What are UNIX commands? Before we answer this question, we will need to understand what is Unix. Because of their power utilities and features that aid in the development of secure and robust applications, UNIX and UNIX-like systems are ruling the development world. However, this powerful development necessitates a solid understanding of the UNIX Command Line Interface.
If you argue that 'why don't we use the graphical user interface (GUI) available in UNIX-like systems,' you should be aware that a large number of development tasks also take place on Virtual Machines, which do not provide any kind of graphical user interface.
As a result, as a developer, you should have a solid grasp of a sufficient number of commands. This article will look at some of the best and lesser-known UNIX and UNIX-like systems command available.
What is UNIX?
UNIX is an operating system that was created in the 1960s and has been constantly improved since then. It is a stable, multi-user, multi-tasking operating system for servers, desktops, and laptops that serves as the foundation for many different operating systems such as macOS, Ubuntu, and others. In the below section, we will discuss a few popular UNIX commands.
UNIX Shell/Terminal
The shell is a command-line window where a user can type instructions for the kernel to perform them. The default shell for UNIX and UNIX-like systems is the “Bash”. The “Bash” is a shorthand for “Born Again Shell”. This is an improvement over Bourne Shell. Nowadays, it is used as the default login shell in most Linux kernel distributions. Bash was also the default shell in most of the macOS versions that were released prior to 2019.
Best UNIX Commands [UNIX command list]
1. at
This command is used to execute a command at a given time of the day. Please note that the command will only execute once. The following command schedules a job at 2:45 on 11th September 2021
at 2:45 091121
Using -l option lists all the awaited jobs that need to be executed.
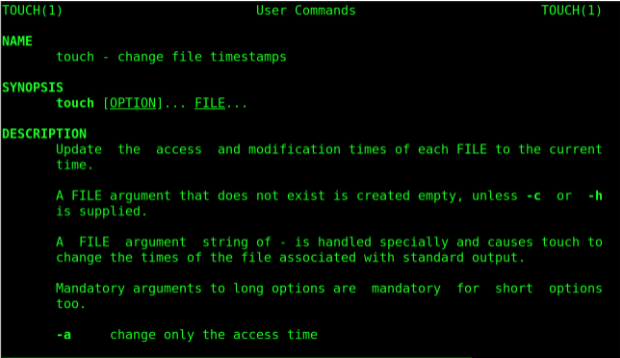
2. man
It is a shorthand for “manual”. The man command in Linux is used to display the user manual for every command that may be performed from the terminal. It shows a thorough view of the command, including the Name, Synopsis, Description, Options, and Return values, among other things. Let's write a manual for touch commands in Linux.
3. Sudo
This command, which stands for "SuperUser Do," (Sudo), lets you do administrative or root-level tasks. However, it is not suggested to use this command on a frequent basis since an error may occur if something goes wrong.
Its syntax is as follows:
sudo [command]
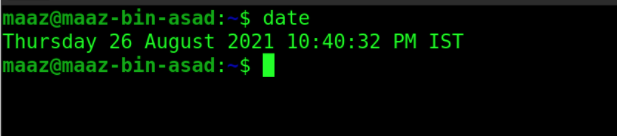
4. date
This is among the basic UNIX commands. The name of the command is quite self-explanatory; it prints the current date of the system.
 5. vi
5. vi
This command opens the vi editor that was primarily built for the UNIX operating system.
The improved version of this editor is the vim editor that is widely used today.
6. Who
This command is also self-explanatory. This standard UNIX command who displays a list of users who are currently logged into the operating system. This is similar to w command, which also displays other statistics along with the names.
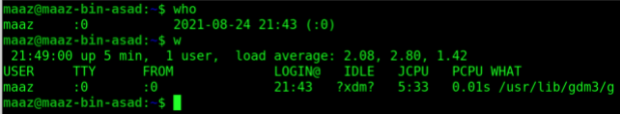
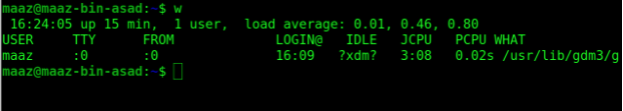
7. w
The w command displays who is currently logged into your system. It displays a list of logged-in users as well as additional information such as system uptime and load.
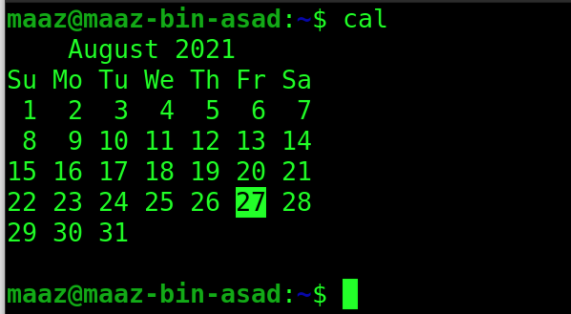
8. cal
This is a shorthand for “calendar”. This displays the calendar of the current month
Intermediate UNIX Commands
1. alias
It is a popular Linux command among system administrators since it allows them to replace a word in a file with another string straight from the terminal. This is one of the best terminal commands for customising the shell and controlling environment variables, among other things.
alias CD="cd Downloads"
2. wget command in UNIX
When downloading files from the web straight from the terminal, this is one of the most helpful Linux commands for network managers to utilise. This is one of those handy terminal commands that may be used in scripts or cron tasks to access the HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP internet protocols. The command's syntax is as follows:
wget http://website.com/files/file.zip
3. wait
The wait command is integrated into the UNIX shell. It waits for the process's state to change, i.e. for any ongoing processes to complete, and then returns the exit status. The following is the syntax of the wait command.
wait PID
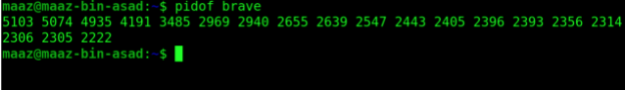
PID is the unique ID for each process. You can check the PID of a process using pidof command as shown below.
pidof <process_name>
The following example lists the PIDs of all the tabs of Brave Browser.
4. pkill
pkill (or process kill) kills the currently running process. This command comes in handy when the programme isn't responding and you wish to forcefully stop it. The syntax for the command is
pkill <application_name>
5. jobs command in UNIX
The jobs command lists all active jobs as well as their statuses. A job is simply a procedure or process that is started by the shell.
The -l option displays process IDs in addition to the standard information. The syntax is as follows:
jobs [options]
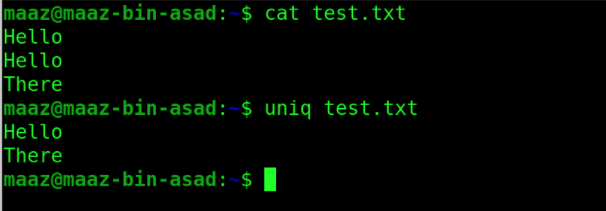
6. uniq
This is analogous to the word “unique”. In UNIX and UNIX-like systems, the uniq command is a command-line programme that reports or filters out repeated lines in a file.
7. write
This command is used to send messages to other logged in users in the same operating system.
The syntax for the command is:
write <user> <tty>
tty option is necessary when a user is logged in to more than two terminals.
8. batch
If you're looking for a convenient programme that will run system tasks on a preset schedule, the batch command is your saviour.
Another helpful Linux command for creating automation shell scripts; this handy little tool has the potential to significantly increase your UNIX productivity.
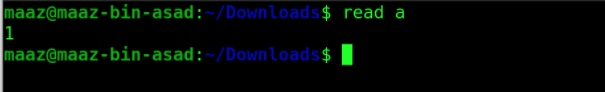
9. read
This command is used to read input from the user. This is usually used while making shell scripts in UNIX-like systems.
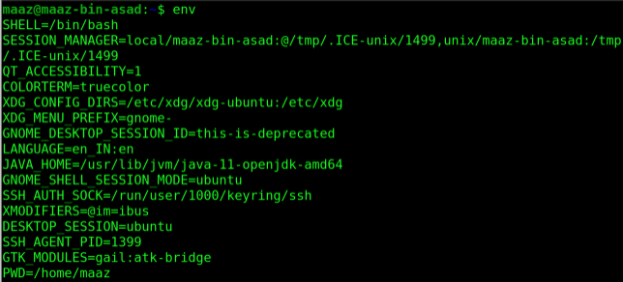
10. env
This is shorthand for “environment”. env is used to print or display environment variables. It may also be used to run a utility or command in a specific environment. Without any option, it simply lists all the environments as shown below.
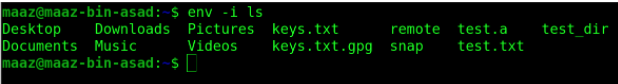
We can use the -i option to execute a command by ignoring environments.
11. hash command in UNIX
The analogy for this command can be made using “hash maps”. A hash is a UNIX command that is used to display a list of recently performed commands in a hash table. It remembers the locations of recently performed programmes and displays them anytime we wish to see the Following example lists the last three commands that the current user used.
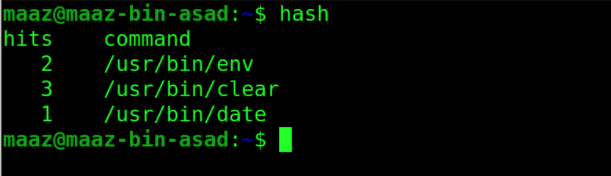
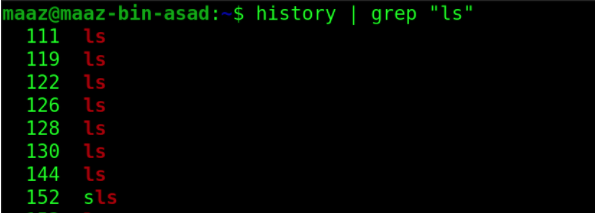
12. history
This command is one of the most helpful commands in UNIX and UNIX-like operating systems. This lists all the previously used commands in our machine. We can use it with grep command to filter out our required commands. For instance, the following example shows how we can list all the previously used commands with substring “ls”.
13. make
This command identifies which parts of a big programme need to be recompiled and issues the commands to recompile them automatically. Make may be used with any programming language whose compiler can be invoked through a shell command. It compiles the programmes in the current working directory by default.
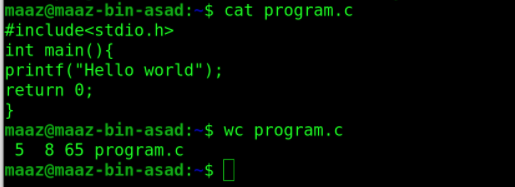
14. wc
This is shorthand for “word count”. This command is used to count words, lines and characters present in a file.
The first column displays the number of lines in the requested file, the second column displays the number of words in the file, the third column displays the number of characters in the file, and the fourth column displays the file name.
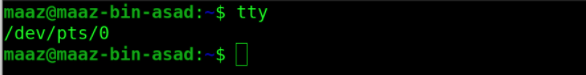
15. tty
tty is a command that prints the file name of the terminal connected to standard input in Unix and Unix-like operating systems.
Advanced UNIX Commands
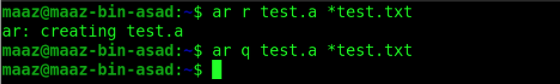
1. ar
The ar command is used to create, edit, and extract files from archives. An archive is a set of other files that have a certain structure from which individual files may be taken.
Using -r option is used to create archives and insert files into them.
Using -q option deletes an archive member.
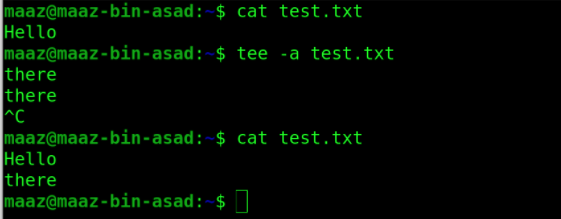
2. tee
The tee command reads standard input and writes it to standard output as well as one or more files. Using the -a option with the command appends to existing files rather than overwriting them.
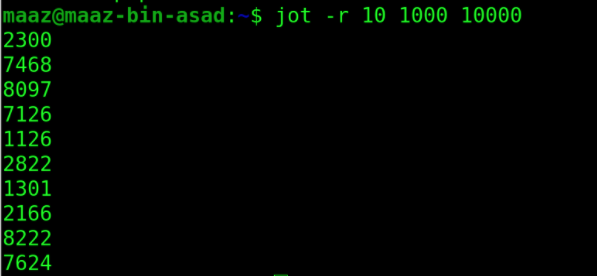
3. jot
As the name implies, jot generates text ranging from numbers to characters and gibberish.
Let’s use the -r option and print random numbers with the command.
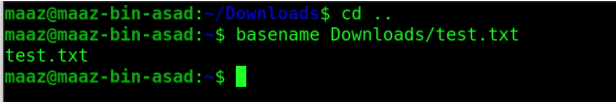
4. basename
Basename is a command usually used in shell scripts on Unix and Unix-like operating systems. When provided with a pathname, the basename will remove all prefixes up to the final slash ('/') character and return the result. Below is an example of this command.
5. awk
awk command in UNIX is a scripting language that is used to manipulate data within a given file. The awk command programming language does not need compilation.
awk is a utility that allows a programmer to create efficient programmes by defining text patterns to be searched for in each line of a document and the action to be done when a match is discovered inside a line. The following example prints all lines having “Hello” string in them.
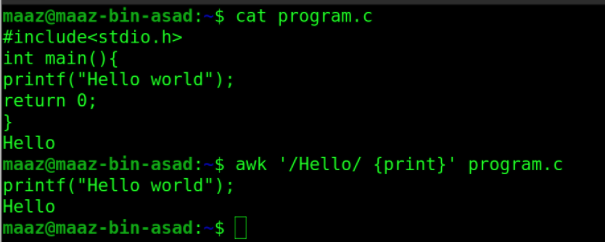
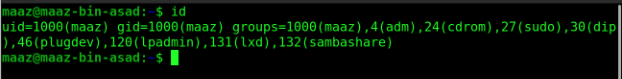
6. id
The id command is used to obtain the user and group names and the numeric IDs (UID or group ID) of the current user or any other user on the system. This command may be used to retrieve the following data:
- Username and authenticated user-id
- Determine the particular User's UID.
- Display the UID as well as any groups connected with a user.
- List all of the groups to which a user belongs.
- Show the security context of the current user.
7. yacc
Yacc (Yet Another Compiler-Compiler) is a Unix operating system command. It is a Look Ahead Left-to-Right (LALR) parser generator, creating an LALR parser (the component of a compiler that attempts to make syntactic sense of the source code) based on a formal grammar expressed in Backus–Naur Form notation (BNF).
8. dd
This is one of the most often used Linux commands by expert users to copy and convert files from one type to another. The intriguing aspect of this little but potent command is that it is commonly used in combination with other terminal commands when creating bootable live USB devices.
To transfer a hard disc to another using the dd command, use the sync option to copy everything using synchronised I/O.
# dd if = /dev/sda of = /dev/sdb conv=noerror, sync
To create an image of a hard disk:
# dd if = /dev/hda of = ~/hdadisk.img
Conclusion
This article discussed some of the basic UNIX commands for playing around with the system. You may have noticed how efficiently UNIX systems are developed to support these tools. It allows you to do a lot of things with just one command, such as compiling, directory navigation, controlling your system's resources, and so on. This is the reason why these commands are still used in modern UNIX-like systems.
People also read:






![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)