Working with Linux is very simple as it offers various simple commands to carry out multiple tasks. One of the most basic commands that every Linux administrator uses is the ls command which will allow you to check what files and directories are present in the Linux system.
This command is available with many options that will display the directory’s contents in different ways and with additional details such as the permission of the file or directory and ownership.
In this article, we will be focusing on the ls command and its options that will impact the command results. You can go through this article to get detailed knowledge of how the ls command will work.
For a deeper understanding of keeping your Linux environment secure while using commands like ls, check out our comprehensive guide on Linux Server Security.
How to Use the ls Command in Linux
With the help of the ls command, you will get the details of the files and directories stored on your Linux system. You can use the Linux ls command even in its most basic form, that is, without mentioning any option or passing any argument to this command. Using the ls command alone will display all the files and directories present within the current working directory.
But, before you run any command on Linux, make sure that you have the Linux system and the appropriate access to run the commands on the command-line prompt. For running the ls command, you can use the following syntax. We also suggest to read the article list running services in Linux.
ls [options]
[options] - will allow you to add additional parameters to the ls command.
1. List Files and Directories in Linux
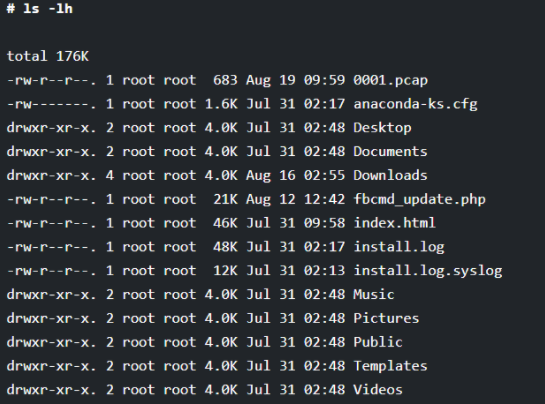
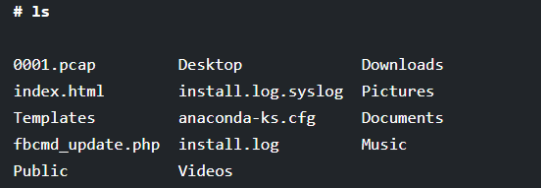
In the below example, we execute the ls command without any option and argument. You will see that the result will only display the files and directories only without any additional information such as time of creation, ownership, and others.
# ls
2. Long Listing of Files in Linux
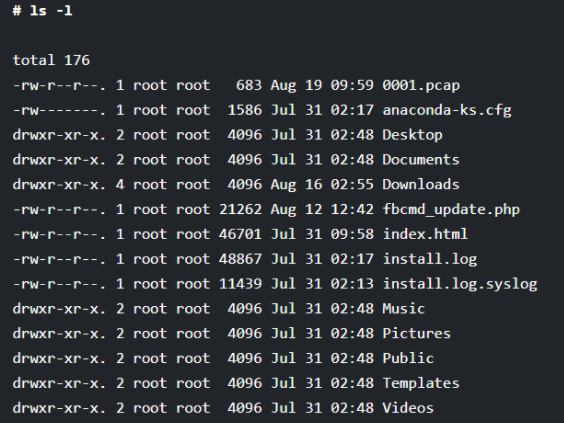
For getting the complete details about any file and directory present in the current working directory, you can execute the ls command along with the “-l” option. The “-l” option will determine the long listing of all the files and directories, including various details, as shown below.
# ls -l
3. View Hidden Files in Linux (ls hidden files)
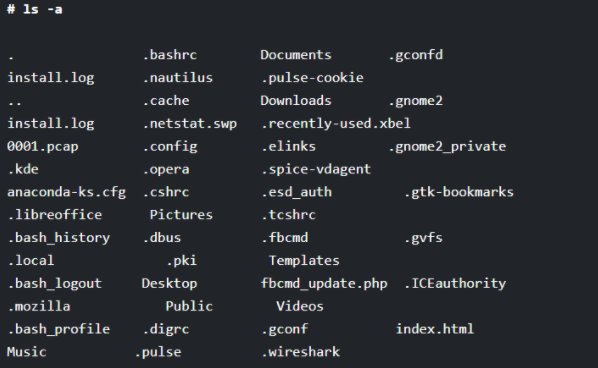
If you are new to Linux and its commands, you might not know that several hidden files will not be displayed on the screen by running the basic ls command. For getting the details of hidden files, you need to provide the “-a” option along with the ls command in UNIX, as shown below. You will see some of the file names starting with “.” specify the hidden files.
# ls -a
4. Listing available Files with Human Readable Format
Earlier, we have used the ls command along with the “-l” option, but that command displays information like the size of the file in bytes that is not easily understandable by people. Thus to get the details in human-readable format, we will use the “-lh” option along with the Linux ls.
# ls -lh
5. Listing all the Files and Directories using the ‘/’ character at the end
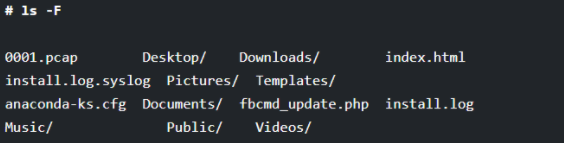
Whenever you run the ls command, the names of files and directories will get displayed on the screen. But it is not always possible to distinguish between the files and directories if the list is too long to check. Thus, Linux offers you a fantastic option that can be used along with the ls command for making that difference. The choice is “-F”, which will distinguish the directory from the files by adding the “/” character at the end of each directory.
# ls -F
6. Listing all the Files in Reverse Order in Linux
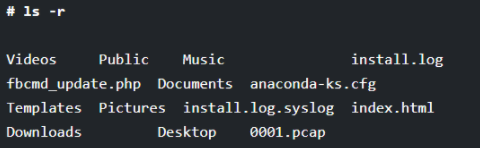
For getting the files and directory details in reverse order, you can use the “-r” option along with the ls command.
# ls -r
7. Listing Sub-Directories in Linux recursively
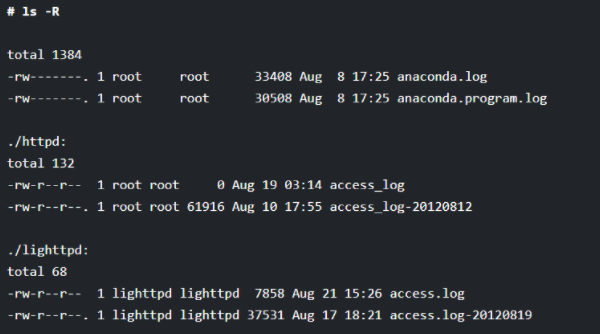
If you want to get the details of the files and directories in the Linux system in a very long listing format, then you can use the “-R” option along with the ls command. You can see the below example to get an understanding of this option.
# ls -R
8. Listing Files and Directories in Reverse Order
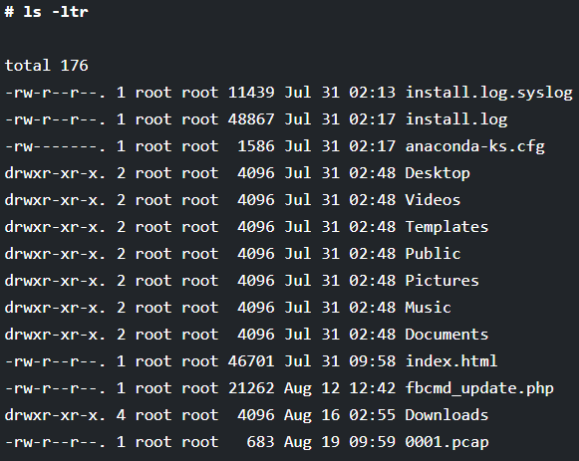
If you want to get the details of the files and directories as per the last modified date or in the reverse order, then you can use a combination like “ltr” along with the ls command as shown below (ls sort by date).
# ls -ltr
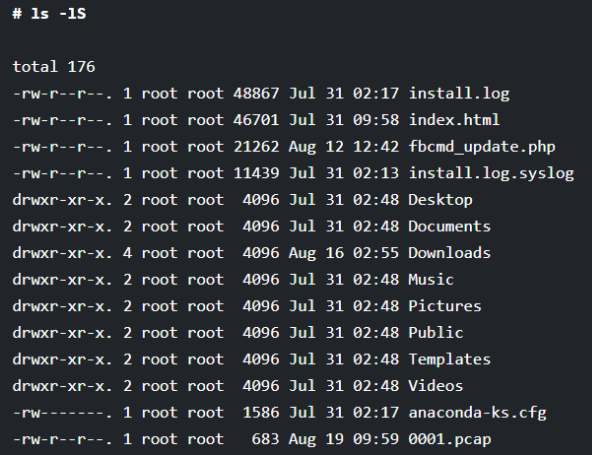
9. Sorting the Files by their Size in Linux
If you want to display the list of the files and directories in the order of the file size, then you can use the “IS” option along with the ls command. This option will display the biggest file at first.
# ls -lS
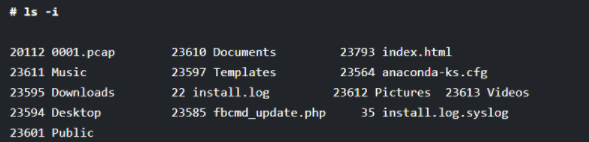
10. Displaying the specific Inode number of File or Directory
If you have noticed the output of the ls command when run with the “-l” option, you can see number numbers printed before the file or directory name. With the help of the “-i” option, you can list the file or directory with an inode number.
# ls -i
If you ever need to manage processes in Linux, such as terminating one that is causing issues, check out our guide on how to kill a process in Linux to learn effective methods for process management.
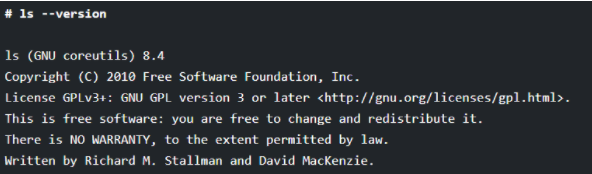
11. Shows Version of ls Command
Every command has a version number for checking the version of the ls command you are using. You can run the ls command with the “--version” option.
# ls --version
12. Show ls Command Help Page
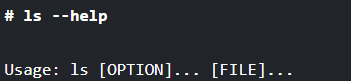
To get more details about the ls command, you can run the ls command along with the “--help” option. It will display all the options that can be used with the ls command.
# ls --help
13. List Directory Information in Linux
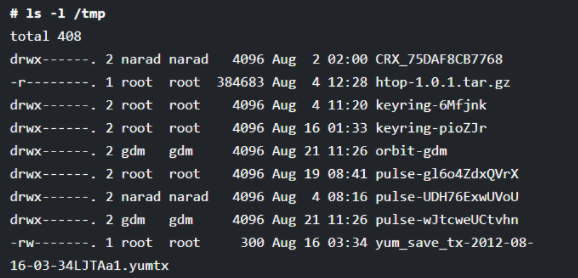
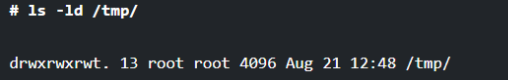
Whenever you run the ls command with the “-l” option, you will get the details of all the files and directories that are present in the /tmp directory. But if you use the “-ld” option with the ls command, you will get the detail of the /tmp directory as shown below.
# ls -l /tmp
14. Display UID and GID of Files
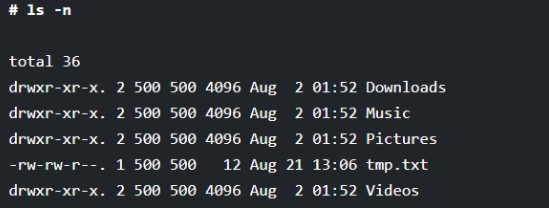
With the help of the “-n” option along with the ls command, you will get the UID and GID of the files and directories.
# ls -n
15. ls command and its Aliases
With Linux, you can create an alias for any command. But the ls command is already an alias for the “ls -l” by default. Thus, the ls command alone will display the long listing of the files and directories.
# alias ls="ls -l"
There are some other Linux commands that are already been aliased. You can check those commands using the “alias” command, as shown below.
# alias
For removing an alias that has been previously defined, you can use the following unalias command.
# unalias ls
If you're looking to explore more about Linux and its core capabilities, check out our detailed guide on Linux features to deepen your understanding of this versatile operating system.
Conclusion
Now, you have detailed information on how the ls command will work and its various options. You can even combine multiple options and use them with the ls command to get the combined effect of those options.
For those exploring Linux environments further, understanding the benefits of a Linux Dedicated Server can provide deeper insights into harnessing the full power of Linux systems for robust and secure hosting solutions.
Some of them we have mentioned in this article. You can create your combinations also once you get a complete understanding of how they work. So start learning and implementing this interesting command of Linux. You can also buy linux vps to practice it on a routine basis.
Also, people read: