What is htop? How do I install htop on CentOS 7? We will cover these two questions throughout the article. Htop is an interactive process viewer for CentOS 7 systems. Many Linux administrators are familiar with the standard process management and activity monitor top.
However, in some cases, the top does not provide all the information you might be searching for. This is where htop comes into play with a real-time and interactive interface with more features than the top.
From CPU utilization to sorting processes to setting priorities: all possible directly from htop. Htop is the predecessor for top command with many advantages. If you ever find yourself locked out and need to reset your root password on CentOS, check out our guide on how to reset the forgotten root password on CentOS for step-by-step instructions.
- Coloured output resource usage stats.
- Ability to end or kill processes.
- Htop allows mouse usage.
- Higher performance compared to the top command.
To learn more about htop, pay a visit to the official website.
Prerequisites
To install htop on CentOS 7, you will need:
- A CentOS 8 machine
- Basic knowledge of Linux commands and the ability to use the shell.
By default, htop comes pre-installed on CentOS 8. However, if it’s missing on your system, use the following commands to set it up.
How to install htop on CentOS 7
Step 1:
- Install the EPEL repository.
yum -y install epel-release
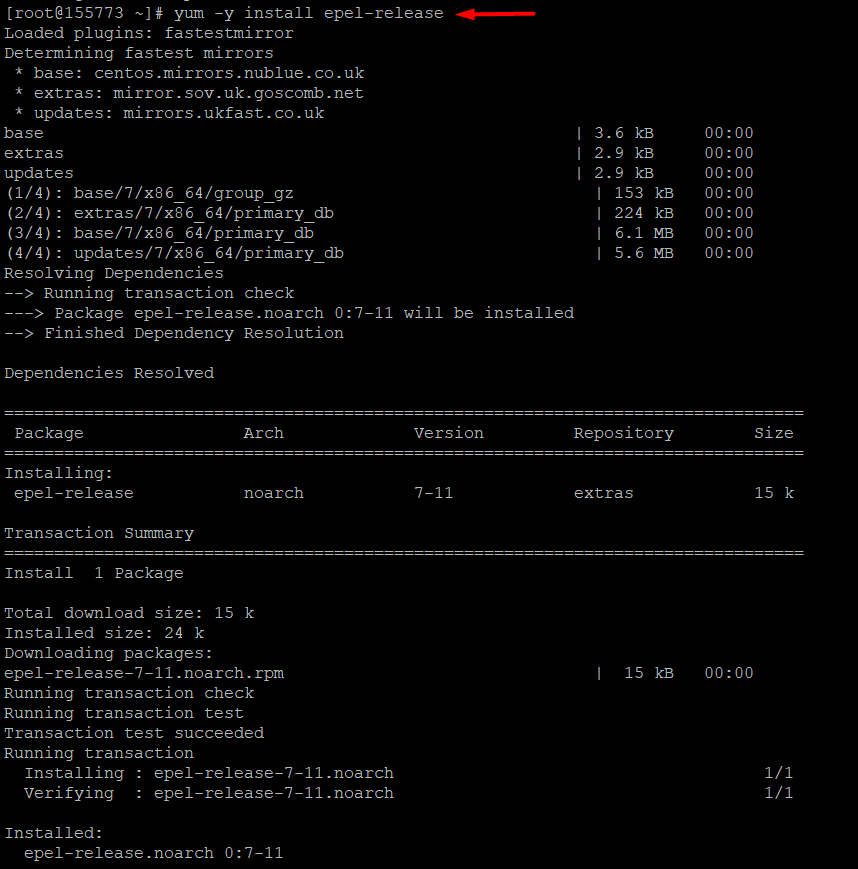
- After enabling the EPEL repository, update the system.
yum update -y
Step 2:
- With the repository added, you can install the htop process monitoring tool.
yum install htop -y
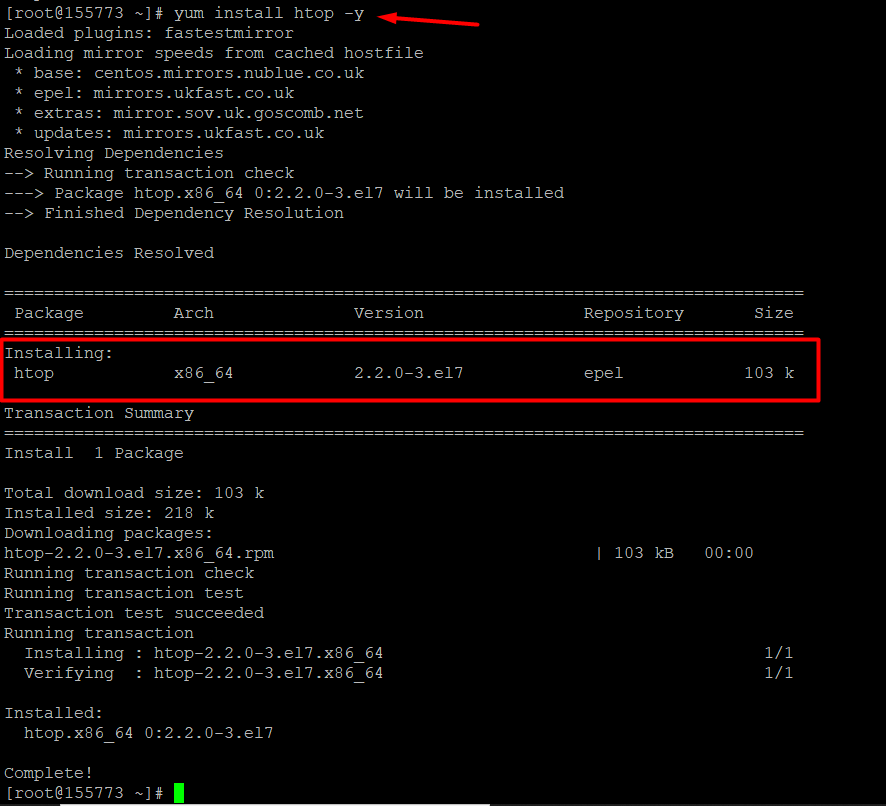
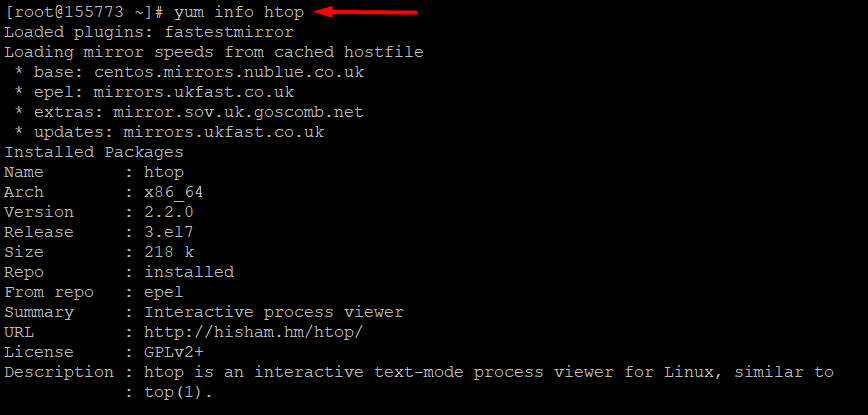
- Once the installation is complete, you can find detailed information about htop.
yum info htop
Step 3:
- Launch htop.
htop
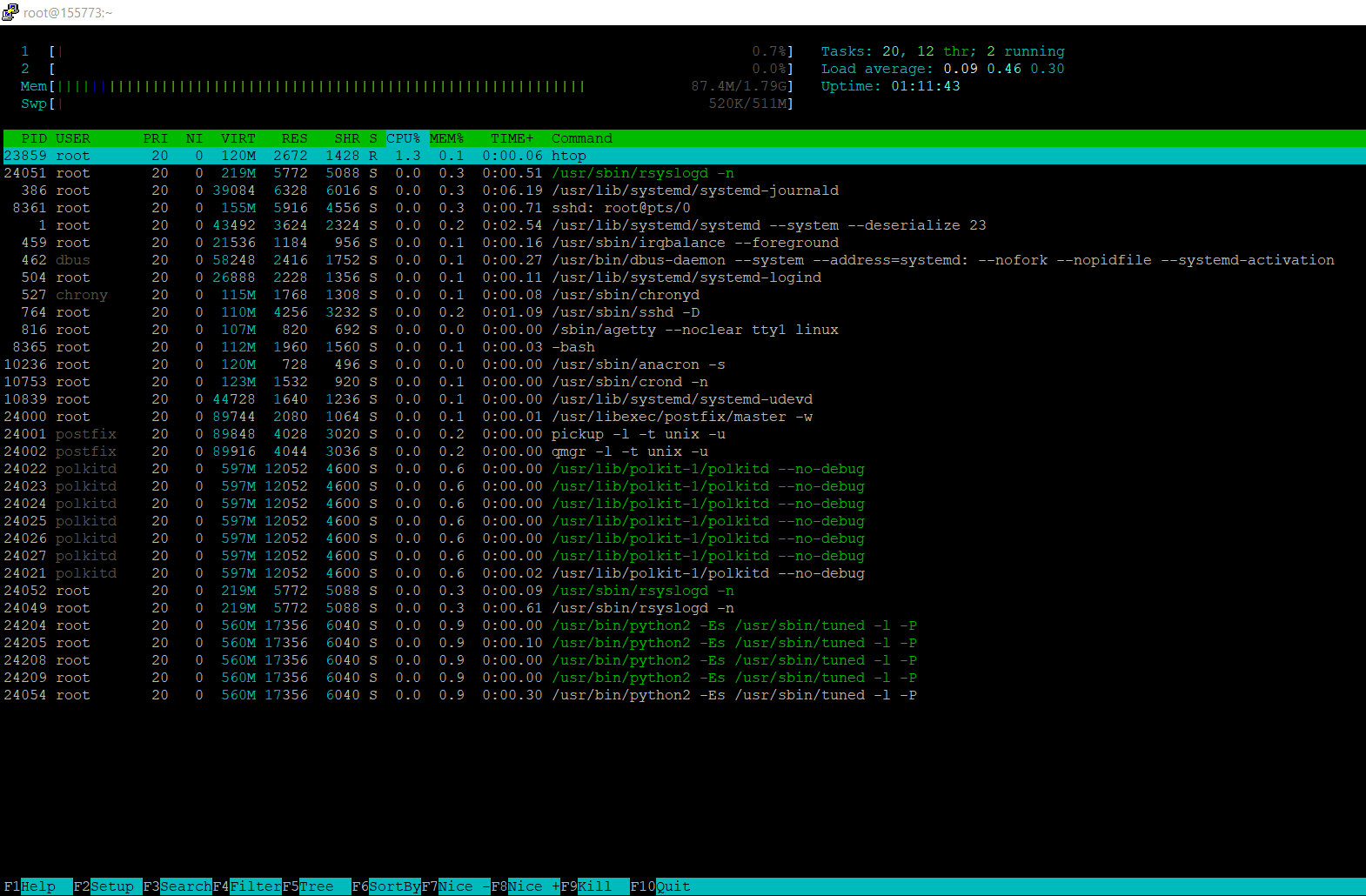
Htop keyboard shortcuts
While inside htop, you can use the following commands.
|
Command |
Description |
|
Up arrow key |
Select (highlight) the previous process in the process list. Scroll the list if necessary. |
|
Down arrow key |
Select (highlight) the next process in the process list. Scroll the list if necessary. |
|
Left arrow key |
Scroll the process list left. |
|
Right arrow key |
Scroll the process list right. |
|
Space |
Tag or untag a process |
|
Pg Up / Pg Dn |
Scroll the process list up or down one window. |
|
Home |
Scroll to the top of the process list and select the first process. |
|
End |
Scroll to the bottom of the process list and select the last process. |
|
u |
Show only processes owned by a specified user. |
|
s |
Trace process system calls |
|
m |
Sort by memory usage (top compatibility key). |
|
p |
Sort by processor usage (top compatibility key). |
|
t |
Sort by time (top compatibility key). |
|
k |
Hide kernel threads: prevent the threads belonging to the kernel from being displayed in the process list. (This is a toggle key.) |
|
Ctrl + L |
Refresh the screen. |
|
F1 |
See the help menu. |
|
F2 |
Setup |
|
F3 |
Search |
|
F4 |
Filtering: type in part of a process command line, and only processes whose names match will be displayed |
|
F5 |
Tree view. |
|
F6 |
Sorting |
|
F7 |
Increase the selected process’s priority (only by a root user). |
|
F8 |
Decrease the selected process priority |
|
F9 |
Kill process |
|
F10 |
Quit |
CentOS htop alternatives
There are many htop alternatives also. We will note down the top 5 htop replacements that are free and Open Source.
- Glances: This is a CLI curses-based monitoring tool for GNU/Linux and BSD OS.
- GNOME System Monitor: Manage running processes and monitor system resources.
- Bashtop: Easy to use with a game-inspired menu system.
- KSysGuard: designed to make simple process control available to the user without any particular setup.
- vtop: Uses Unicode braille to chart CPU and memory usage.
Conclusion
During this short tutorial, we covered the procedure to install htop on CentOS 7, a popular and efficient option for monitoring system processes. We also went through some basic keyboard shortcuts that can be used in htop to enhance productivity. For those looking to further improve their remote desktop experience on CentOS, you may find it helpful to check out our guide on how to install XRDP on CentOS.
In addition to that, we reviewed some of the htop alternatives that can be utilized on your CentOS VPS, offering flexibility depending on your server's needs. If you're new to CentOS or want to learn more about CentOS for server optimization and management, be sure to explore related resources. Many other powerful features come packed with htop, which you can discover on the official website. If you found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends.
If you're looking to optimize your CentOS server further, consider checking out our guide on how to install the LAMP stack on CentOS 7, which will equip you with essential tools for web development and server management.
People also read:





![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![Debian vs CentOS: Differences You Should Know [Comparison] Debian vs CentOS: Differences You Should Know [Comparison]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2021/02/debian-vs-centos-comparison993-750xAuto.jpg)


