The general device or system uses hostnames to easily identify a machine within a network through a human-readable format—basically, a name was given to your Linux system. By default, the system hostname is set during the installation process.
In this article, we will go through the process of changing the hostname in Linux systems. Before we get to the step-by-step process, let’s quickly got through what exactly is a hostname. The following tutorial contains commands that will work for the following Linux distributions: CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, LinuxMint and most other Linux distros.
What is a hostname?
A hostname is a label assigned to a machine (PC, server, printer, etc.) to identify the devices on the network. Therefore each device on the network should have a unique hostname. Usually, the hostname is set during the installation, and it’s relatively easy to change it to something different.
This is not something that many people care about, and usually, when getting a VPS, the datacenter will automatically set it. If you manage multiple servers (like me) or don’t like the current hostname on your system, then this is for you.
Personally, I need to see the relevant information on the SSH screens by different hostnames. This will give the relevant information swiftly on what system I am logged in to.
The hostname can be a simple string containing letters, numbers, dots, and hyphens. Whereas if the machine is connected to the internet, it is recommended to use a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) as the system hostname.
To learn how to change the hostname on a Windows Server, you can follow this guide on changing the hostname in Windows Server to manage hostnames across different operating systems efficiently.
How to change the hostname: temporary
Here's how to temporary change the hostname on your Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora or Debian system. The following commands are the same for all the distributions.
Changing the hostname is not complicated at all; you need a single command.
- To display the current hostname on your Linux system, type in:
hostname
![]()
- To output the FQDN of the system:
hostname --fqd
- To change the hostname of your system:
hostname NEW_NAME
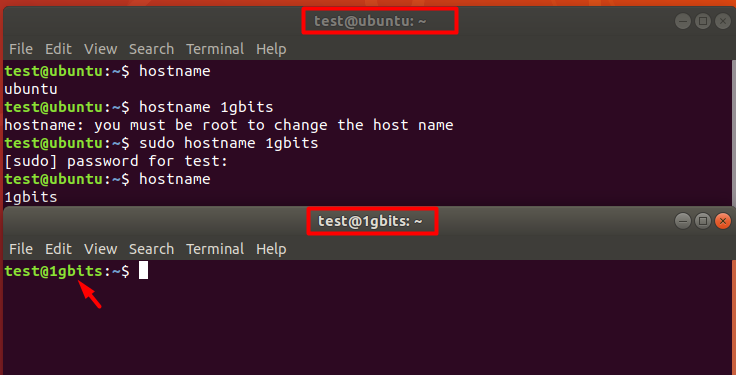
As you see here, the “NEW_NAME” was replaced with the actual hostname that was needed. However, to perform this action, you will need to be the root user or have root privileges (check the above picture).
You will most probably need to exit the current shell to see the changes in your shell prompt.
That’s all and good, but this is a temporary solution and will be reverted to the original upon the next reboot. To make the hostname permanent, you will have to change some configuration files.
To ensure your system is up-to-date while configuring settings like the hostname, it’s a good idea to update your Linux system. Regular updates can improve security and compatibility with new configurations.
How to change hostname permanently in Linux (CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora)
Method 1
New versions of different Linux distributions like CentOS, Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, etc. comes with systemd. This is a system and service manager which provides the hostnamectl command which will be used in this tutorial to manage the hostnames.
Note: To run this command, you will need to be a root user or have sudo privileges.
- Run the command:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname NEW_NAME

Here set the NEW_NAME as the preferred name of your system.
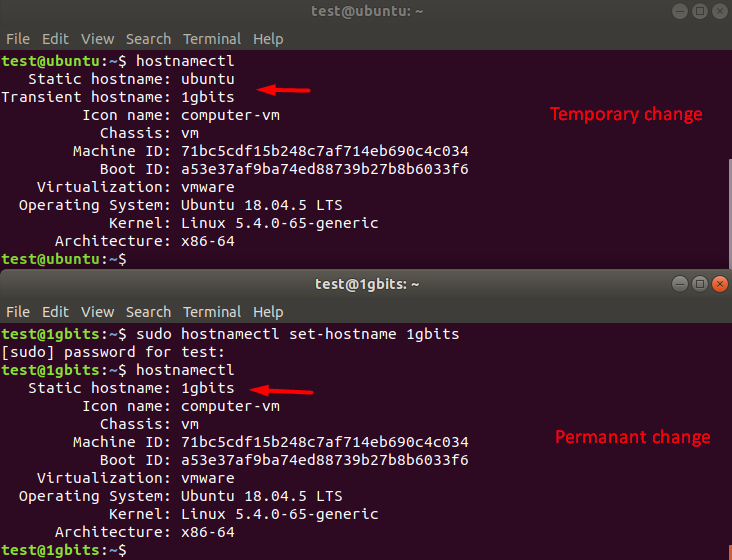
- Verify if the hostname was successfully changed.
hostnamectl
In the output, you will see the new system hostname and additional kernel information.
To learn more about Linux commands, we made a beginners guide (check it out).
Method 2
This method will edit the system file containing the hostnames and then run that specific file to activate the changes.
Note: To continue this process, you will need to be a root user or have sudo privileges. This tutorial will use the nano text editor; however, you can use any other text editor.
- Enter the new hostname:
sudo hostname NEW_NAME

- Enter the following command and update the hostname.
sudo nano /etc/hostname
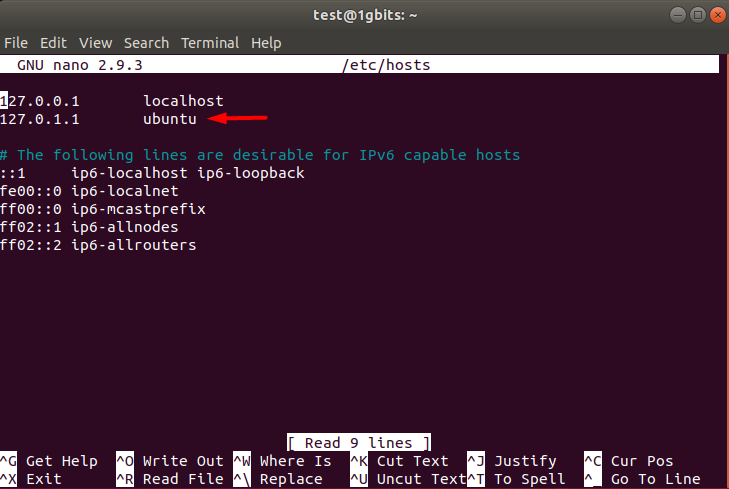
- Now, as the final step, update the lines that read your old hostname:
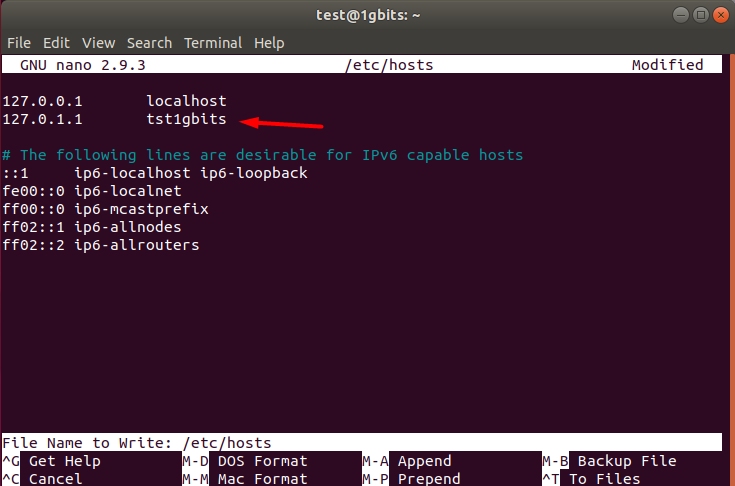
sudo nano /etc/hosts
- In the appeared window, check here, as shown in the picture below:
- Now change the name from the old name to the new one:
127.0.1.1 OLD_NAME
127.0.1.1 NEW_NAME
- Save and close the file!
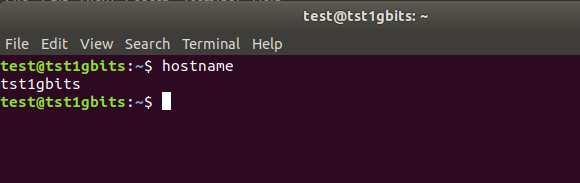
- Check for the changes.
hostname
Conclusion
Congratulations! You made it to the end and successfully changed the hostname of your Linux system. The above commands were done and tested on Ubuntu 20.04. However, the commands are similar for all other Linux distributions.
Be careful when changing the hostname permanently using the VPS server as it might make some connection errors when using the SSH client.
In some cases, depending on the Linux distribution, the commands might change slightly. If you will come across any problems, let us know in the comments below.
When you buy linux vps, it is important to consider factors such as the level of technical support provided, the security measures in place, and the cost of the hosting plan. we offer you best services.
People Are Also Reading:





![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)