Windows Server with Hyper-V has become the mainstay of Microsoft’s integrated virtualization, enabling users to create multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server and utilize its resources.
By 2025, this combination will be crowned as essential in IT infrastructures that seek efficient, large-scale control over their resources at a low cost. The Hyper-V role installation on Windows Server allows IT personnel not only to consolidate their resources and segregate them accordingly but also to manage them without requiring extra hardware.
The audience will learn about skimming through virtualization configuration, optimization, and security that will yield increased performance, flexibility, and less complicated backup management in modern data centers and cloud-connected environments alike.
⚙️ What Is Hyper-V on Windows Server?

Windows Server with Hyper-V combines Microsoft’s operating system with a powerful built-in virtualization platform. It enables organizations to run multiple virtual machines efficiently on a single server, reducing hardware costs while maximizing performance and resource utilization.
By integrating the Hyper-V role in Windows Server, administrators gain centralized control, enhanced scalability, and enterprise-grade virtualization capabilities that fit both on-premises and hybrid cloud environments.
🧩 Definition & Overview
Hyper-V is Microsoft’s native hypervisor technology that allows users to create, manage, and run multiple virtual operating systems simultaneously on one physical machine. Each virtual machine operates independently, sharing resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage through the hypervisor layer. This Hyper-V Windows Server setup delivers better hardware utilization, isolation, and system reliability across all hosted workloads.
🏗️ Role of Hyper-V in Windows Server
The Hyper-V Role in Windows Server enables virtualization functionality by transforming a standard installation into a hypervisor host. Once installed through Server Manager or PowerShell, it allows the creation of virtual switches, network adapters, and dynamic storage configurations.
Through Hyper-V Manager or Windows Admin Center, administrators can easily monitor performance, adjust resource allocation, and automate VM operations.
🧾 Which Windows Server Versions Include Hyper-V?
Microsoft Windows Server with Hyper-V is available in several versions, starting from Windows Server 2008 and continuing through 2019, 2022, and the upcoming 2025 release.
Both Standard and Datacenter editions include Hyper-V, with the Datacenter edition offering advanced features like live migration and unlimited VMs. These capabilities make Windows Server with Hyper-V 2022 a leading choice for virtualization in enterprise and cloud-based infrastructures.
⚖️ Windows Server with Hyper-V vs Standalone Hyper-V Server
Both Windows Server with Hyper-V and Standalone Hyper-V Server deliver virtualization capabilities, but they differ in management tools, licensing, and feature depth. Understanding these distinctions helps administrators choose the right platform for their business, balancing flexibility, performance, and cost efficiency.
|
Feature / Aspect |
Windows Server with Hyper-V |
Standalone Hyper-V Server |
|
Licensing |
Includes OS and Hyper-V role in one package; requires Windows Server license |
Free to use but requires separate licenses for guest OSs |
|
Management Tools |
Managed via Server Manager, PowerShell, Hyper-V Manager, and Windows Admin Center |
Managed remotely; limited local GUI, uses PowerShell and Hyper-V Manager remotely |
|
Features |
Full Windows Server functionality (Active Directory, DHCP, file services) plus virtualization |
Focused purely on virtualization; lacks full Windows Server roles |
|
Backup & Integration |
Integrated with Windows Server Backup and supports third-party backup tools |
Requires external tools or remote management for backup and monitoring |
|
Performance |
Slightly higher overhead due to OS services running alongside Hyper-V |
Minimal overhead; optimized solely for VM hosting |
|
Best For |
Enterprises needing a multipurpose server with built-in virtualization |
Dedicated hypervisor hosts, test labs, or lightweight VM clusters |
Standalone Hyper-V Server VS Windows Server Hyper-V
Windows Server with Hyper-V offers a versatile, all-in-one platform ideal for organizations that need both system services and virtualization in one environment. On the other hand, the Standalone Hyper-V Server is best suited for minimalistic, performance-focused deployments where simplicity and cost efficiency take priority.
If you’d like to explore how Microsoft’s solution compares to VMware, read our detailed comparison of Hyper V vs VMware for deeper insights into performance, scalability, and management tools.
🛠️ Installing & Activating Hyper-V on Windows Server
Installing Hyper-V on Windows Server is a straightforward process that can be done using either Server Manager or PowerShell. Proper configuration ensures stable virtualization performance, efficient networking, and compliance with licensing requirements for Microsoft Windows Server with Hyper-V.
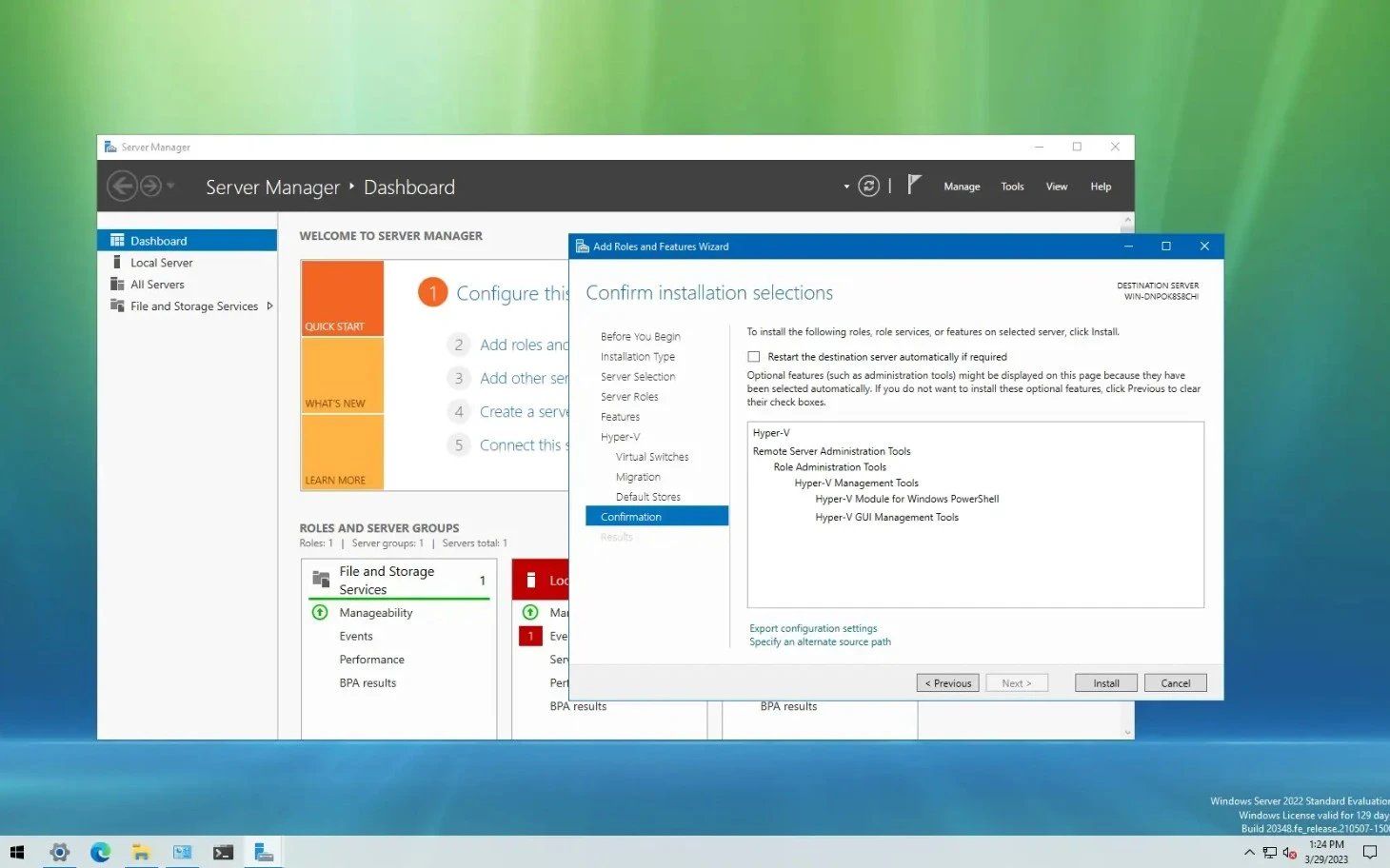
Windows server hyper v activation
-
Open Server Manager → click Add Roles and Features → choose Role-based or feature-based installation.
-
Select your server and check the Hyper-V box under “Server Roles.”
-
Follow the prompts to install management tools such as Hyper-V Manager and restart your system when prompted.
-
Alternatively, install via PowerShell with the command:
-
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Hyper-V -IncludeManagementTools -Restart
-
After installation, open Hyper-V Manager to create and configure your first virtual machine.
-
Configure Virtual Switches via the Virtual Switch Manager, selecting External, Internal, or Private network modes depending on your setup.
-
Set up storage options such as fixed-size or dynamically expanding VHDX files for efficient disk management.
Once installed, your Windows Server with Hyper-V 2022 environment will be ready for virtual machine deployment and network configuration. Proper activation and setup guarantee full performance, compliance, and long-term stability for enterprise-grade virtualization.
To see how these principles apply in real hosting environments, review our step-by-step guide on Windows VPS Configuration.
💡 Virtualization Concepts & Best Practices
Understanding the fundamentals of Windows Server Hyper-V and virtualization helps administrators build efficient, scalable, and secure infrastructures. Whether you’re deploying virtual machines or managing containers, applying best practices ensures stable performance and simplified management.
Virtual Machines (VMs):
Independent instances that emulate physical computers within Microsoft Windows Server with Hyper-V, allowing multiple OS environments to run simultaneously.
Containers:
Lightweight, isolated environments that share the same OS kernel, ideal for microservices and DevOps deployments.
Resource Allocation:
Assign CPU, memory, and storage resources carefully to prevent contention between active workloads.
Integration Services:
Tools that improve performance and synchronization between host and guest systems, including time sync, heartbeat monitoring, and data exchange.
Dynamic Memory:
Enables automatic adjustment of RAM based on workload demand, enhancing resource efficiency.
Snapshots (Checkpoints):
Capture the state of a VM at a specific time, allowing safe rollback during updates or testing.
Hyper-V Backup on Windows Server:
Use Windows Server Backup or third-party tools to perform consistent backups of running VMs, ensuring minimal downtime and easy recovery.
Adopting these Windows Server with Hyper-V best practices improves reliability, resource optimization, and operational efficiency.
For a better understanding of how Hyper-V compares to Linux-based hypervisors, check out our comprehensive guide on KVM vs Hyper-V.
🚀 Performance Tips & Optimization
Optimizing Windows Server with Hyper-V ensures that virtual machines deliver stable, high-speed performance under heavy workloads. Fine-tuning CPU, memory, and storage configurations can drastically improve virtualization efficiency and reduce latency across your infrastructure.
-
CPU Tuning: Allocate virtual processors (vCPUs) based on the host’s physical cores and workload demand, and avoid overcommitting CPU resources for critical VMs.
-
Memory Optimization: Use Dynamic Memory to automatically adjust RAM between VMs, maintaining efficiency during fluctuating workloads.
-
I/O Performance: Enable I/O threading and use virtual SCSI controllers for better disk performance compared to IDE emulation.
-
Storage Options: Consider pass-through disks for near-native performance or VHDX virtual disks for flexibility and portability across hosts.
-
NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access): For large servers, enable NUMA awareness to optimize memory access patterns across multi-CPU systems.
-
Synthetic vs Emulated Devices: Use synthetic devices wherever possible; they communicate directly with the hypervisor for faster performance than legacy emulated devices.
With proper tuning, Hyper-V Windows Server can rival dedicated hardware performance while offering flexibility and scalability.
🧰 Common Challenges & Troubleshooting
Even the most optimized Windows Server with Hyper-V setups can face issues related to networking, storage, or configuration. Identifying common problems and their quick fixes ensures smooth operation, system stability, and minimal downtime in virtualized environments.
|
Issue |
Possible Cause |
Solution / Fix |
|
VM Connectivity or Network Issues |
Misconfigured virtual switch, wrong NIC assignment, or firewall restrictions |
Verify Virtual Switch Manager settings, ensure the external network is properly mapped, and adjust firewall rules. |
|
Storage or Disk Performance Bottlenecks |
Overloaded disk I/O, fragmented VHDX files, or insufficient bandwidth |
Use pass-through disks, defragment VHDX files, or move VMs to faster SSD-based storage. |
|
Hyper-V Role Conflicts or Activation Errors |
Incomplete installation, role dependency issues, or licensing mismatch |
Reinstall the Hyper-V role, ensure all updates are installed, and confirm Windows Server Hyper-V activation status. |
|
Hyper-V Manager Issues |
Corrupt configuration, missing permissions, or outdated management tools |
Run PowerShell to verify settings, reset the management console, and update Hyper-V Manager components. |
|
Backup Failures |
Incorrect VSS configuration or insufficient permissions |
Configure Volume Shadow Copy Service, ensure backup tools have full access, and test restore functionality regularly. |
By following these solutions, administrators can resolve most Hyper-V Windows Server errors without extensive downtime. Regular maintenance, monitoring, and keeping both host and guest systems updated significantly reduce the likelihood of recurring issues.
🧪 Use Cases & Scenarios
Windows Server with Hyper-V is a platform suitable for a wide range of business and technical needs. From production workloads to software testing, its flexibility makes it a valuable solution for both enterprises and developers.
Running Multiple VMs (Web, DB, Apps):
Host various workloads such as web servers, databases, and application services on a single Microsoft Windows Server with Hyper-V, ensuring optimal hardware usage and easy management.
Nested Virtualization:
Run Hyper-V inside a virtual machine, ideal for training environments, container-based workflows, or developers testing virtualization setups.
Hyper-V for Lab and Development Environments:
Create isolated sandboxes for software testing, security research, and CI/CD pipelines without risking production infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud Scenarios:
Integrate Windows Server Hyper-V and virtualization with Azure or other cloud services to create scalable hybrid solutions.
Disaster Recovery and Backup Labs:
Replicate and restore environments quickly using Hyper-V backup on Windows Server for resilience and continuity.
These diverse applications showcase how Hyper-V Windows Server bridges the gap between cost efficiency and performance.
Conclusions
The ability to use Windows Server with Hyper-V to its fullest extent is a significant benefit to companies that want very modern and efficient virtualization environments within their current infrastructure. This platform is capable of being installed and licensed, tuned and troubleshooted, thus providing the necessary scalability and reliability for the data centers of 2025.
If you want even more virtualization, turn to professional infrastructure solutions from 1Gbits. We offer instant setup, 24/7 expert support, and global data centers, providing secure and optimized hosting environments perfect for running Hyper-V and virtual machines.
For reliable, high-performance hosting built for virtualization, explore our range of Windows VPS solutions with instant setup.






![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)



