Modern technology connects workers to their workplace to share files and apps, making remote desktops the new norm. But the majority of people who lack technical expertise find the technology to be incomprehensible. In this blog post, we'll explain VDI vs RDP and describe each one's functions, applications, and similarities and differences so you may decide which one is best for you.
What is VDI?
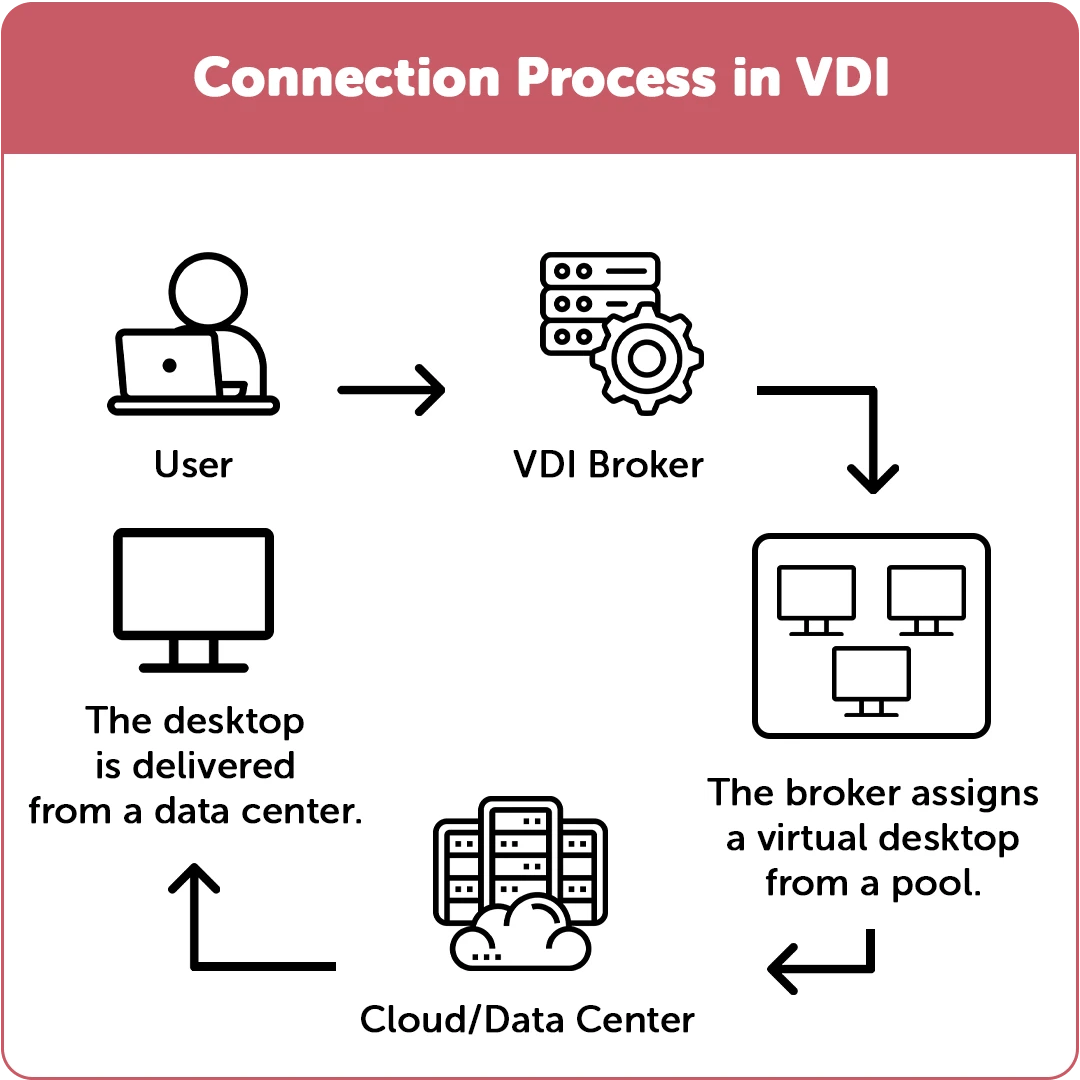
VDI stands for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, which gives each user their virtual machine (VM). The virtual machine operates on an OS housed in a data center, either locally or through a cloud service like Azure. The desktops of each user are completely separate from those of other users.
