Virtualization has gained popularity and is widely used for software and operating system testing—users from every field to skilled developers leveraging the benefits of virtualization. If you are using server virtualization, you can run various operating systems on the same physical resources, reducing the need for physical dedicated servers.
Using the hypervisor, you can easily create a virtualization layer abstracting the guest machines and other operating systems. It results in the emulation of the resources so that the guest machine feels like they are consuming the physical resources without knowing that the host OS and VM are using the same resources.
We have come across two types of hypervisors- first is type 1, the bare metal hypervisor that can be effortlessly installed on the physical server you want. The second is Type 2, the hosted hypervisors that can be easily installed on the top of the host operating system.
If you are running a large and complex production environment, then type 1 is more suitable, while you can use the type 2 hosted hypervisors for running VMs on a personal system. Virtualbox and VMware are the two widely and commonly used type 2 hypervisors available in the market.
This article will focus on VMware vs Virtualbox hypervisors, their pros and cons, and their differences.
What is a VirtualBox?
Virtualbox is one of the virtualization software offered by Oracle. You can use it for free; it is available as an open-source and is distributed under the GNU general public license version 2. With this software, you will be able to run virtual machines on the host operating machine.
You can also create a connection between the virtual machines and the host. Virtualbox comes with the support for various operating systems like Linux, Windows, Mac OS, and Oracle Solaris. In 2010, a VirtualBox extension was introduced by Oracle. It is a closed-source complementary package offering a wide range of features. It comes with support for USB2/USB3 and RPD.
Benefits of using Virtualbox
Below are the benefits of using Virtualbox.
- It provides easy integration between the host machine and the virtual machine.
- It comes with support for various operating systems.
- It gives the dynamic size for the virtual hard drive space.
- It comes with an efficient peripheral integration.
- It offers you dynamic display resizing along with the changing window size.
Limitation of Virtualbox
Below are the limitations that you may face while using Virtualbox.
- It provides an outdated user interface.
- Users need to download and provide the ISO themselves rather than the process should be automated for the open-source operating systems.
- You could automate the process of installing the guest additions to the virtual machines using a single sign-on.
- It does not provide easy documentation for every feature.
- There is no facility for implementing common tasks to all VMs simultaneously.
What is VMware?
VMware is a powerful virtual machine software that offers a wide range of virtualization products, making it an essential tool for both individual users and businesses. With VMware, you can efficiently manage and create virtual machines, allowing you to run multiple instances of the same operating system or different OS versions on x86-based devices. This flexibility is particularly useful for testing, development, and running applications across various environments. For Windows and Linux hosts, VMware provides a free version of its software, making it accessible for personal and small-scale use. However, if you're working on larger projects or require more advanced features, VMware Workstation Pro is available, offering enhanced functionality and better performance.
If you're seeking a more robust and dedicated solution, consider opting for a VMware dedicated server. This option allows you to fully leverage VMware's capabilities in a dedicated environment, providing the resources and control needed for enterprise-level applications and critical workloads. With a VMware dedicated server, you can achieve higher levels of performance, security, and customization, tailored to meet the demands of your specific business needs.
Benefits of using VMware
Below are some benefits that you can enjoy using VMware.
- It comes with solid and active community support for resolving all your issues.
- It provides you with an advanced feature for seamless working.
- You do not require security patches for controlling the components of the layer.
- It provides you with all AWS applications for various uses.
- There is no need for an external operating system to manage the components.
Limitations of VMware
Below are some limitations you may face using VMware.
- It has a steep learning curve, making it difficult to learn and understand.
- You can only use its limited feature sets with its free version.
- If you want to run some complex devices, it will slow down the initialization process.
- If you, by any chance, use the corrupt external code, it may lead to a server crash, and you may face downtime.
VirtualBox vs VMware: Comparison Table
Below is the tabular difference between VMware and Virtualbox based on some categories, making it easier for you to decide which one you want to opt for in your environment.
|
Comparison |
VirtualBox |
VMware |
|
Software Virtualization |
Available |
Not Available |
|
Hardware Virtualization |
Available |
Available |
|
Available Host Operating Systems |
Linux, Windows, Solaris, macOS, FreeBSD |
Linux, Windows + macOS (with VMware Fusion) |
|
Available Guest Operating Systems |
Available for OSs like Linux, Windows, Solaris, macOS, FreeBSD |
Linux, Windows, Solaris, FreeBSD + macOS (along with VMware Fusion) |
|
Available User Interface |
Graphical User Interface and Command Line Interface |
Graphical User Interface and Command Line Interface |
|
Snapshots |
Available |
Available only for paid virtualization products, excluding VMware Workstation Player |
|
Available Virtual Disk Format |
Available in VDI, VMDK, VHD, HDD |
VMDK |
|
Available Virtual Disk Allocation Type |
Available in Preallocated-fixed disks; dynamically allocated disks; |
Available in Pre-allocated provisioned disks and Dynamically allocated thin-provisioned disks; |
|
Provided USB Devices Support |
USB 2.0/3.0 support needs the Extension Pack (free) |
support for USB device |
|
API for Developers |
Requires API and SDK |
Supports Different APIs and SDKs |
|
Cost and Licenses |
Available for free under the GNU General Public License |
VMware Workstation Player is free, but other VMware products require a paid license |
Differences between VMware and Virtualbox
We have mentioned some differences based on various aspects and depending on the features they offer.
Software and Hardware Virtualization
Software virtualization is available for Virtual box but not for VMware. Software virtualization is vital because it helps emulate the computer system and allows the guest to run on top of it. Using the software virtualization, you will be able to run virtual machines with different platforms than the host. But somehow, it leads to slow performance of the virtual machine compared to the hardware virtualization.
Virtualbox and VMware support hardware virtualization. Using this, you will be able to emulate the hardware devices from the respective host. It allows you to run the code directly on the hardware, which will enhance the VM performance. For hardware virtualization, you will be required to use the Intel VT-x or AMD-V CPU features. Also, you will be able to run guests that will use the same platform as the host.
Operating Systems
One of the major deciding factors is the host operating system. Virtualbox shows support for a wide range of OS, but it is not the case with VMware. Virtualbox can be efficiently run on various operating systems like Linux, Windows, Solaris, macOS, and FreeBSD. At the same time, you can run VMware Player and VMware Workstation work only on Linux and Windows.
Both virtualizations offer the support of the most guest operating systems, which will include the OS like Linux, Windows, Solaris, macOS, and FreeBSD. The main difference between both virtualizations is that VMware needs Fusion/Fusion Pro to run on macOS virtual machines.
User Interface (UI)
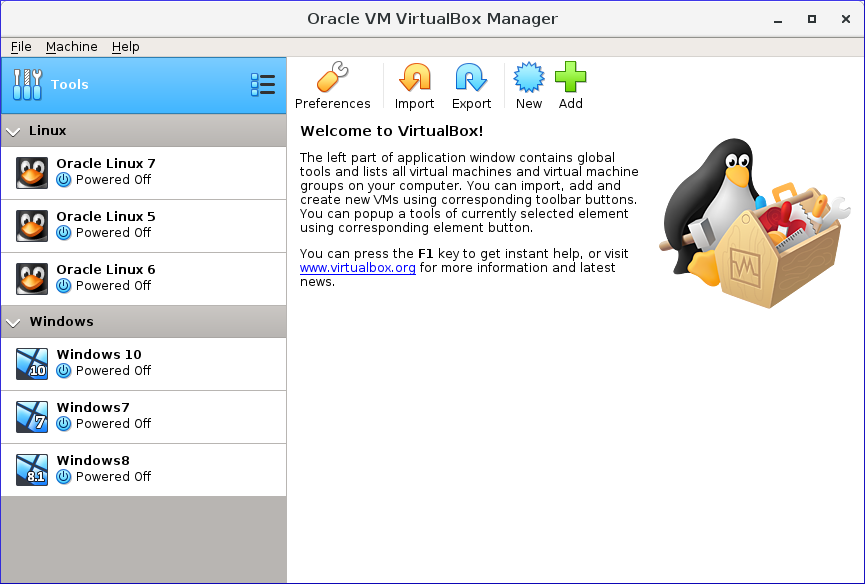
With Virtualbox, you can use both GUI and CLI (VBoxManage). The CLI helps you manage the virtual machines using the host command line, providing a wide range of features and tools.
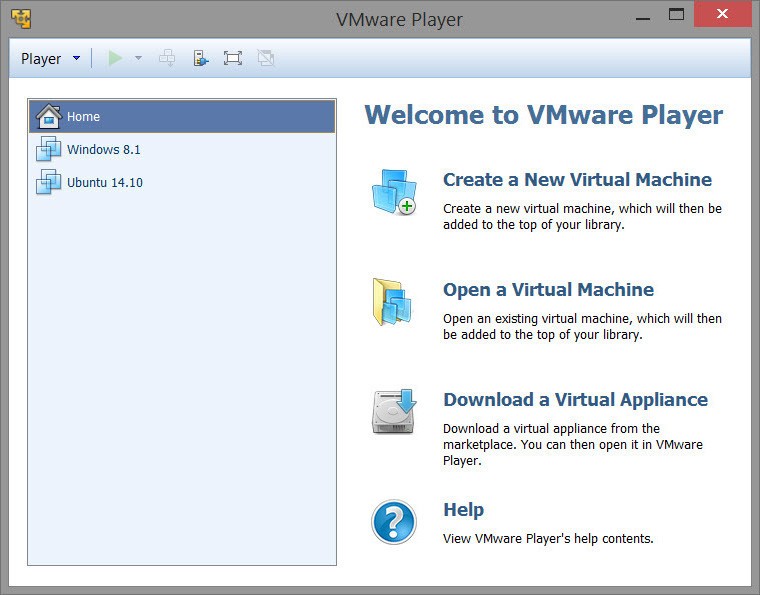
VMware comes with the facility of both a graphical user interface and a command line. The VMware Workstation offers you more UI features that are available for VMware Player GUI.
Snapshots
Snapshots help store the virtual machine's actual image at any instant, allowing you to provide a backup for any failure. It enables you to roll back the complete system to that state without impacting the other running applications. You can take as many images of the virtual machine in various VM states. But if you keep taking snapshots, it will slow down the performance of your virtual machine.
With VirtualBox, you will be able to take snapshots for free, while VMware allows this on its paid virtualization products.
Virtual Network Modes
You can work in any of the network nodes as per your choice. For this, you need the configuration of each networking adapter for your VM separately.
USB devises support
For a USB connection to a guest machine, you can attach it to the host. Both VMware and Virtualbox come with support for USB devices.
VirtualBox comes with the support for USB 1.0, requiring the installation of the VirtualBox Extension Pack for USB 2.0 and USB 3.0.
While with VMware, you can only use up to 2 USB devices and have the USB port enabled by default.
Integrations
In addition to the support for various virtual disk formats (VMDK, VHD, HDD, etc.), Virtualbox provides you access to many integration tools like Docker, Vagrant, etc.
While VMware does not show support for such a wide range of virtual disk formats. You need a conversion utility for running configurations different from VMware's VMDK.
Common features of VirtualBox and VMWare
Below are some common grounds for both Virtualbox vs VMware.
- They both support the shared folders, requiring a bit of set-up. This allows you to mount a folder on the host as a network share for the guest. It will enable both of them to share the data between them.
- Apart from the shared folders, it allows you to drag and drop the files between the host and the guest. You can copy the file to the clipboard on one system and paste it to another.
- The Virtualbox's seamless mode and VMware's utility mode allow you to pull windows out of the guest and move them onto the host. It helps in interacting with both the OS at the same time.
- Both use encrypted virtual machines, preventing unauthorized access to VMs.
Conclusion
Looking at the features and functionalities of both VMware vs Virtualbox, it might be a difficult choice for every user. But you have to sort out your priorities based on every aspect and make a choice that suits better for your company. You can even consider their price plans; it will help you restrict to one option.
You might go for VirtualBox if you want to move virtual machines between hosts or if you want to support open-source software.
You can go for VMware if your main focus is stability, if you are using an older machine where performance optimization matters or if you are ready to pay for the Pro version.
People also read: