Networking has become a crucial need in today’s world. Everything is connected via networks, from computers to printers to other devices. Networking has made communication easier and smoother than ever. Do you know what is Network Topology? In this article, we will go through the types of networks, network topologies, network architecture and more. Various changes have been made to ensure efficient transmission. Different network types have fulfilled the requirements of different business needs.
Networking is a vast field and growing exponentially. Latest tools, technologies, and techniques have made it more advanced, catering to the needs of people across the globe. This article will discuss computer networking, its evolution, different network types, common terminologies used, and other essential information.
What is Computer Networking?
Computer networking means different machines are connected via wired or wireless to transmit data or resources. You can create a computer network using hardware, such as routers, switches, cables, etc., and software, such as operating systems, applications, etc., only this, and a computer network also connects one or more networks. The computer network can be based on what protocols you use to communicate, the arrangement of various network components, and its purpose. Sometimes, you can use the geographic location to define the computer network, such as LAN, WAN, etc.
The scope of networking is not only limited to a single field. It has expanded to all areas such as education, healthcare, media, entertainment, etc. Every work relies on networking, speed, efficiency, performance, etc.
Different types of networks
With the evolution in the need for networking, different networks cater to different needs. We have mentioned different types of networks.
- LAN (local area network): This network connects different computers covering a short distance and allows them to share data, files, and resources. For example, a LAN connects all the computers within an office, school campus, or hospital. LANs are owned and managed privately for direct access.
- WLAN (wireless local area network): This network works as a LAN but covers a larger area. The devices are connected wireless using Wi-Fi.
- WAN (vast area network): This network connects computers over a wide area, covering different regions or continents. Various models have been used for managing the WAN. The internet is an example of a large WAN that connects several computers worldwide.
- MAN (metropolitan area network): this type of network typically has a more extensive range than LANs but a smaller range than WANs. Cities and government entities mostly use this network.
- PAN (personal area network): This network serves one person. For example, iPhone and a Mac allow you to set up a PAN to share and sync content, such as text messages, emails, photos, and more.
- SAN (storage area network): this type of network is a specialized network providing access to block-level storage that is a shared network that looks like a storage drive that’s physically attached to a computer.
- CAN (campus area network): This network is more significant than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, connecting colleges, universities, and business campuses.
- VPN (a virtual private network): this type of network is a secure, point-to-point connection between two or more networks. It provides an encrypted channel to secure the user’s identity, credentials, data transferred, etc.
Different types of network architecture
Network architecture defines the logical and structural layout, types of available transmission equipment, available communication protocols, software and hardware used, and the types of data transmission and connectivity among various devices. The two commonly used network architectures are- peer-to-peer and client-server architectures. We will describe them briefly for better understanding.
Peer-to-Peer architecture
In this type of network architecture, each device has been assigned an equal task, as there is no hierarchy, and all connected devices are treated equally. Each device can use the resources equally. This type of architecture does not have a central server but uses a shared drive where each connected device acts as the server for the files stored in the network.
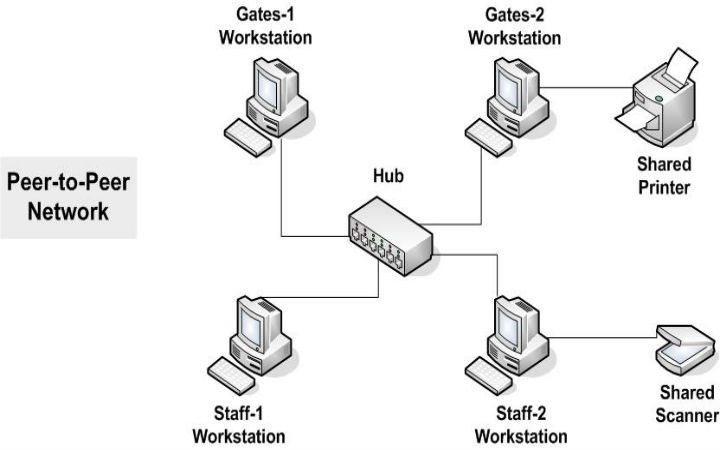
Pros of a peer-to-peer network
You can easily install and set it up with built-in support for the modern operating system. There is no need to install a dedicated server which means it does not incur much cost. Also, if one of the devices stops working, the other devices on the network will work as usual without impact.
Cons of peer-to-peer network
As each device is treated equally and is not managed centrally, you need to ensure security and backups on each device individually. The increase in the number of devices within the network will impact the performance, security, and complexity of handling.
Clinet/server architecture
In this type of network architecture, one device act as a server (centralized), and other devices act as the client that sends the request to the server. Every other device can connect to the server. The server manages all the tasks and provides the required resources to the connected devices. All the resources are handled on a priority basis by the server. Whenever the server receives the request, it starts working on it and keeps another incoming request in the queue to process.
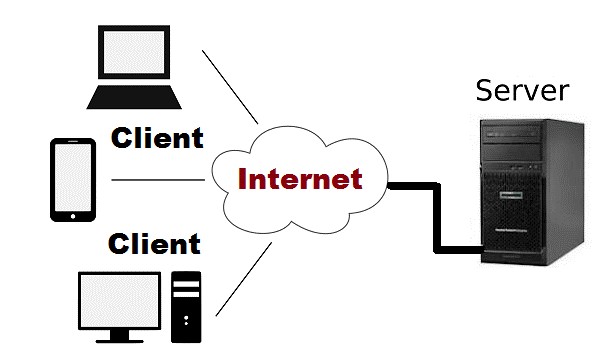
Pros of a client/server network
Each resource and security is managed and maintained by the server. You can even manage the number of devices connected to the server. You can even access the server anywhere and across multiple platforms.
Cons of Client/Server network
It might incur costs due to the servers’ increasing needs, such as installing network devices such as hubs, routers, etc. Whenever the server fails, every device connected to it stops working. You need to hire technical staff to maintain and manage the server’s working efficiently.
Different types of Network topology
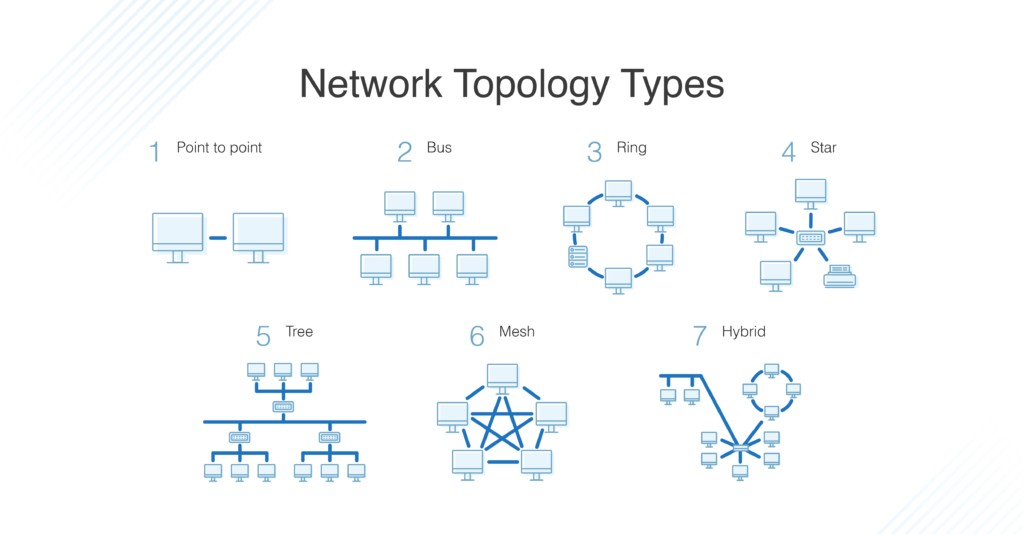
Network Topology Diagram
Another factor that impacts the efficiency of the working of the networks is the network topology. Topology in computer networks specifies how all the nodes (devices) are linked and arranged. Here, nodes specify the devices connected within the network, and the link establishes the link connecting those devices, either wired or wireless.
Understanding the network topologies is necessary to create an efficient and effective network. There are different types of topology available for catering to different networking needs. We have mentioned them below.
Bus topology
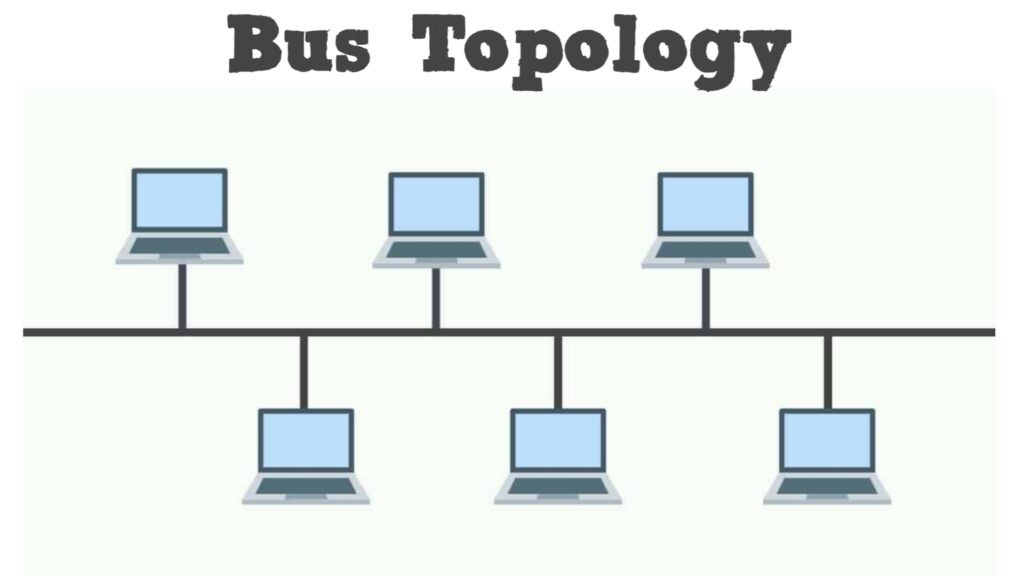
Bus topology diagram
In this type of network topology, all the devices are arranged along a single cable. That cable flows in the same direction from one end to the other end of the network. That is why it is also referred to as the line topology.
The data always flows in one direction. But, if one of the cables fails, the entire network fails. Also, the performance degrades with the increase in nodes per able. It is a cost-effective solution for small networks.
Ring topology
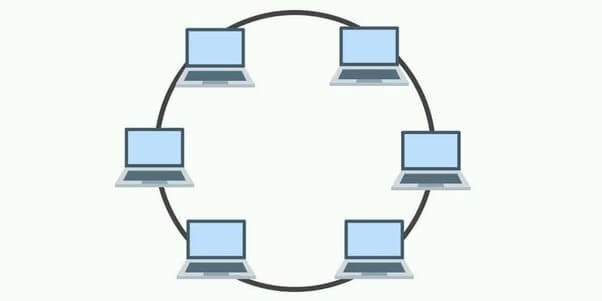
Ring topology diagram
In this type of network topology, the nodes are arranged in a circular manner where a single node has two neighbours. Depending on the requirement, the data flows either in one direction or both. With each node, repeaters are also installed to reduce the data loss in several nodes within the network. It incurs less cost to install and set up. But, it makes troubleshooting complex. The entire network crashes upon the crash of a single node.
Star topology
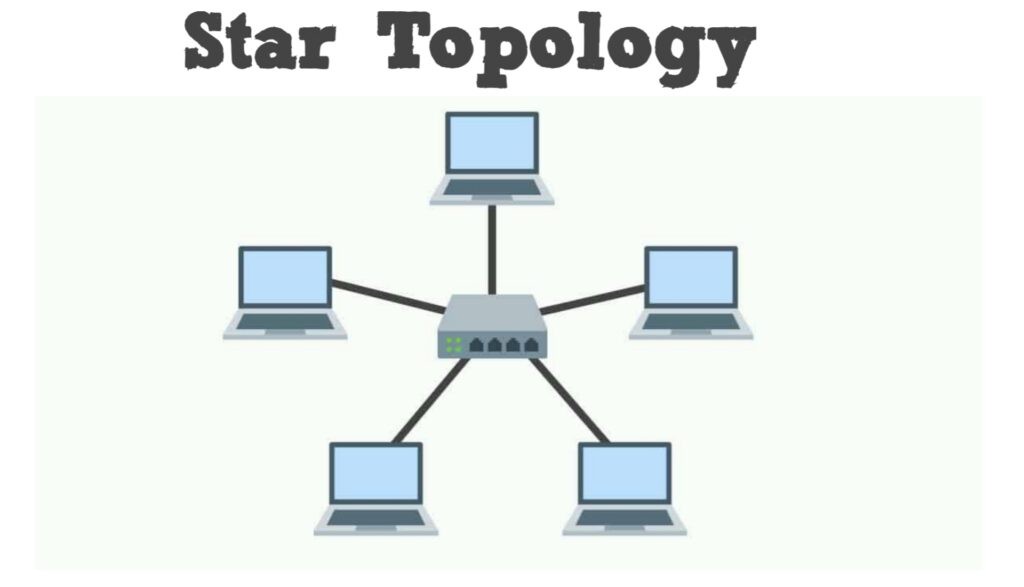
Star topology diagram
In the Star topology or Star network, each node is connected to the central one via coaxial, twisted-pair, or fibre-optic cable. The central node act as a server. The communication between the two devices is done via the central node. The central node also acts as the repeater reducing the data loss. It ensures faster performance. If the central node fails, there will be no communication within the network. In this case, if one node fails, the other will usually work. But, it is expensive to install.
Tree topology
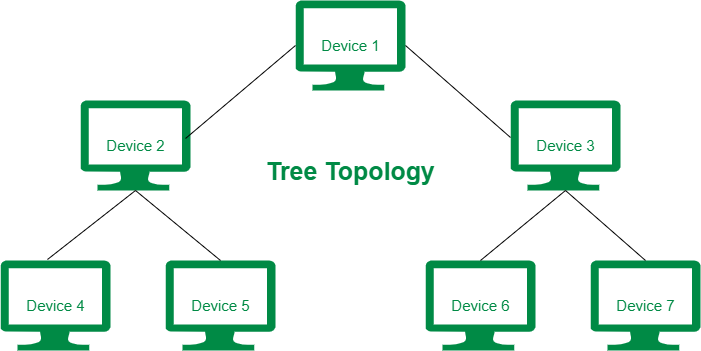
Tree topology diagram
In this network topology, the central node at the top with nodes extending out like branches. All the nodes are directly connected to the central node. It has a parent-child hierarchy. The nodes connected to the central hub are connected linearly to other nodes. Its structure is highly flexible and scalable and is widely used for wide-area networks to support many spread-out devices. You can troubleshoot such topology quickly. It is heavily cabled, thus incurs more cost.
Mesh topology
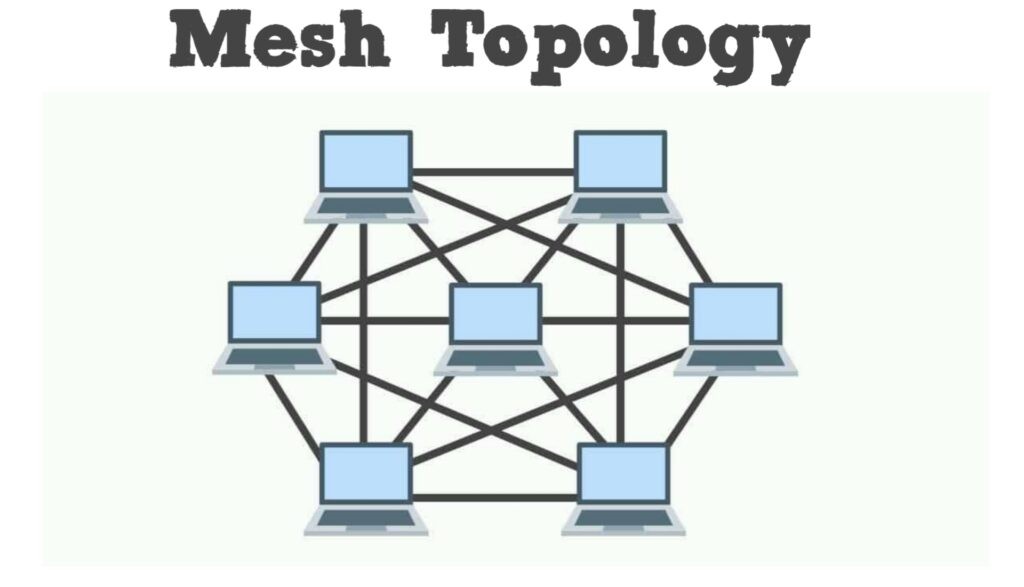
Mesh topology diagram
There are point-to-point connections in this network topology type where the nodes are interconnected. Mesh networks can be complete or partial mesh.
Hybrid topology
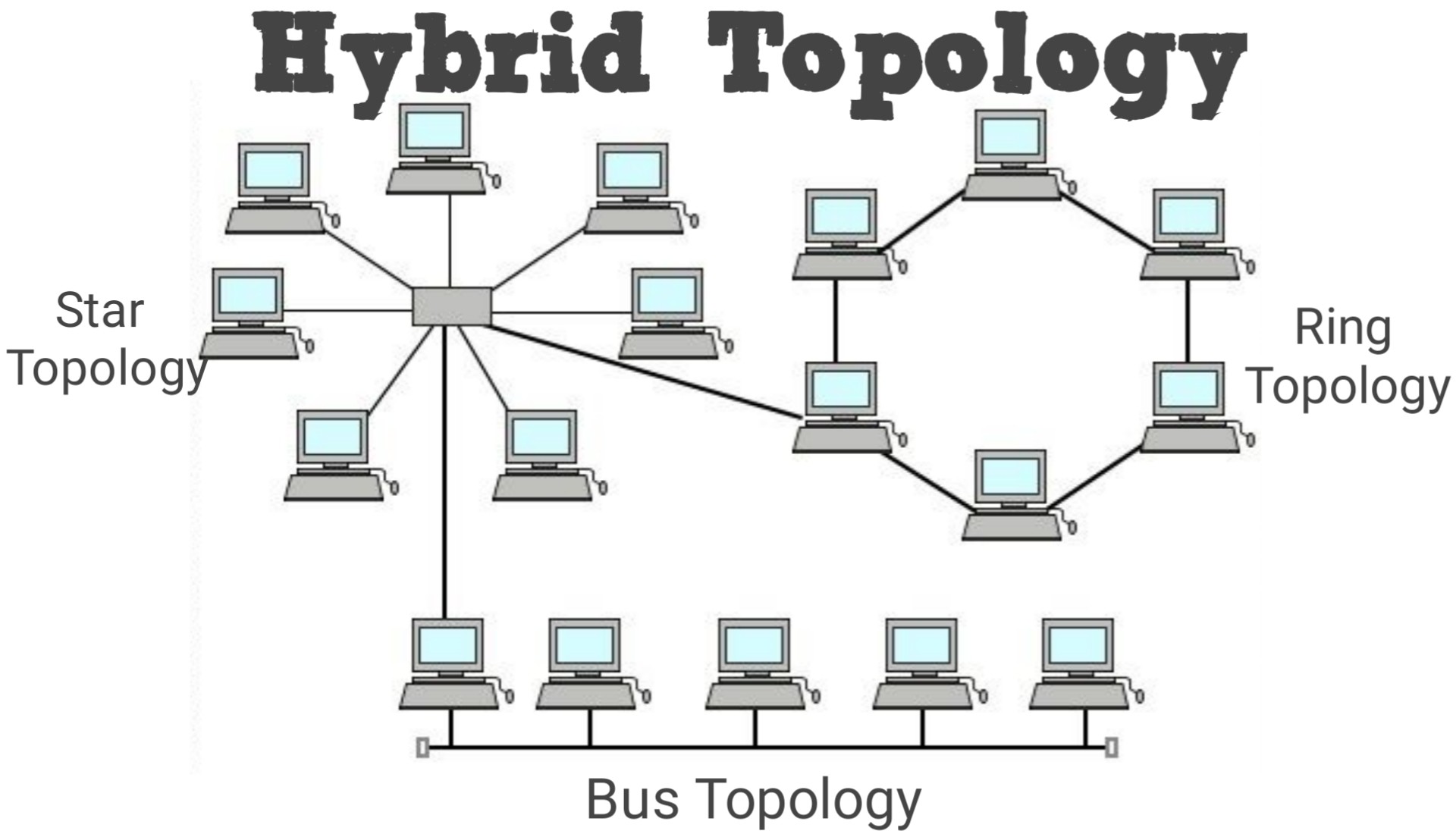
Hybrid topology diagram
In this type of network topology, you can connect more than one type of network topologies at your convenience. It can include the benefits of various topologies. It is complex to integrate several topologies and becomes costly due to different network requirements.
How has computer networking evolved?
Networks have evolved like anything and have embarked in every market field. There is no business can survive without having the right network in place. Due to the changing business demands, networking has also evolved to cater to all their requirements. Networking has evolved for good. We have mentioned their evolution below.
- Software-defined (SDN)- networking has become programmable and automated to cater to digital and modern business needs. It allows the network to adapt quickly to the changing business requirement. In this type of networking, all the traffic is controlled centrally using the proper software-based mechanisms.
- Intent-based networking is built on the SDN principles that have boosted the agility and automated the operations. It results in enhanced performance, highlighting the potential end-points for issues, ensuring high-end security, and integrating the entire process with the business processes.
- Virtualized- in this type of networking, you can partition the underlying physical infrastructure logically and create an entirely different network. Each network is capable of providing different features and fulfilling different requirements.
- Controlled-based- the network controllers play an essential role in scaling and securing the networks. These controllers simplify all the operations and help businesses react quickly to changing business demands. With controllers, you can automate the functions of the network and configure the devices accordingly. These devices then monitor the other devices continuously to ensure high-end performance and security.
- Multidomain integrations- many big enterprises construct individual networks known as networking domains for their offices, WANs, and data centres. These networks can communicate with one another via controllers. Such cross-network generally involves exchanging operating parameters to ensure high performance.
Key Networking Terms
Below are the standard terms you come across while working within the network. We have mentioned only the most commonly used terms. You must know their working and meaning to understand the proper working of the network.
- Open System Interconnection – a model, commonly used as a reference for setting protocols and functionalities of the network.
- Nodes are the devices connected within the network to send and receive network packets.
- Network packets – referred to as the data that is being transmitted.
- Network address translation – routers use it to provide internet service to all the connected devices in public IPs.
- Dynamic host configuration protocol – it provides the dynamic IP addresses to every host with an internet service provider
- Internet service providers – these are the companies that provide the internet connection.
- Hostname – referred t as the unique name of the network with a unique device.
- Internet Protocol address – it specifies the address of the network on the internet browsers
- Media Access Control address – refers to a physical address of each host that helps you determine them uniquely.
- Port – refers to a channel to transfer data from one end to another.
Top Networking Technology Trends
5G and Wi-Fi 6 technology –
The latest 5G or fifth generation cellular technology is known for its high speed, reduced latency, and high flexibility in wireless services. It offers seamless open roaming capabilities between cellular and Wi-FI access. It helps many organizations to extend automation, handling new technologies and applications with increased network capacity and high data rates.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Using ML and AI, you can easily handle complex networks and applications in real-time. Organizations use ML to make business predictions based on hard facts and network data. They use AI to take intelligent actions based on those predictions. It leads to self-operating networking.
Augmented reality and virtual reality
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies have changed every application’s way of working and have enhanced customer experiences to another level. AR is mainly used on smartphones and tablets to cater to different interior designs.
Cloud computing
Cloud has enhanced and improved the transition to remote work and helped people organize remote workplaces more efficiently. Maintaining a consistent network across several clouds using multi-cloud policy management has become more accessible.
Conclusion
Networking has become a necessity in today’s world, and it has brought everyone closer. Networking is the base behind every business, organization, and educational industry. It has made every process more straightforward and smoother. Using the above-mentioned types of network topologies, you can easily set up and use the network that suits you.
Due to advancements in networking, people are today working from home without being disconnected from their teams globally. Networking is not limited to the internet or connecting people. We have mentioned some of the basics of computer networking and how it has evolved.
People also read:
![What is Network Topology [Types of Network Topology] What is Network Topology [Types of Network Topology]](
https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image/width=827,quality=80,format=auto/https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2022/04/what-is-a-network-topology302-847xAuto.jpg
)




![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)