The isolation offers total administrative control to operate programs without worrying about viruses spreading throughout the network. Resources like CPU, memory, and disc space can also be distributed based on user demand.
Simply put, VDI is a set of hardware, software, and network settings that enables the distribution of virtual desktops and virtual servers to end users.
What is RDP?
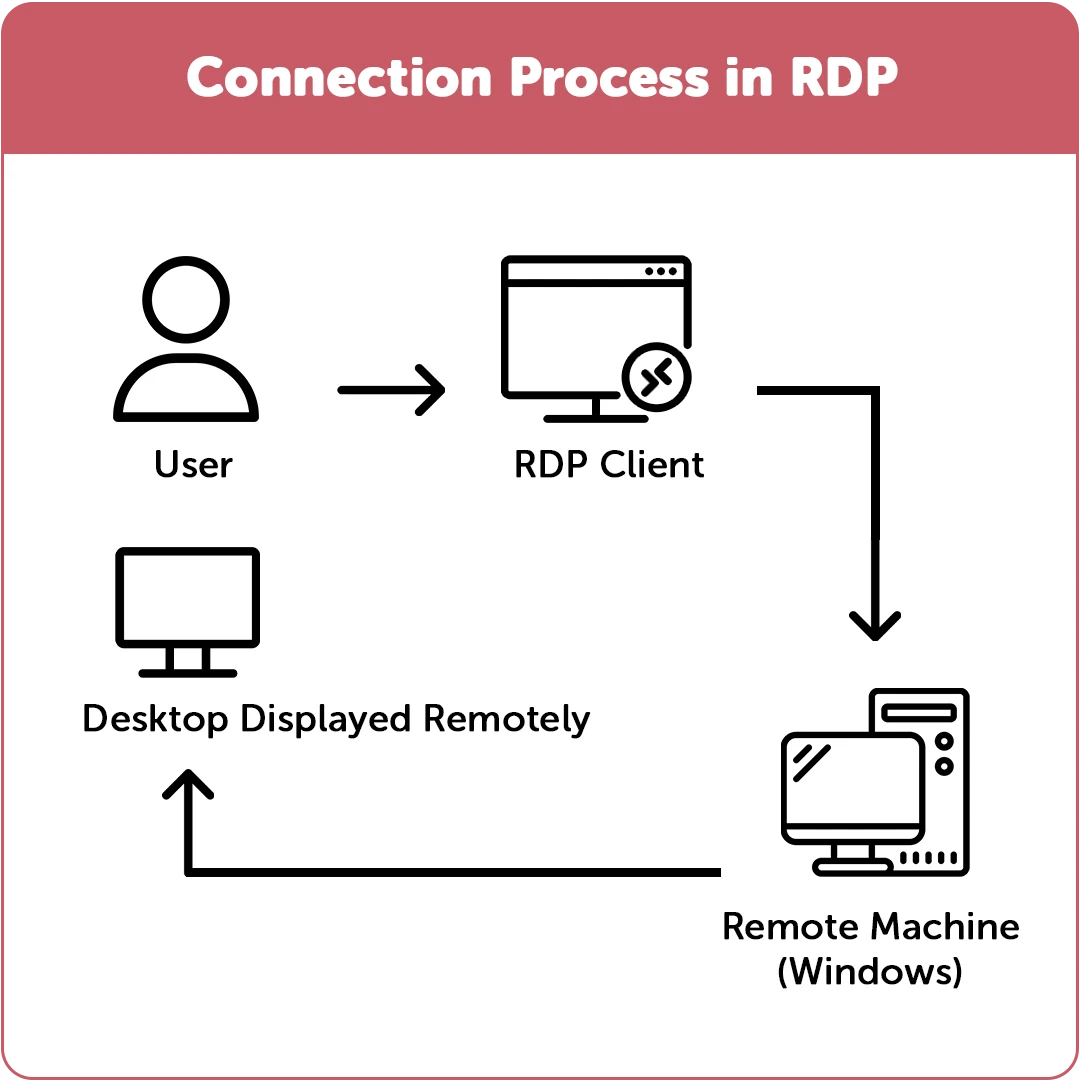
RDP, or Remote Desktop Protocol, is a network communication protocol created by Microsoft. It serves as the foundation and operating system for RDS and VDI. It sends GUI and commands from the server to the client.
RDP's compatibility with VPS hosting servers, which can provide dependable and customizable hosting, is its greatest strength. A dependable RDP Server can be built for a very low cost.
You can use shared RDP accounts or our highly recommended admin RDP servers. For example, a Cloudzy RDP Server is an excellent method to host a quick and powerful remote desktop.
VDI vs RDP: What are they mainly used for?
Let’s find out when it’s better to use VDI and when you should take advantage of RDP.
VDI's primary applications
All VDI users have a dedicated platform they can change. The administrator can establish policies to specify what can be altered and what applies to all virtual systems. Users would experience Microsoft Windows 10 in a more comfortable atmosphere.
VDI offers virtual desktops and applications independently to avoid compatibility issues, making it a safer option for more intricate implementations of various user forms. However, the considerable expense and difficulties of installation and maintenance must be considered.
RDP's primary purposes
In general, enterprises with multiple users requiring the same number of programs and services benefit most from RDP. RDP lacks some customization but is easier to set up and administer than VDI. Sharing server resources among many users reduces capacity and overhead costs but increases the likelihood of application issues.
VDI vs RDP: similarities
They are similar in that they both allow users to access resources hosted on servers by logging into a remote desktop. There are no security risks or data loads on the user's local machine.
Remote connections are made possible by VDI and RDP, enabling employees to work from home while still having access to corporate data stored on the servers. They give customers access to a desktop with the same local feel they may have had on their own devices.
As far as the user is concerned, their performance is fairly comparable in speed and latency.
⚙️ Customizable and efficient – 1Gbits VPS hosting empowers you to tailor your server to fit your unique needs, all while maximizing performance. ???
VDI vs RDP: comparison
|
Feature |
VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) |
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) |
|
Performance |
Provides a dedicated desktop experience with independent resources for each user. |
Shares server resources among multiple users, which may reduce performance. |
|
Security |
Higher security due to full desktop isolation and centralized control. |
Lower security as resources are shared and there is potential for user interference. |
|
Cost |
Higher cost due to the need for complex infrastructure and greater management. |
Lower cost due to simpler deployment and fewer resource requirements. |
|
Scalability |
Hardware limitations may restrict scalability. |
Higher scalability due to the lack of physical constraints. |
|
Best Use Cases |
Suitable for organizations needing personalized desktops and high security. |
Ideal for organizations needing simple and cost-effective remote access. |
RDP is the basic protocol that enables remote connection in any system, whereas VDI is thought of as the modern technique of remote desktop connection where users have customized desktops with complete customization possibilities. We must delve into the details to understand the whole list of differences:
Compatibility with OS
Each user can have their operating system using VDI, including iOS, Mac, and even Android. In contrast to RDS (Remote desktop service) which can only be used on Windows servers, RDP is also very compatible with Mac OS X, iOS, and Android. So both technologies perform well in terms of OS flexibility.
Amount of servers
While RDP and RDS are frequently placed on a single server that supports multiple users, VDI uses servers to the extent the number of users requires. Therefore, when comparing RDP with VDI, RDP has the advantage regarding the number of servers.
Scalability
RDP appears to have no physical limits; however, VDI has hardware restrictions that prevent connections from growing beyond a specific number. RDP is, therefore, more scalable than VDI.
Resource distribution
The user who needs resources the most gets them thanks to VDI's improved resource allocation system. However, despite their different roles within the network, RDP is tied to a single allocation system where resources are distributed equally to users.
In the battle between VDI and RDP, VDI offers a more intelligent resource allocation system.
Ease of administration
VDI is a complicated system that requires technical expertise to manage. RDP, however, provides a straightforward configuration process that even non-technical users can establish. However, in contexts with several users, the setup may become challenging, which is readily fixed with the help of a wealth of internet resources. Overall, RDP is simpler to administer.
Flexible device design
The "Bring Your Own Device (BYoD)" feature of VDI enables you to select your own device (phone, tablet, laptop, or pc). RDS is only available on PCs because it uses Windows Server, although RDP is also available on mobile devices. Therefore, considering VDI vs RDP, users have a choice of devices thanks to both apps.
Desktop customization
Persistent and non-persistent desktops are the two types available with VDI, and they differ in personalization. While the non-persistent type randomly selects a desktop from a pool, the persistent type enables the user to have a customized OS and programs.
On the other hand, RDP users can utilize a designated desktop with preloaded generic apps because these services do not provide this capability. The desktop is based on a session-based shared VM, meaning it is disposable when the session ends. Therefore, when comparing desktop customization between VDI and RDP, VDI wins.
Internet accessibility
RDP and RDS require an always-on internet connection for users to connect and work, whereas VDI provides a sync feature that enables users to work offline and only sync data when they are back online. As a result, users of VDI appear to have more options for internet connectivity with VDI than with RDP.
Overall cost
Regarding overall cost, VDI provides each user with a virtual instance that includes customized apps and data. According to the number of users, this will necessitate licenses and subscriptions that can quickly pile up in cost. Costs associated with hardware and administration are also high.
RDP, on the other hand, is cost-free because Windows has included it since XP. Only the Windows setting needs to be changed to enable it. All users must log in to the same server using RDP, and RDS requires a single instance of Windows server to be deployed on a single server.
The sole restriction on users is the capability of the underlying hardware. However, if the server is housed on-site, a Client Access License (CAL) is required; otherwise, an Azure subscription is necessary.
RDP is, therefore, more cost-effective than VDI.
VDI vs RDP: which one should you use?
It depends on your organization's needs and finances, is the truthful response. RDP is still the default option because it is cost-free, and all remote desktop systems require it. And it is a good idea to invest in RDS if you have a sizable number of customers who utilize generic apps and require the same amount of processing power because the overall cost of license, resources, and administration will be lower.
However, VDI can be a better option if you have various user types using unique programs with various computing resources. It gives consumers access to the resources and customization they require. However, for most users, RDP is sufficient to meet their needs for a dependable and quick remote desktop experience.
Conclusion
There is little doubt that businesses can find various hosted solutions to meet their needs in today's demanding computing environments, where budgets are smaller and expectations for technological returns on investment are higher. Hardware and required support can be some of the biggest cost factors for business desktop computing users. But there are reliable desktop PC choices if you want to use software to accomplish more.
Hosting desktop environments on a central server is known as virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). It is a type of desktop virtualization because the particular desktop images are distributed to end users via a network and run inside virtual machines (VMs). RDP is the most widely used protocol for remote desktop software, but other options include Independent Computing Architecture (ICA), virtual network computing (VNC), and others.
Individuals who want to use remote desktop technology to access their computer(s) from a distance can benefit from this article. Whether you're a professional looking to manage business operations remotely, a student needing to access school resources from home, or simply someone who wants to securely access their personal files while traveling, the information provided here will guide you through the benefits and features of using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) servers. To get started with your own remote desktop solution, you can easily buy RDP server services that offer reliable, high-speed connections and robust security features to meet your specific needs.
People also read:









