Remote desktop services (RDS) and remote desktop protocol (RDP) are two terms that are often used interchangeably. However, they are not the same thing. RDP is a protocol that allows users to connect to a remote desktop, while RDS is a suite of tools that enables remote access to desktops and applications.
Understanding the differences between RDS and RDP is important for anyone who needs to manage remote access for their organization. This article will explore the key differences between RDS and RDP and how they are used.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
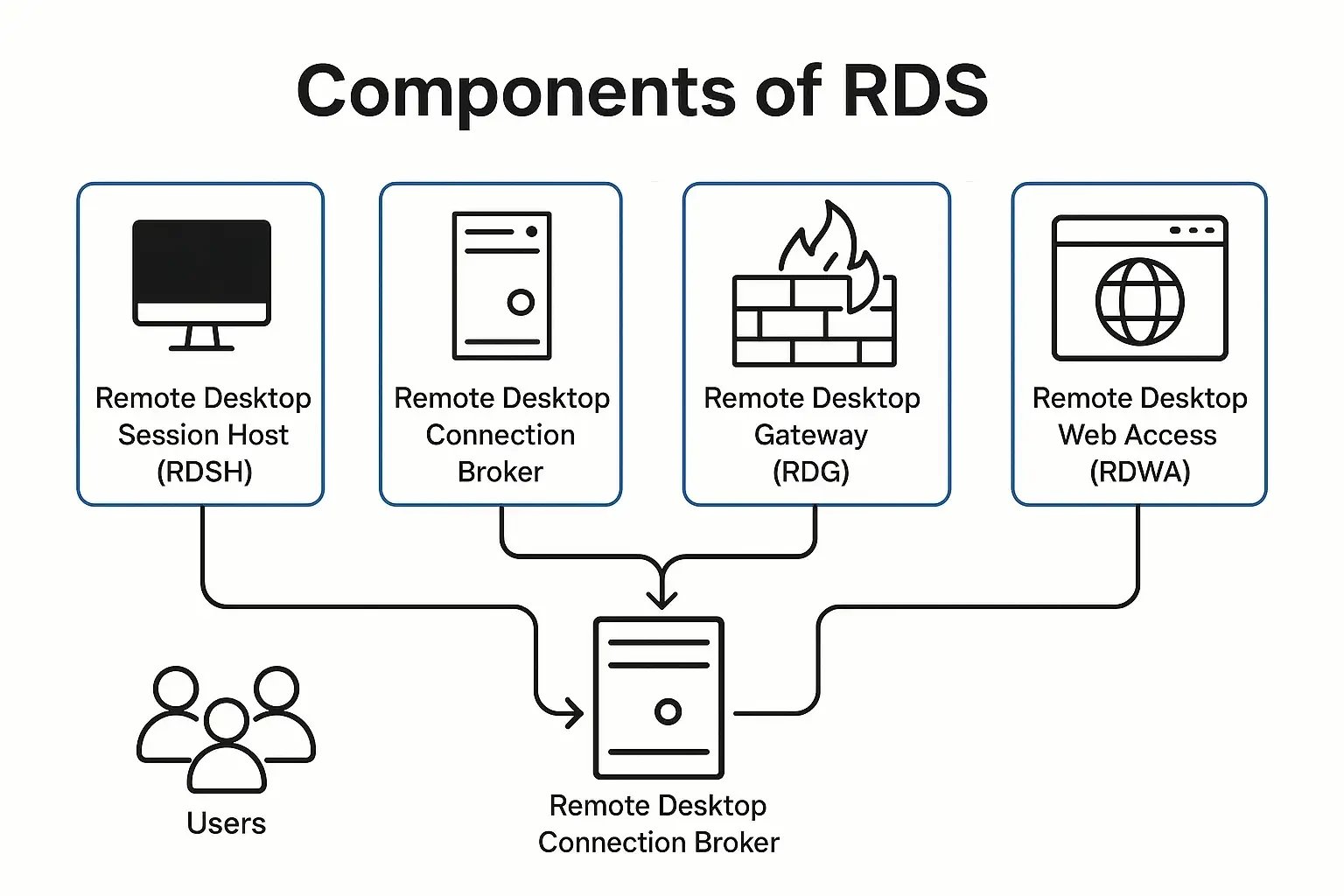
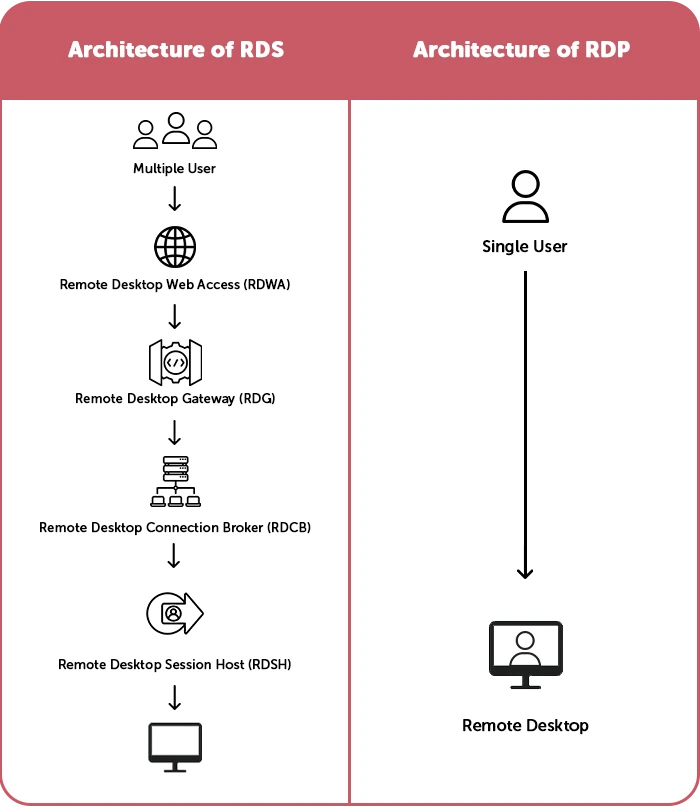
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a suite of tools that enables remote access to desktops and applications. RDS includes several components that work together to provide a complete solution for remote access. These components include:
- Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH): This component hosts remote desktop sessions on a Windows server.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker (RDCB): This component manages user connections to remote desktop sessions and distributes those connections across multiple RDSH servers.
- Remote Desktop Gateway (RDG): This component provides a secure connection between remote clients and RDSH servers.
- Remote Desktop Web Access (RDWA): This component provides a web-based interface connecting remote desktops and applications.
- Remote Desktop Virtualization Host (RDVH): This component allows users to access virtual desktops hosted on a Windows server.
RDS is designed to provide a comprehensive solution for remote access to desktops and applications. It is often used by organizations that need to provide remote access to their employees or customers.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a protocol developed by Microsoft that enables users to access a remote desktop or applications on a remote machine. It is built into the Windows operating system and can be used to connect to remote desktops running Windows. RDP is a simple protocol that provides basic remote access functionality, which allows users to connect to their home or work desktops from remote locations. It is also used by organizations that need to provide remote access to a small number of users.
One of the primary benefits of RDP is that it enables users to access their desktops and applications from anywhere in the world as long as they have an internet connection. This is particularly useful for individuals who travel frequently or work remotely, as it allows them to stay connected to their work or personal computer from any location.
RDP can also access specific applications on a remote machine, without accessing the entire desktop. This is known as RemoteApp, and it allows users to run specific applications on a remote desktop without accessing the entire desktop. This makes it easier for users to work remotely, as they can access the specific applications they need without accessing the entire desktop.
In addition to providing remote access to desktops and applications, RDP can also be used for remote administration of servers. For example, system administrators can use RDP to remotely manage servers running Windows Server, allowing them to perform tasks such as installing software, configuring settings, and monitoring system performance.
Despite its many benefits, RDP has some security risks that users must be aware of. Because RDP requires users to open up a port on their firewall to allow incoming connections, it can be vulnerable to attacks from hackers looking to exploit protocol vulnerabilities.
To mitigate these risks, securing RDP connections, such as using strong passwords and two-factor authentication, limiting the number of users with RDP access, and keeping software up-to-date with the latest security patches. Monitoring RDP connections for suspicious activity and implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems to block unauthorized access is also important.
In addition to security concerns, RDP can also be affected by network latency and bandwidth limitations. This can result in slow performance and lag when using remote desktops or applications. To address this issue, users can optimize their network settings, upgrade their network hardware, or use a remote desktop service that provides higher bandwidth and lower latency connections.
Overall, Remote Desktop Protocol is a powerful tool that can provide users with remote access to their desktops and applications from anywhere in the world. While it does come with some security risks and performance limitations, these can be mitigated by taking appropriate precautions and following best practices for securing RDP connections. With the increasing trend of remote work and the need for flexible work arrangements, RDP has become an essential tool for individuals and organizations.
? Discover the freedom of 1Gbits VPS hosting – take control of your hosting environment and enjoy unparalleled reliability and blazing-fast speeds. ???
RDS vs RDP: Key Differences
Now that we have explained what RDS and RDP are let's examine the key differences between them:
Functionality
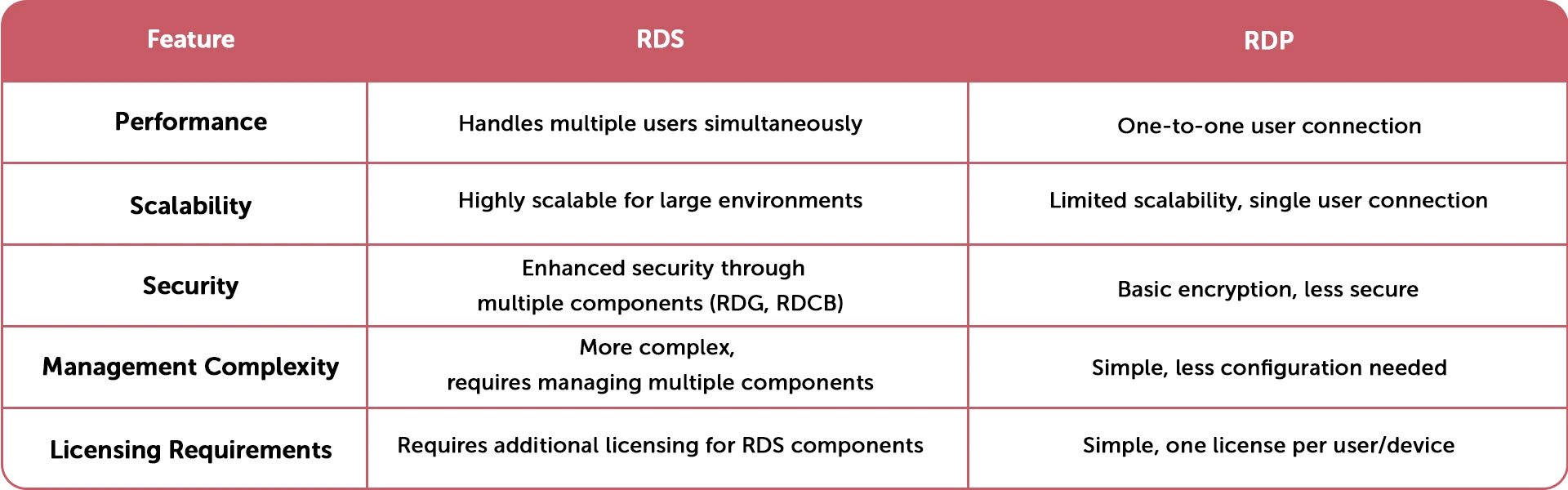
RDS provides a comprehensive solution for remote access to desktops and applications, while RDP provides basic remote access functionality.
Scalability
RDS is designed to be scalable and can support many users, while RDP is designed for use by a few users.
Security
RDS includes several components that provide enhanced security features, such as the Remote Desktop Gateway, which provides a secure connection between remote clients and RDSH servers.
Management
RDS includes several components that work together to provide a complete solution for remote access, making it more complex to manage than RDP.
Licensing
RDS requires a separate license for each user or device that connects to the RDS environment, while RDP is included with Windows and does not require a separate license.
Which One Should You Choose?
When providing remote access to desktops and applications, organizations have two options: Remote Desktop Services (RDS) and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). Both solutions can provide remote access, but their capabilities and features differ. The choice between RDS and RDP depends on your organization's specific needs.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a comprehensive solution that allows organizations to provide remote access to desktops and applications for many users. RDS includes advanced security features such as two-factor authentication, identity federation, and session encryption. It also includes load balancing and user profile management features, making it easier to manage remote access for many users.
RDS is ideal for organizations that need remote access to many users. It is also a good choice for organizations that must comply with specific security requirements, such as those in the healthcare or finance industries. RDS can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, making it a flexible solution that can meet various organizational needs.
On the other hand, Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a simpler solution that provides basic remote access functionality. RDP is built into Windows and can connect to remote desktops running Windows. RDP is ideal for organizations that only need remote access to a few users and do not require advanced security features.
RDP is a great choice for organizations with a small number of remote workers or employees who need occasional access to their work computer from home. It offers a simple and cost-effective solution for these situations, allowing users to securely and efficiently connect to their office desktops. Furthermore, RDP is an excellent option for organizations that may not have the resources or technical expertise to deploy and manage a more complex remote access solution. For businesses seeking to streamline their remote access capabilities without the complexity of intricate setups, considering an RDP purchase can be a wise decision, offering both simplicity and reliability in one package.
In summary, the choice between RDS and RDP depends on your organization's needs. If you need to provide remote access to many users and require enhanced security features, RDS is the better choice. However, RDP may be sufficient if you only need to provide remote access to a small number of users and do not require advanced security features. It is important to evaluate your organization's needs and budget when making this decision and to consult with IT professionals to determine the best solution for your organization.
Conclusion
RDS and RDP are two terms often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. RDS is a suite of tools that enables remote access to desktops and applications, while RDP is a protocol that allows users to connect to a remote desktop. Understanding the differences between RDS and RDP is important for anyone who needs to manage remote access for their organization.
FAQs
What is RDS?
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a comprehensive solution that allows organizations to provide remote access to desktops and applications for many users. It includes advanced security features such as two-factor authentication, identity federation, and session encryption. It also includes load balancing and user profile management features, making it easier to manage remote access for many users.
What is RDP?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a simpler solution that provides basic remote access functionality. It is built into Windows and can connect to remote desktops running Windows. RDP is ideal for organizations that only need remote access to a few users and do not require advanced security features.
What are the main differences between RDS and RDP?
The main difference between RDS and RDP is the level of complexity and the range of features offered. RDS is a comprehensive solution with advanced security features and management tools for providing remote access to many users. RDP, on the other hand, is a simpler solution that provides basic remote access functionality and is ideal for organizations that only need remote access to a few users.
Which one should I choose: RDS or RDP?
The choice between RDS and RDP depends on your organization's specific needs. If you need to provide remote access to many users and require enhanced security features, RDS is the better choice. However, RDP may be sufficient if you only need to provide remote access to a small number of users and do not require advanced security features.
Can RDP be used for remote administration of servers?
Yes, RDP can be used for remote administration of servers. System administrators can use RDP to remotely manage servers running Windows Server, allowing them to perform tasks such as installing software, configuring settings, and monitoring system performance. However, if you need to provide remote access to many users for server administration, RDS may be a better choice as it includes advanced management tools for managing remote access for many users.
People also read: