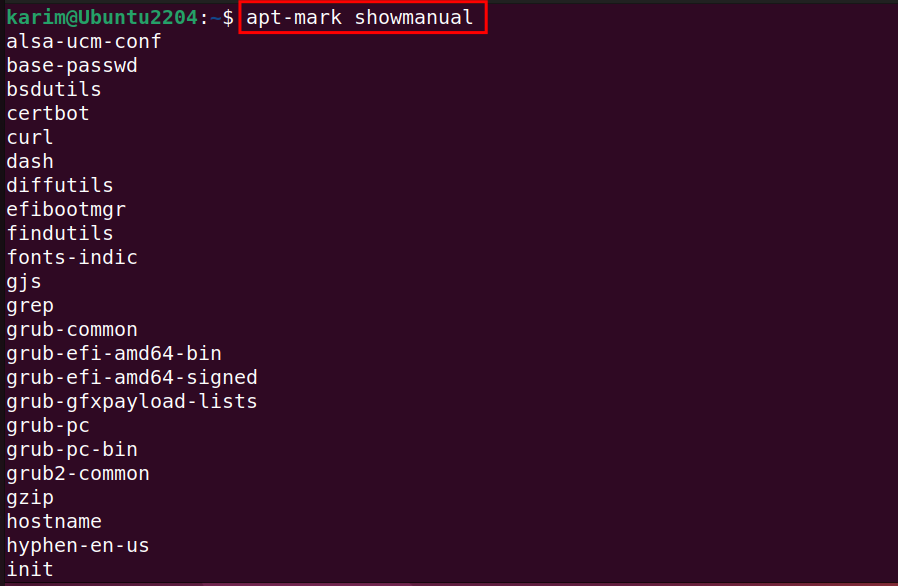
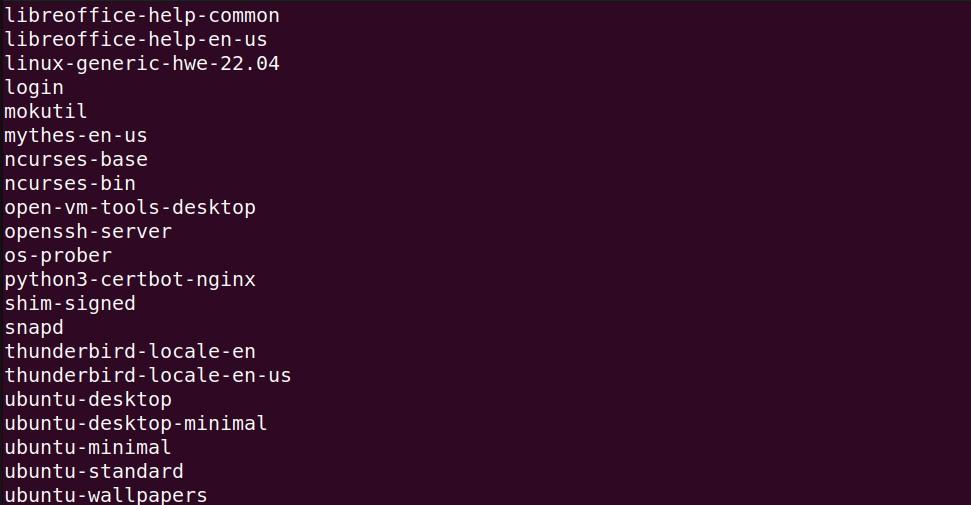
To display a comprehensive list of packages on Ubuntu that a user personally installed, you can run the following command:
apt-mark showmanual
Ubuntu list all packages installed by user will be shown.
Moreover, if you're curious about the total number of packages you've manually installed, you can use the following command:
apt-mark showmanual | wc -l
Executing this in your terminal will promptly present the total count of such packages, providing you with a quick overview of your system's customization.
You can also explore how to set up and work with Django on your Ubuntu system by checking out this comprehensive guide on How to Install Django on Ubuntu. This can help you enhance your development environment with ease.
Ubuntu list installed packages without dependencies
To Linux Ubuntu list installed packages without including their dependencies, you can use the `deborphan` tool. apt-get list available packages versions is used to do that. Here's how to do it:
Install `deborphan` if you haven't already:
sudo apt-get install deborphan
Once installed, you can use `deborphan` to list installed packages without their dependencies:
deborphan --no-show-section
This command will list only the packages that were explicitly installed and not their dependencies.
Alternatively, you can use `apt-mark` to achieve a similar result. Here's how:
-
List all installed packages:
apt list --installed
-
Pipe the output to `grep` to filter out the dependencies:
apt list --installed | grep -v -E 'automatically|automatic'
This command filters out packages that were installed automatically as dependencies, showing only explicitly installed packages.
Choose the method that suits your preference and requirements best!
Ubuntu list installed packages by name
To list installed packages on Ubuntu by their names, you can use the `dpkg` command. Here's how:
dpkg-query -l | awk '{print $2}'
If you want to sort the list alphabetically, you can use `sort`:
dpkg-query -l | awk '{print $2}' | sort
This will list the installed package names sorted alphabetically.
If you want to filter the list by a specific package name or pattern, you can use `grep`. For example, to list packages containing "apache" in their names:
dpkg-query -l | awk '{print $2}' | grep apache
Replace "apache" with the desired package name or pattern you want to filter by.
Ubuntu list installed packages by specific name
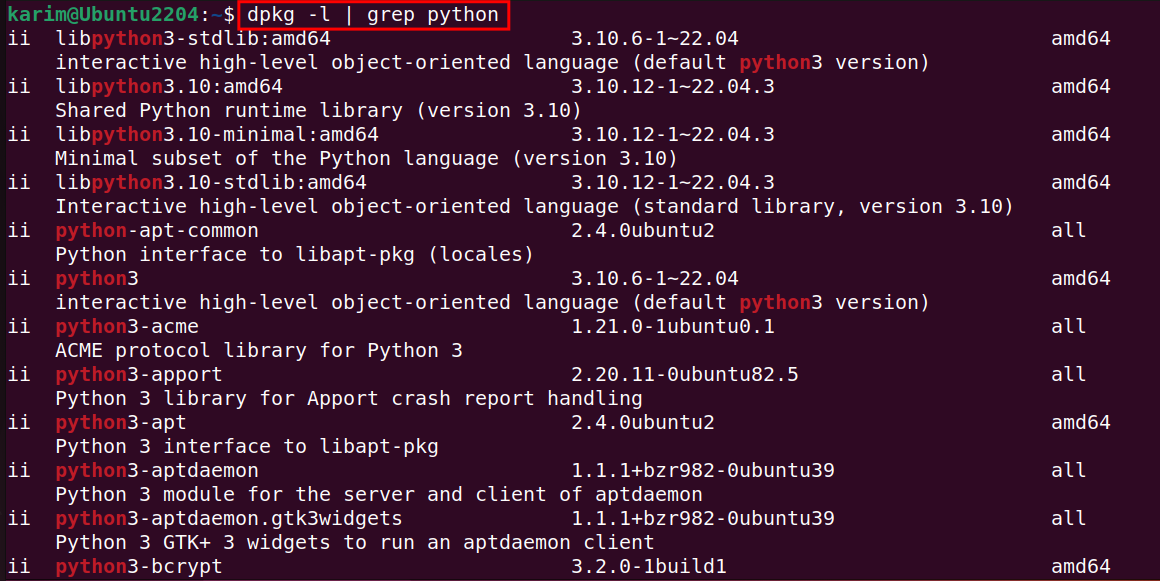
To find a specific package, like "python," within your Ubuntu 22.04 system, use the following command:
dpkg -l | grep python
This command sifts through your installed packages and isolates those related to "python," presenting them in a filtered list.
How to list or find out if a specific package installed or not
To determine whether a specific package is installed on your system, you can use the following command:
apt list -a <package_name>
For instance, to check if the `sudo` package is installed, you would execute:
apt list -a sudo
If the package is installed, its version and other relevant information will be displayed. If it's not installed, the output will indicate that it's not found.
For users looking to set up a web server on Ubuntu, consider checking out our guide on how to install Lighttpd on Ubuntu for a lightweight and efficient server solution.
How to count the installed packages on Ubuntu
You can easily count the number of installed Linux packages using a simple command. It's quite similar to listing the packages, but instead of viewing them, you'll employ a word count command.
Here's how you can do it:
sudo dpkg-query -f '${binary:Package}\n' -W | wc -l
This command utilizes `dpkg-query` to list installed packages and then pipes the output to `wc -l`, which counts the number of lines. The result is the total count of installed packages.
When you execute this command, you'll see the total number of installed packages displayed in your terminal.
Alternatively, you can achieve the same result using `apt`:
sudo apt list --installed | wc -l
This command provides a similar outcome by listing installed packages via `apt` and then counting the lines to determine the total number of installed packages on your system.
You may want to know How to install packages in Linux.
How to list upgradeable packages
To ensure you're checking for available updates in the repository, include the `--upgradeable` option in your `apt` command. Before doing so, synchronize the repository to fetch the latest information using the following command:
sudo apt update
Once the repository is synced, you can proceed to detect upgradable packages by executing:
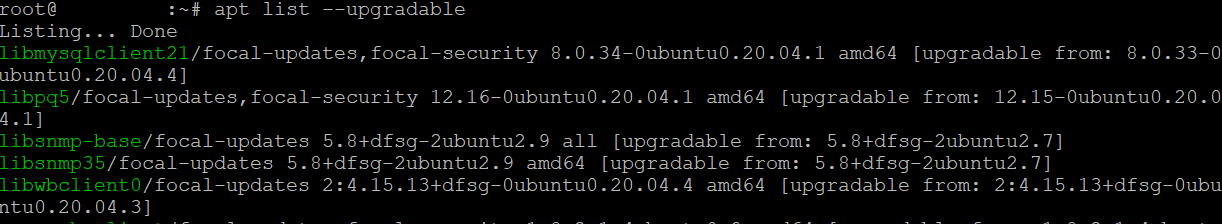
sudo apt list --upgradeable
The output in your terminal will resemble something like this, providing details on available updates for your installed packages.
List installed snap packages
Snap serves as an alternative package manager system. It's worth noting that the previously mentioned commands do not include packages installed through Snap.
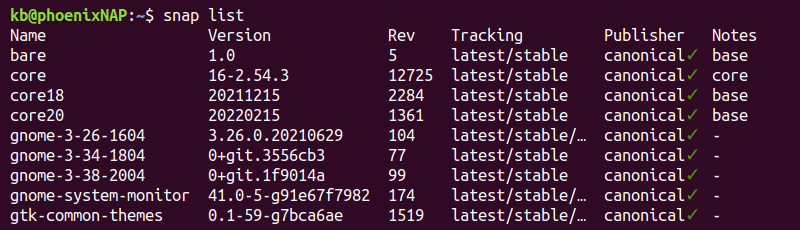
To view a list of installed Snap packages, simply execute:
snap list
This command provides an overview of all Snap packages currently installed on your system.
Conclusion
Being able to list installed packages on your Ubuntu system provides useful information about the software and dependencies that are currently in use. The list installed packages and commands provide full support for exploring packages and their versions, as well as removing or updating them as appropriate. Using this knowledge, you may keep a structured and up-to-date Ubuntu system that matches your particular needs. For those managing an Ubuntu VPS or an Ubuntu RDP server, this capability becomes even more critical as it helps in maintaining system efficiency and security. Regularly checking and managing installed packages ensures that your Ubuntu VPS or RDP server operates smoothly and securely, allowing you to focus on your tasks without worrying about outdated or conflicting software. So, now you know how to check installed packages in Linux command.
People also read:







![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)