Algorithmic trading has become a core part of modern financial markets, especially at crypto and cash-based exchanges, which prioritize speed and execution precision. The main function of spot algorithmic trading uses automated trading rules together with spot trading algorithms to execute instant asset trades, which eliminate the risks that come with derivative and margin-based trading systems.
Traders want to understand three main things because algorithms control both market liquidity and price movements: how to identify algorithmic trading activities in actual markets, whether these systems deliver an advantage to traders, and whether algorithmic trading maintains its effectiveness across various market conditions.
The article uses an algorithmic spotlight approach to explain how spot algorithmic trading operates, guide both beginners and experienced traders in identifying this trading method, and describe the necessary infrastructure for responsible participation, which requires neither hype nor shortcuts or unrealistic promises.
🤖 What Is Spot Algorithmic Trading?
Automated rule-based systems execute trades in spot markets through their use of algorithmic trading systems. The system uses algorithms to analyze real-time data, which includes price and volume and order book information to execute and control trades in cash markets, thereby making risk assessment easier than it is in derivative or margin trading systems.
Spot trading algorithms use fully funded positions as their operational foundation, which creates a new framework for developing trading strategies and handling potential risks, unlike forex and futures algorithms, which require high levels of leverage combined with rollover expenses and contract specifications to function.
To better contrast spot trading algorithms with leveraged systems, it helps to understand What is a Forex Trading Robot is and how broker-based execution shapes forex automation.
⚙️ How Spot Algorithmic Trading Works?
Spot algorithmic trading follows a structured process that transforms raw market data into automated trade decisions executed in real time on spot exchanges. Each stage is designed to reduce human error while maintaining tight control over execution and risk.
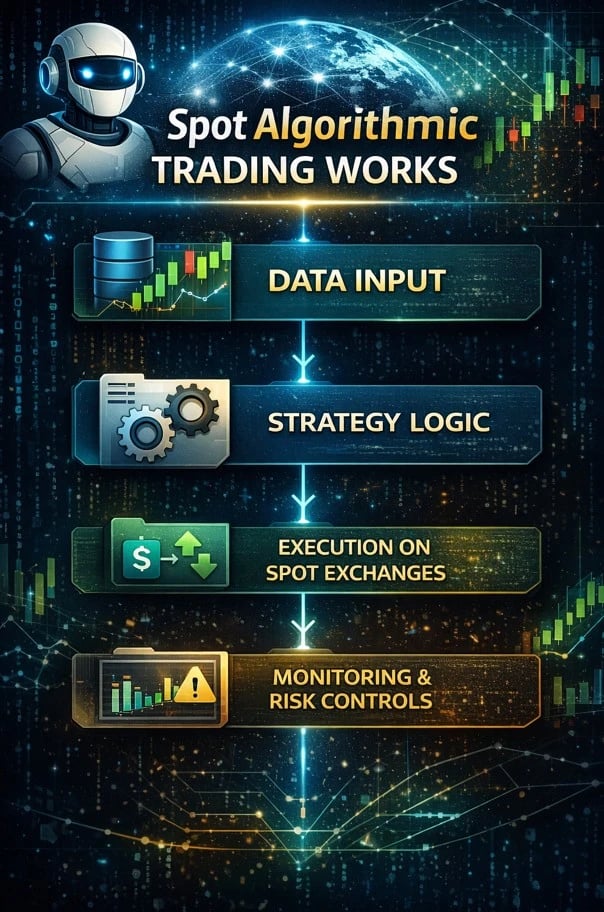
-
Data input: The algorithm continuously reads live price feeds, traded volume, and order book depth to understand current market conditions.
-
Strategy logic: Predefined rules analyze the data to determine when to enter, exit, or adjust positions using spot trading algorithms.
-
Execution on spot exchanges: Orders are sent directly to spot markets, where trades settle immediately without leverage or contract rollover.
-
Monitoring & risk controls: The system tracks performance, enforces position limits, and reacts to abnormal conditions such as volatility spikes or liquidity drops.
Together, these components explain how spot algorithmic trading operates as a disciplined, repeatable workflow rather than a black-box system, helping clarify how to spot algorithmic trading behavior in live markets and assess whether algorithmic trading works depends largely on execution quality and risk management.
📊 Common Spot Trading Algorithms
Spot trading algorithms are designed to operate without leverage, focusing on execution efficiency, liquidity provision, and short- to medium-term price behavior in cash markets. Understanding these models provides an algorithmic spotlight on how different strategies interact with spot market structure.
|
Spot Trading Algorithm |
Core Objective |
Typical Market Condition |
Key Characteristics |
|
Market Making |
Capture bid–ask spread |
High liquidity, ranging markets |
Places continuous buy and sell orders, adapts spreads based on volatility |
|
Mean Reversion |
Trade price deviations |
Sideways or range-bound markets |
Assumes prices revert to an average after short-term extremes |
|
Trend Following |
Ride sustained price moves |
Strong directional markets |
Enters in the direction of momentum using price and volume signals |
|
VWAP / TWAP |
Optimize execution price |
Large orders, stable markets |
Breaks orders into smaller parts based on time or volume |
|
Arbitrage (Spot-only) |
Exploit price differences |
Multi-exchange environments |
Buys and sells the same asset across spot markets without leverage |
Each of these spot trading algorithms leaves distinct footprints in price action and order flow, making them essential references when learning how to spot algorithmic trading and evaluating whether algorithmic trading works under varying spot market conditions.
🔍 How to Spot Algorithmic Trading in Real Markets?
Spot algorithmic trading often leaves observable patterns in live markets because machines execute orders faster and more consistently than humans. Learning how to spot algorithmic trading starts with understanding how these systems interact with the order book and liquidity.
-
Order book behavior: Rapid appearance and cancellation of orders at specific price levels, often refreshing within milliseconds.
-
Repeating order sizes: Identical trade sizes appearing again and again, suggesting automated position sizing rather than manual decisions.
-
Reaction speed: Near-instant responses to price changes, news, or liquidity shifts that are impossible to replicate manually.
-
Liquidity absorption patterns: Large passive orders absorbing aggressive market orders without significant price movement.
When these signals appear together, they form a practical algorithmic spotlight that helps explain how spot trading algorithms shape price behavior rather than relying on guesswork or speculation.
For readers evaluating whether remote infrastructure is necessary, What is Forex VPS and How to Use provides a clear breakdown of how VPS environments support algorithmic execution beyond local setups.
🧭 How to Spot Algorithmic Trading for Beginners?
For beginners, spotting algorithmic trading does not require advanced math or insider access, but it does require disciplined observation. The goal is to recognize repeatable patterns without assuming every unusual move is algorithm-driven.
-
Beginner-friendly signals: Consistent micro-movements, stable spread control, and repeated executions at similar intervals.
-
Tools: Order book heatmaps, volume footprint charts, and basic exchange trade history data.
-
What not to assume: Not every fast move or loss is caused by manipulation or hidden algorithms.
By focusing on observable behavior instead of narratives, beginners can safely learn how to spot algorithmic trading while avoiding exaggerated or conspiratorial interpretations.
📈 Does Algorithmic Trading Work in Spot Markets?
Whether spot algorithmic trading succeeds depends heavily on market conditions, execution quality, and realistic expectations. There is no universal answer to whether algorithmic trading works, especially in non-leveraged spot environments.
-
When it works: High-liquidity markets, stable infrastructure, low latency, and clearly defined strategy logic.
-
When it fails: Thin liquidity, sudden regime changes, poor execution, or untested strategy assumptions.
-
Market conditions that matter: Volatility structure, spread behavior, exchange reliability, and fee models.
In spot markets, algorithmic trading can be effective but never guaranteed, and understanding both strengths and limitations is essential for evaluating spot trading algorithms with an informed, EEAT-driven perspective.
⚔️ Spot Algorithmic Trading vs Forex Algorithmic Trading
Spot algorithmic trading and forex algorithmic trading are often grouped, but they operate under very different market mechanics and risk structures. A clear comparison helps avoid confusion and explains why strategies, infrastructure, and expectations differ between the two.
Traders who are new to currency markets and want a foundational context before comparing automation models may benefit from reviewing Forex Trading for Beginners to understand how manual forex trading differs from spot algorithmic trading.
|
Factor |
Spot Algorithmic Trading |
Forex Algorithmic Trading |
|
Leverage |
No leverage, fully funded trades |
High leverage is common |
|
Fees |
Exchange trading fees only |
Spreads, swaps, and commissions |
|
Volatility |
Asset-dependent, often structural |
Influenced by macro events and news |
|
Risk Profile |
Capital-based, transparent exposure |
Amplified risk due to leverage |
|
Infrastructure Needs |
Low-latency execution, stable API |
Ultra-low latency, broker-dependent routing |
Spot Algorithmic Trading vs Forex Algorithmic Trading Table
For readers interested in leveraged markets and automation, this distinction becomes clearer when comparing spot systems with concepts explained in Forex Algorithmic Trading, which highlights how leverage and broker infrastructure fundamentally change algorithm design and execution risk.
🖥️ Infrastructure Requirements for Spot Algo Trading
Infrastructure plays a decisive role in whether spot algorithmic trading performs as expected or fails due to execution issues. Even simple spot trading algorithms depend on stable connectivity, predictable latency, and continuous uptime.
|
Infrastructure Element |
Why It Matters in Spot Algo Trading |
|
Latency Importance |
Faster execution reduces slippage and missed fills |
|
VPS vs Local Machine |
VPS offers stability and 24/7 availability |
|
Uptime & Stability |
Prevents strategy downtime during volatile periods |
|
Geographic Proximity |
Closer servers reduce network delay to exchanges |
Infrastructure Requirements Table
Although designed for forex systems, the practical steps outlined in How to Setup a VPS for Forex Robot Trading also apply to spot algorithmic trading environments that rely on continuous uptime and stable execution.
✅ Conclusion
Traders use spot algorithmic trading as their primary method for executing actual trades, which require immediate settlement because the success of their operations depends more on execution excellence and their risk management systems than on their ability to foretell market events.
The study of spot trading algorithms, live market identification methods for detecting algorithmic trading patterns, and algorithmic trading performance metrics enables traders to establish their trading choices based on actual market facts instead of speculative market reports. The need for reliable infrastructure to run algorithms becomes essential because system performance depends on latency, uptime, and system stability.
For traders running spot algorithmic trading systems who prioritize low latency, global data centers, and uninterrupted execution, using a professional Forex VPS from 1Gbits offers a reliable infrastructure layer backed by instant setup and 24/7 technical support.






![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)

