The world is experiencing data growth at an exceptional rate because organizations require different access speeds and processing capabilities for their various data types. The explanation of cold data storage should begin with its definition, as it has become a vital requirement for current information technology systems. The term cold storage in information technology describes an optimal storage solution that provides businesses with economical storage options for data that they seldom need to access during extended periods of time.
Businesses need to understand cold storage systems because they store data that requires long-term preservation, so organizations need to be aware of cold storage systems to handle their storage costs while maintaining compliance with regulations and keeping their archival materials intact.
This guide presents the definition of data cold storage, which includes an explanation of cold storage in cloud systems, an analysis of cold data storage costs through different pricing systems, and a study of cold storage operations, which includes both its structural design and functional processes.
❄️ What Is Cold Data Storage?
What is cold data storage? In simple terms, the data cold storage definition refers to storing infrequently accessed data in low-cost infrastructure designed for long-term retention rather than immediate availability.
The cold data storage meaning within IT environments answers what cold storage in IT is and what cold storage in data: it is a strategic storage tier used to archive information that must be preserved but does not require fast retrieval.
Organizations building cold data storage infrastructure should first understand the role of a storage-optimized system; our guide on What is storage server explains how high-capacity servers are designed specifically for long-term data retention and archive workloads.
☁️ What Is Cold Data Storage in Cloud Computing?
What is cold data storage in cloud computing? In cloud environments, what is cold storage in cloud refers to archive-based object storage tiers where infrequently accessed data is moved to lower-cost archive tiers, such as Glacier-like services that operate on a pay-per-retrieval model.
Unlike on-prem cold storage, which relies on dedicated hardware like tape libraries or high-capacity HDD arrays, cloud cold storage eliminates infrastructure ownership while introducing retrieval delays and usage-based cold data storage costs.
🗄️ What Is Stored in Cold Storage?
What is stored in cold storage typically includes data that must be preserved for long periods but is rarely accessed in daily operations. The purpose of cold storage is to reduce infrastructure costs while maintaining durability, compliance, and long-term retention. Organizations use data cold storage to protect historical, regulatory, and backup information without paying premium performance-tier pricing.
-
Full system backups and disaster recovery archives
-
Compliance and regulatory archives required by law
-
Legal records and contractual documentation
-
Medical imaging files, such as MRI or CT scan archives
-
Historical customer data retained for audit purposes
-
Large media archive,s including raw video and production files
Cold storage is used for data that is critical to keep but does not require immediate retrieval.
🧊 What Is Cold Data Storage Example?
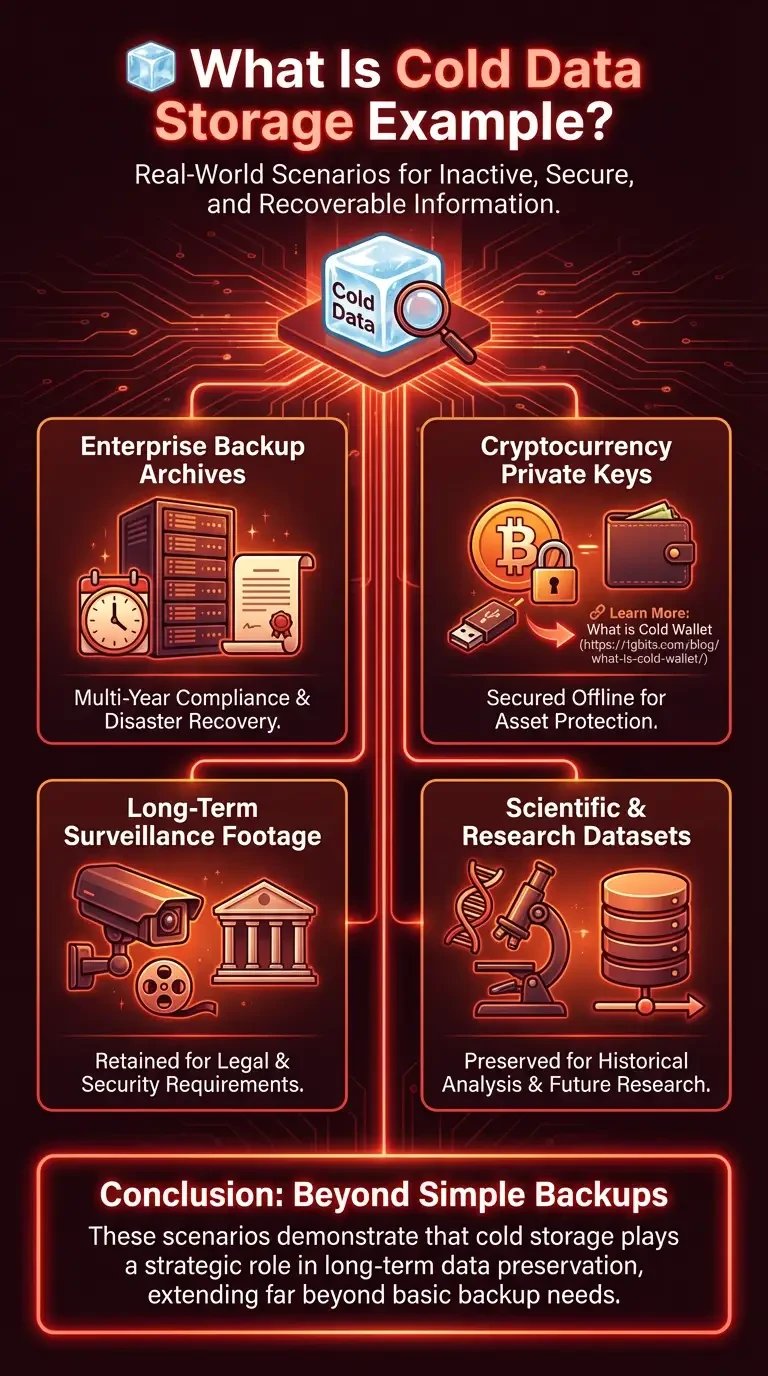
Understanding what cold data storage example scenarios are helps clarify what cold storage of data is in real-world environments. Cold data storage is designed for information that remains inactive for months or years but must stay secure and recoverable. Below are practical examples that illustrate how cold storage works across industries.
-
Enterprise backup archives stored for multi-year disaster recovery compliance
-
Cryptocurrency private keys are secured offline, similar to the concept explained in What is Cold Wallet
-
Long-term surveillance footage is retained for legal or security requirements
-
Large scientific or research datasets preserved for historical analysis
These scenarios demonstrate that what is cold storage used for extends far beyond simple backups and plays a strategic role in long-term data preservation.
🔄 How Does Cold Data Storage Work?
How does cold storage work in practical IT environments? In simple terms, how cold data storage works begins with a defined data lifecycle policy that automatically moves information from active tiers to archive tiers based on usage patterns.
Data transitions from Hot to Warm and finally to Cold storage, where it is placed on low-access storage media designed for durability rather than speed, introducing retrieval delays but significantly lowering cold data storage costs through optimized cost structures.
🔥🌤️❄️ Hot vs Warm vs Cold Data Storage
The hot, warm, cold data storage model classifies data based on access frequency, performance needs, and cost efficiency. When comparing cold data vs hot data, the key differences lie in retrieval speed, infrastructure pricing, and operational purpose.
|
Type |
Access Speed |
Cost |
Use Case |
|
Hot Storage |
Instant / Real-time |
High |
Active databases, applications, transactional systems |
|
Warm Storage |
Moderate / Minutes |
Medium |
Infrequently accessed business data, analytics archives |
|
Cold Storage |
Slow / Hours |
Very Low |
Backups, compliance archives, and long-term retention data |
Cold storage is not inferior storage; it is strategically optimized for cost-efficient preservation rather than performance.
🏗️ Cold Data Storage Architecture
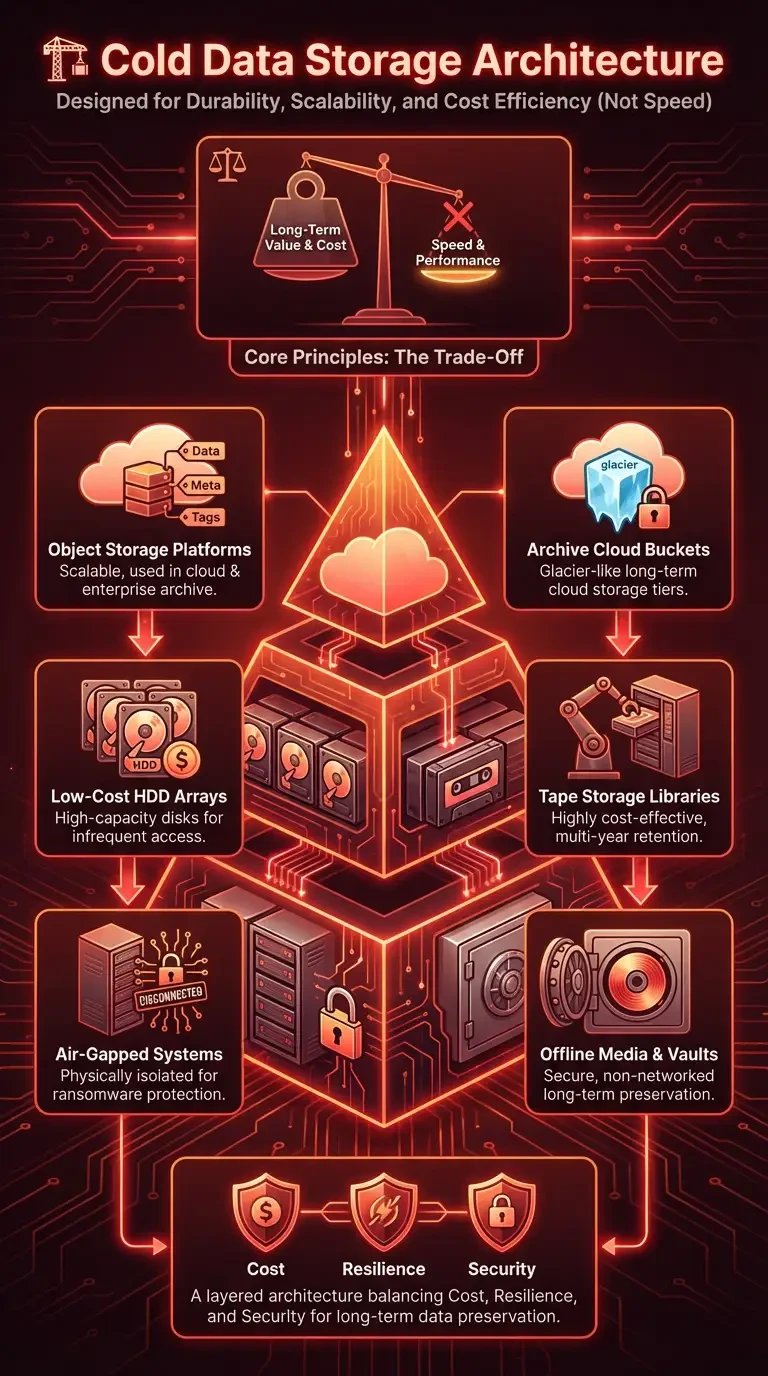
Cold data storage architecture is designed around durability, scalability, and cost efficiency rather than high-speed performance. Data cold storage combines different infrastructure layers to ensure long-term retention with minimal operational overhead. The architecture of what is cold storage in IT typically includes distributed systems, offline media, and cloud archive services working together.
-
Object storage platforms: Scalable systems that store data as objects with metadata, commonly used in cloud and enterprise archive environments.
-
Tape storage libraries: Traditional yet highly cost-effective archival systems ideal for multi-year retention.
-
Low-cost HDD arrays: High-capacity disks optimized for infrequent access workloads.
-
Archive cloud buckets: Glacier-like storage tiers designed for long-term cloud cold storage.
-
Air-gapped systems: Physically isolated backups used for ransomware protection and maximum security.
These components form a layered architecture that supports what is cold storage of data while balancing cost, resilience, and security.
💰 Cold Data Storage Costs & Pricing Models
Cold data storage costs are significantly lower than hot storage, but the pricing structure is more complex than simply paying per gigabyte. Understanding cold data storage price models requires analyzing storage capacity fees, retrieval charges, and policy-based retention rules. Unlike performance storage, what is cold storage for data focuses on long-term affordability with usage-based access billing.
-
Storage per GB cost: Typically, the lowest price among storage tiers, optimized for volume retention.
-
Retrieval fees: Charges applied when archived data is accessed or restored.
-
Data transfer fees: Costs associated with moving data out of the storage environment.
-
Minimum retention charges: Penalties or billing requirements for deleting data before a defined retention period.
🧩 Cold Data Storage Options
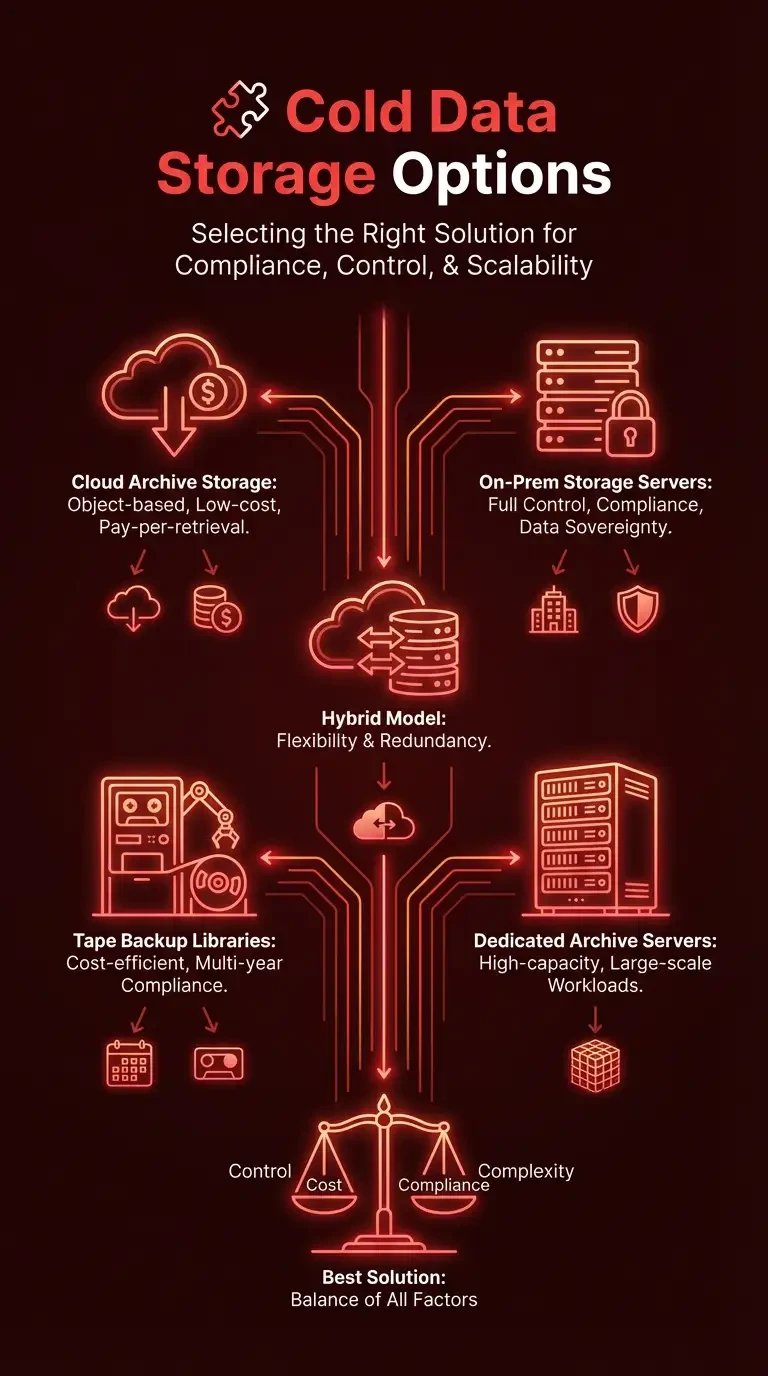
Choosing the right cold data storage options depends on compliance needs, infrastructure control, and long-term scalability. Today’s cold data storage providers offer flexible cold data storage solutions ranging from fully managed cloud archives to enterprise-owned hardware. Understanding what is cold storage used for helps organizations select the appropriate deployment model for their retention strategy.
-
Cloud archive storage: Object-based archive tiers in public cloud platforms designed for low-cost, pay-per-retrieval data retention.
-
On-prem storage servers: Locally managed infrastructure that gives full control over performance, compliance, and data sovereignty.
-
Hybrid model: A combination of on-prem cold storage and cloud archive tiers for flexibility and redundancy.
-
Tape backup libraries: Cost-efficient long-term archival systems ideal for multi-year compliance storage.
-
Dedicated archive servers: High-capacity systems built specifically for large-scale archival workloads.
Businesses that require full control can deploy a high-capacity server to manage long-term archive workloads efficiently while maintaining predictable cold data storage costs.
📊 Cold Data Storage Market Overview
The cold data storage market is expanding rapidly as global data volumes continue to grow exponentially. Regulatory compliance requirements, industry retention mandates, and enterprise governance policies are driving demand for structured archive strategies. At the same time, AI data archiving and analytics-driven historical data retention are increasing the importance of scalable cold storage infrastructure.
-
Explosive data growth across the enterprise, media, healthcare, and finance sectors
-
Stricter compliance and data sovereignty regulations worldwide
-
Rising demand for AI model training using historical datasets
-
Long-term retention requirements for legal, financial, and research records
As organizations generate more inactive data, structured data cold storage strategies are becoming a foundational component of modern IT architecture rather than an optional add-on.
📊 Cold Data Storage Market Overview
The cold data storage market is expanding rapidly as global data volumes continue to grow exponentially. Regulatory compliance requirements, industry retention mandates, and enterprise governance policies are driving demand for structured archive strategies. At the same time, AI data archiving and analytics-driven historical data retention are increasing the importance of scalable cold storage infrastructure.
-
Explosive data growth across the enterprise, media, healthcare, and finance sectors
-
Stricter compliance and data sovereignty regulations worldwide
-
Rising demand for AI model training using historical datasets
-
Long-term retention requirements for legal, financial, and research records
As organizations generate more inactive data, structured data cold storage strategies are becoming a foundational component of modern IT architecture rather than an optional add-on.
⚖️ Advantages and Disadvantages of Cold Data Storage
Cold data storage offers significant financial and operational benefits, especially for organizations managing large volumes of inactive data. However, understanding what is cold storage in data also means recognizing its performance limitations and management requirements.
|
Category |
Factor |
Explanation |
|
Advantage |
Very low cost per GB |
Cold data storage costs are among the lowest in the storage hierarchy, making it ideal for large archives. |
|
Advantage |
Scalability |
Data cold storage solutions can scale to massive volumes without major infrastructure redesign. |
|
Advantage |
Ideal for compliance |
The purpose of cold storage often includes regulatory retention, audit logs, and legal documentation. |
|
Advantage |
Energy efficient |
Low-access infrastructure consumes less power compared to high-performance storage systems. |
|
Disadvantage |
Slow retrieval |
Accessing archived data may take minutes or hours, depending on the storage medium. |
|
Disadvantage |
Retrieval fees |
Many cold data storage providers apply charges when data is restored. |
|
Disadvantage |
Not for real-time apps |
Cold storage is unsuitable for workloads requiring instant data access. |
|
Disadvantage |
Lifecycle management complexity |
Improper tiering policies can increase cold data storage prices and create operational risks. |
Cold storage is extremely cost-efficient for long-term retention, but it requires careful lifecycle planning to avoid performance and pricing surprises.
🧑💻 What Is Cold Storage in Software?
What is cold storage in software refers to logical data tiering within applications, databases, and enterprise systems rather than physical hardware alone. In this context, database cold partitions separate inactive records from active datasets, archive logs preserve historical transactions, and data lifecycle automation moves information between tiers based on predefined policies.
Storage class rules within software platforms define what is cold storage for data by automatically assigning low-access data to archive classes to reduce cold data storage costs without manual intervention.
🗂️ Cold Data Storage vs Secondary Storage
Cold data storage is often confused with secondary storage, but they are not identical concepts. Cold storage is a specific tier within a broader data management strategy, while secondary storage refers to non-primary storage systems used for backups, archives, and extended retention. In fact, cold storage is often part of a broader Secondary Storage strategy for long-term data retention, especially when implementing structured hot, warm, and cold data storage models.
🔐 Is Cold Data Storage Secure?
Cold data storage can be highly secure when properly implemented with encryption at rest, strict access control policies, and immutable storage configurations that prevent unauthorized modification. Air-gapped backups further strengthen protection by isolating archived data from network-based threats such as ransomware.
Conclusions
Every organization needs to know what cold data storage means because they manage digital assets that require long-term storage. The research shows cold storage services help organizations by providing a strategic solution that decreases their infrastructure expenses while they meet compliance requirements and sustain operational capacity for their systems.
Businesses that need predictable cold data storage costs, full hardware control, and enterprise-grade reliability can deploy a high-capacity Server for Storage from 1Gbits, backed by 24/7 technical support, instant setup, global data centers, and competitive pricing, making it a practical solution for secure and scalable archive workloads.
![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](
https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image/width=827,quality=80,format=auto/https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-1200xAuto.webp
)





![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)



