Managing a modern IT infrastructure can be a daunting task. In large organizations, administrators are responsible for hundreds or thousands of servers and client machines, each requiring consistent configuration, security enforcement, and software deployment. This is where Windows Server Group Policy becomes an essential tool.
By understanding what is Group Policy in Windows, how Group Policy Objects (GPOs) work, and best practices for configuration and management, administrators can minimize manual interventions, reduce configuration errors, and streamline IT operations.
This guide covers everything from the basics to advanced administration techniques, including step-by-step configuration for Windows Server 2019 and 2022, troubleshooting tips, and real-world examples.
What Is Group Policy in Windows Server? Definition & Purpose
Windows Server Group Policy is a key feature that allows administrators to centrally manage and configure operating system, application, and user settings on computers running Windows Server and Windows client systems. Using Group Policy, IT teams can enforce security standards, streamline desktop and server configurations, and automate administrative tasks across the network.
Group Policy is implemented through Group Policy Objects (GPOs), which are collections of settings that can be applied to users or computers in an Active Directory (AD) environment. A GPO contains policy settings, security permissions, and the scope of management (SOM).
The main purposes of Windows Server Group Policy include:
-
Enforcing security settings such as password policies and account lockout policies.
-
Configuring system-wide settings, including firewall rules, automatic updates, and power management.
-
Standardizing user environments, including folder redirection, mapped network drives, and desktop configurations.
-
Managing server-specific operational tasks, such as service settings and security hardening.
How Group Policy Works in Active Directory
When integrated with Active Directory, GPOs are linked to sites, domains, or organizational units (OUs). Each object in AD queries applicable GPOs based on its location in the hierarchy. Policy settings are applied at:
-
Computer startup for system-wide settings.
-
User logon for settings specific to user accounts.
The Group Policy infrastructure relies on Client-Side Extensions (CSEs) to process specific settings delivered by GPOs. Think of CSEs as specialized agents that apply the settings assigned to their category, such as security, software installation, or network drives.
GPO vs Local Group Policy
|
Feature |
Local Group Policy |
Group Policy Object (GPO) in AD |
|
Scope |
Single computer |
Multiple users/computers in AD |
|
Storage |
Local machine |
AD + SYSVOL replication |
|
Management |
gpedit.msc |
Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) |
|
Targeting |
Applies to local user or computer |
Can target OUs, domains, or sites |
|
Replication |
None |
Replicated across all domain controllers via FRS/DFSR |
Key Components of Windows Server Group Policy
-
Group Policy Container (GPC) – Stored in the AD domain partition; contains version info, permissions, and links.
-
Group Policy Template (GPT) – Stored in SYSVOL; contains actual policy settings (registry, scripts, ADM/ADMX files).
-
Client-Side Extensions (CSEs) – Modules on clients or servers that process GPO settings (e.g., registry updates, security policies).
-
Scope of Management – Determined by AD structure (OU, domain, site) and optional filters (security, WMI).
By combining these components, Windows server group policy 2022 ensures centralized, consistent, and secure management of IT infrastructure.
How Windows Server Group Policy Works
Group Policy Processing Order (LSDOU)
GPOs are applied in a specific order, often remembered with the acronym LSDOU:
-
Local – Policies applied on the local machine.
-
Site – Policies linked to the Active Directory site.
-
Domain – Policies linked at the domain level.
-
Organizational Unit (OU) – Policies applied to OUs, including nested OUs.
Settings applied later in the sequence override earlier conflicting settings, unless Block Inheritance or Enforced flags are used.
GPO Inheritance, Precedence & Filtering
Inheritance allows child OUs to automatically adopt policies from parent containers. Precedence controls which GPO settings take effect when multiple GPOs are linked to the same object. Administrators can also apply security filtering or WMI filters to target specific users or computers, improving precision and reducing unnecessary policy processing.
User vs Computer Configuration
-
Computer Configuration: System-wide settings; applied at startup. Includes Windows settings, security policies, scripts, and software deployment.
-
User Configuration: Applied at logon; includes desktop settings, mapped drives, and preferences.
|
Category |
Computer Configuration |
User Configuration |
|
Applies at |
Startup |
Logon |
|
Examples |
Firewall rules, automatic updates, software installation |
Desktop layout, folder redirection, mapped network drives |
|
Change by user |
No |
Some via Preferences |
Group Policy Management Console (GPMC)
The Group Policy Management Console is the primary tool for creating, editing, and managing GPOs in Windows Server environments. With GPMC, administrators can:
-
View all GPOs in a domain.
-
Create and link GPOs to OUs, domains, or sites.
-
Edit GPOs using the Group Policy Editor.
-
Monitor GPO inheritance, modeling, and troubleshooting.
How to Install and Open GPMC
On Windows Server:
1. Open Server Manager → Manage → Add Roles and Features.
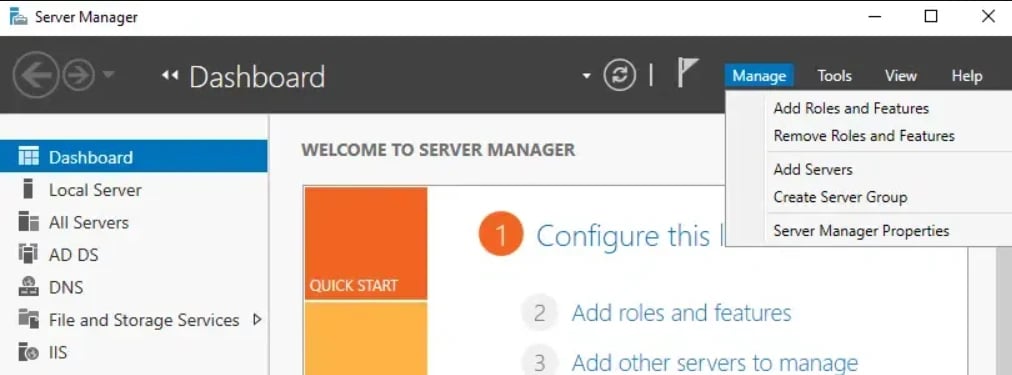
2. Choose Feature-based installation → Next → Select the server.
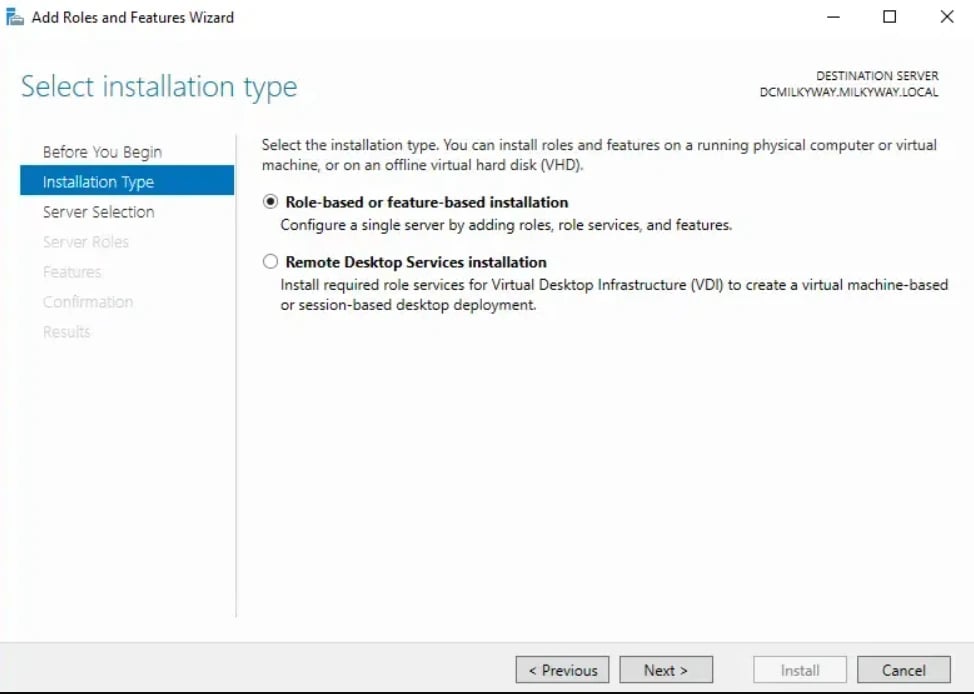
3. Scroll to Group Policy Management, check it, and complete installation.
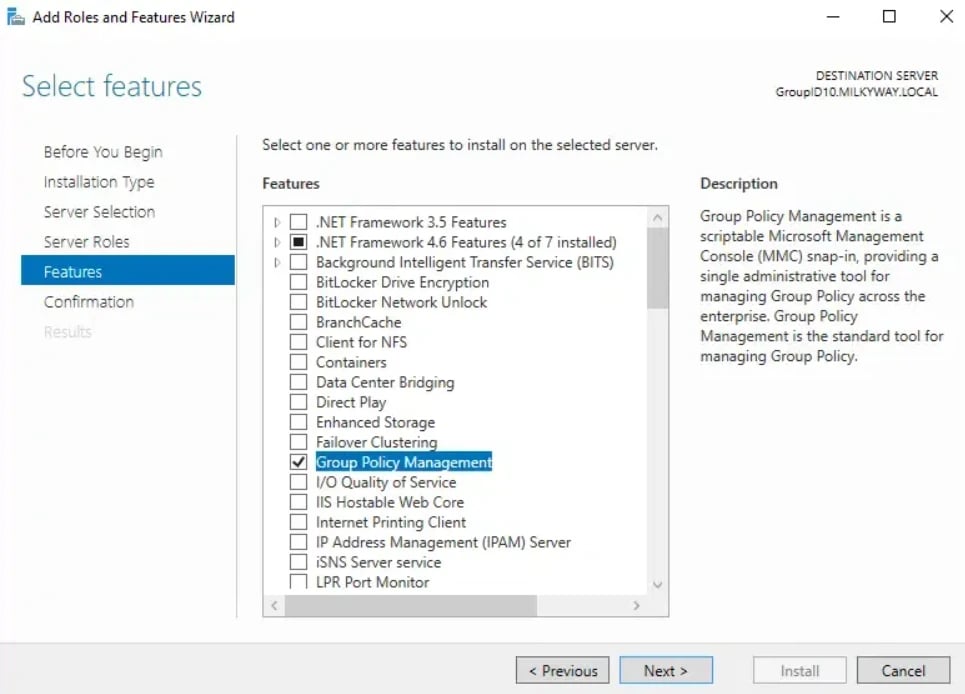
On Windows 10/11 (RSAT):
- Open Settings → Optional Features → Add a feature.
- Select RSAT: Group Policy Management Tools → Install.
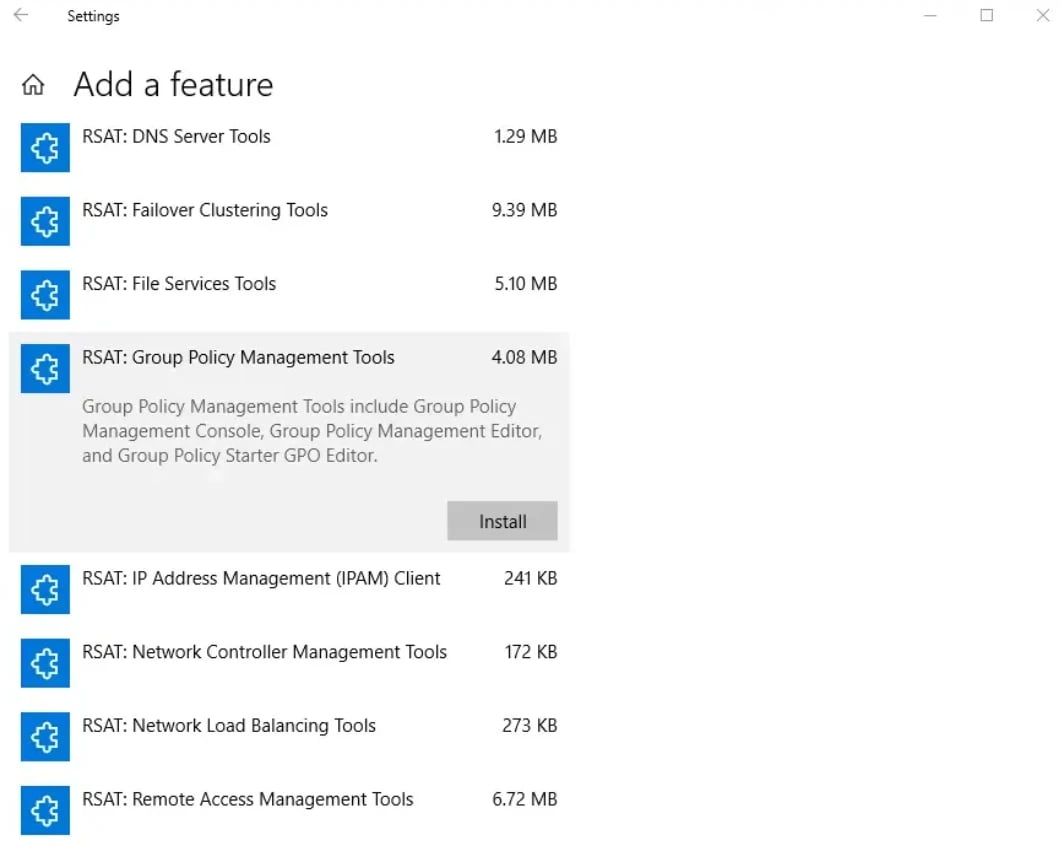
Once installed, run gpmc.msc to launch the console.
For a more detailed installation, check: Windows Server Installation
Administrative Templates (ADMX/ADML)
ADMX/ADML files define registry-based policy settings. ADMX files store the settings themselves, while ADML files contain language-specific descriptions. Keeping templates updated ensures that Windows server group policy 2022 and previous versions (2019, 2016) can manage new OS features and security policies.
Windows Server 2019 & 2022 GPO Template Updates
Microsoft periodically releases updated ADMX templates for newer OS versions. Administrators should replace older ADMX files in the central store to maintain consistency and access to the latest policy settings, including:
-
Password complexity policies
-
Automatic updates
-
Security baseline settings
Advantages of Using Windows Server Group Policy
Implementing Windows Server Group Policy offers numerous benefits for both administrators and organizations:
1. Centralized Management
Instead of manually configuring each machine, administrators can deploy settings to multiple computers and users from a single console. This ensures consistency and reduces administrative overhead.
2. Enhanced Security
Group Policy enforces password policies, account lockouts, firewall rules, and security auditing across all machines. By standardizing security configurations, organizations reduce the risk of breaches and unauthorized access.
3. Automated Software Deployment
Administrators can use Group Policy to automatically install software packages (MSI) on target computers without requiring user intervention. This is ideal for deploying antivirus solutions, productivity tools, or custom applications.
4. Simplified User Environment Management
Settings like desktop layout, mapped network drives, printer assignments, and folder redirection can be automatically configured for users. This improves user experience and reduces support tickets.
5. Efficient Compliance and Auditing
By enforcing policies uniformly across the domain, organizations can easily comply with internal IT standards or external regulatory requirements. Additionally, auditing and logging features help administrators track changes to policies.
Real-World Examples of Group Policy in Action
To understand the practical value of Windows server group policy 2022, consider these examples:
Example 1: University IT Department
A university with 5,000 students and staff uses Group Policy to:
-
Enforce password complexity rules for all accounts.
-
Automatically map network drives to department-specific shares.
-
Deploy antivirus software to all campus computers.
-
Redirect student documents to a central server for backup and security.
Example 2: Corporate Enterprise
A multinational company implements Group Policy to:
-
Enforce security baselines on all domain-joined servers.
-
Schedule automatic Windows updates on workstations without interrupting employees.
-
Apply printer and VPN configurations automatically for remote users.
-
Audit login events and failed access attempts to meet compliance requirements.
Example 3: Small Business Environment
Even a small office with 50 machines can benefit from Group Policy:
-
Restrict USB access to prevent data leaks.
-
Configure a uniform desktop environment for all staff.
-
Automatically map shared drives for teams.
-
Simplify onboarding by applying settings to new computers automatically.
These examples demonstrate that Windows Server Group Policy is not just for large enterprises—it scales to any environment where centralized management is beneficial.
How to Configure Group Policy (Step-by-Step)
Configuring Windows Server Group Policy allows administrators to enforce consistent settings across users and computers. Below is a detailed guide for Windows Server 2019 and 2022.
How to Configure Group Policy in Windows Server 2019 Step by Step
1. Open Server Manager → Tools → Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
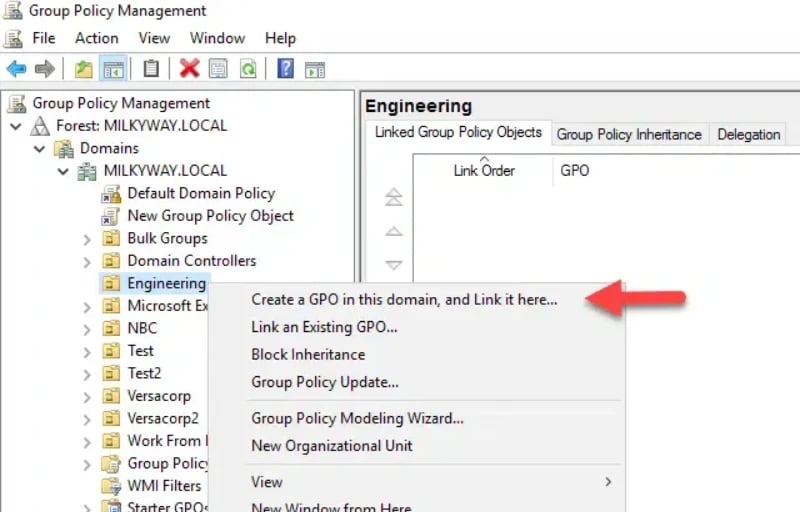
2. Expand your domain, right-click the target OU, domain, or site, and select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here….
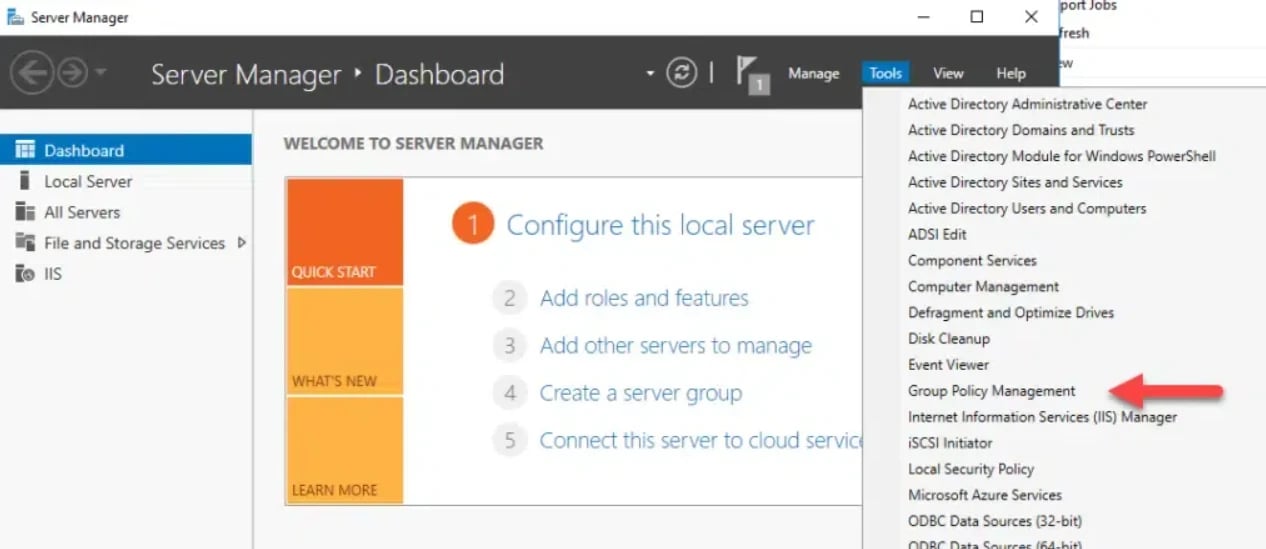
3. Enter a descriptive name for the Group Policy Object (GPO) and click OK.
4. To edit the GPO, right-click it → Edit → opens Group Policy Editor.
5. Navigate through Computer Configuration or User Configuration to apply settings:
- Policies: Password policies, firewall, security restrictions.
- Preferences: Mapped network drives, desktop shortcuts, printers.
6. After making changes, apply them by running gpupdate /force on client computers.
7. Verify applied policies using gpresult /r or the Group Policy Modeling feature in GPMC.
How to Configure Group Policy in Windows Server 2022 Step by Step
-
Launch GPMC from Server Manager → Tools.
-
Right-click the target OU or domain → Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here….
-
Name your GPO appropriately and click OK.
-
Right-click the GPO → Edit → Group Policy Editor.
-
Configure Computer Configuration and User Configuration as needed:
-
Example: Enforce Windows Server Group Policy password complexity settings, configure mapped drives, or enable automatic updates.
-
Apply the GPO with gpupdate /force, then verify with gpresult.
By following these steps, you ensure consistent policy application for both Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server 2022.
Common Group Policy Scenarios (With Examples)
Here are practical examples of Windows server group policy 2022 in action.
Password Complexity Policy
-
Purpose: Enforce strong passwords for security compliance.
-
Configuration:
-
Edit the GPO → Computer Configuration → Policies → Windows Settings → Security Settings → Account Policies → Password Policy.
-
Enable Password must meet complexity requirements.
-
Effect: Users are required to create passwords that include uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters.
Mapping Network Drives via GPO
-
Purpose: Automatically assign network drives to users.
-
Configuration:
-
Navigate to User Configuration → Preferences → Windows Settings → Drive Maps.
-
Right-click → New → Mapped Drive.
-
Configure drive letter, path, and connection options.
-
Effect: All users in the linked OU automatically get the mapped drive without manual setup.
Enabling Automatic Updates
-
Purpose: Keep servers and clients up-to-date with Windows updates.
-
Configuration:
-
Computer Configuration → Policies → Administrative Templates → Windows Update.
-
Enable Configure Automatic Updates → select schedule and options.
-
Effect: Servers automatically download and install updates, reducing administrative overhead.
Applying Security Hardening Policies
-
Harden Windows Server environments by configuring:
-
Firewall rules → Computer Configuration → Policies → Windows Settings → Security Settings → Windows Defender Firewall
-
Account lockout policies
-
Audit policies → track failed login attempts and other security events
Group Policy Troubleshooting
Even with careful planning, there are occasions when Windows server group policy 2022 settings do not apply as expected. Troubleshooting GPO issues is critical to ensure that policies are enforced consistently across the domain. The following sections outline common problems and practical solutions.
Windows Server Group Policy Not Applying
Sometimes, a GPO fails to apply to a user or computer. Common causes include:
-
Network connectivity issues – If a client cannot communicate with a Domain Controller (DC), policies may not apply.
-
Replication delays – GPOs stored in Windows Server Active Directory (AD) and SYSVOL rely on replication between DCs. Delays or failures can prevent policies from being available on all DCs.
-
Incorrect GPO link – The GPO might not be linked to the correct Organizational Unit (OU), domain, or site.
-
Permission restrictions – The client or user might not have sufficient permissions to apply the GPO.
Fixes:
Force a GPO refresh on the client machine:gpupdate /force
-
This immediately reapplies all policies and can resolve temporary issues.
-
Check Active Directory replication:
-
Use repadmin /replsummary to verify replication status between DCs.
-
Ensure the SYSVOL folder is synchronized across all DCs, as GPO templates (ADMX/ADML) reside there.
-
Verify GPO links and permissions:
-
Open Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
-
Check that the GPO is linked to the correct OU, domain, or site.
-
Review security filtering to confirm that the user or computer has Read and Apply Group Policy permissions.
-
Check event logs on client machines:
-
Navigate to Event Viewer → Applications and Services Logs → Microsoft → Windows → GroupPolicy → Operational.
-
Look for errors or warnings related to GPO processing.
By systematically checking these factors, administrators can identify the root cause of GPO application failures.
Using gpresult and Group Policy Modeling
1. gpresult /r Command
The gpresult tool provides a comprehensive report of applied Group Policies for both users and computers.
-
Open Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
Run:gpresult /r
-
Review the sections:
-
Applied GPOs – Lists all policies applied.
-
Denied GPOs – Lists policies that failed due to filtering, permissions, or conflicts.
-
Security Filtering – Confirms which policies the current user/computer can apply.
This report helps administrators verify whether policies are applied as expected and identify potential conflicts.
2. Group Policy Modeling in GPMC
-
Located in GPMC → Group Policy Modeling, this feature allows admins to simulate policy application without enforcing them.
-
Steps:
-
Right-click Group Policy Modeling → Create a new simulation.
-
Select the target OU, site, or domain, along with user and computer objects.
-
Review the simulation results, including applied policies, blocked inheritance, and WMI filter evaluations.
Group Policy Modeling is particularly useful for:
-
Planning new policies before deployment.
-
Predicting conflicts when multiple GPOs are linked to nested OUs.
-
Understanding the impact of WMI filters or security filtering.
Missing Administrative Templates in Windows Server 2012/2019/2022
Older servers may not have the latest ADMX/ADML templates, which can cause newer policy settings to be unavailable. This is common when upgrading servers or managing mixed environments.
Solution:
-
Download the latest ADMX templates from Microsoft:
-
For Windows Server 2019 GPO ADMX: Microsoft Download Center
-
For Windows Server 2022 ADMX: Microsoft Download Center
-
Copy templates to the Central Store:
Path:\\domain.com\SYSVOL\domain.com\Policies\PolicyDefinitions
-
Copy both .admx files (language-neutral) and the .adml files (language-specific) into the corresponding folder.
-
Verify availability in GPMC:
-
Open Group Policy Management Editor.
-
Check that new administrative templates appear under Computer Configuration → Administrative Templates and User Configuration → Administrative Templates.
Keeping ADMX templates updated ensures that administrators can manage all current Windows Server settings without limitations.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips
-
Check network connectivity and Windows Server DNS: Clients must resolve domain controllers correctly to apply policies.
-
Review Group Policy Event Logs: Look for Event IDs 1058 (unable to access GPO) or 1085 (policy conflict).
Force replication: Userepadmin /syncall
-
to synchronize all DCs if replication is delayed.
Reset local Group Policy cache: Sometimes, corrupted local policy cache can block updates. Remove contents from:C:\Windows\System32\GroupPolicy
C:\Windows\System32\GroupPolicyUsers
-
Then run
gpupdate /force.
Windows Server Group Policy Best Practices
To maximize the efficiency and reliability of your Windows Server Group Policy, consider these best practices:
-
Folder Structure: Organize OUs to reflect the administrative and functional structure of your organization.
-
Naming Conventions: Use descriptive names for GPOs (e.g., OU-Name_PasswordPolicy_2022).
-
Minimizing GPO Conflicts: Apply fewer GPOs with clear scope; avoid duplicating policies across OUs.
-
Using WMI Filters: Target specific computers or users based on OS version, hardware, or group membership.
-
Backing Up GPOs: Regularly back up GPOs, especially after significant configuration changes.
-
Updating ADMX Templates: Ensure all administrative templates are up-to-date for consistency across servers.
List of Common Group Policies in Windows Server
Below is a list of frequently used Windows server group policy 2022 settings, categorized for easy reference. This also includes policies relevant to Windows Server 2019.
Security Policies
-
Account Lockout Policy – Lock accounts after a defined number of failed login attempts.
-
Password Policy – Minimum length, complexity requirements, and expiration settings.
-
User Rights Assignment – Define permissions such as logon locally or access network resources.
-
Audit Policies – Track events like logon failures, object access, and policy changes.
-
Windows Firewall – Enable/disable firewall, configure inbound/outbound rules.
Administrative Templates (ADMX/ADML)
-
Software Restriction Policies – Prevent unauthorized applications from running.
-
Windows Update Settings – Configure automatic updates schedules.
-
Desktop Settings – Control start menu layout, taskbar, and control panel access.
-
Network Settings – Configure offline files, folder redirection, and mapped drives.
User Configuration Policies
-
Folder Redirection – Redirect My Documents, Desktop, or other folders to a network location.
-
Mapped Drives – Automatically assign network drives.
-
Printer Deployment – Assign network printers to users.
-
Internet Explorer/Edge Settings – Proxy configuration, home page, and security zones.
Computer Configuration Policies
-
Startup/Shutdown Scripts – Automate scripts during system startup or shutdown.
-
Power Management – Enforce sleep, hibernate, or wake timers.
-
Software Installation – Deploy MSI packages centrally.
-
Security Hardening – Apply password rules, firewall, or antivirus settings.
For a complete List of Group policies in Windows Server 2019, administrators can refer to the Group Policy Management Console and updated ADMX templates, ensuring all new settings are available.
For more insights, guidance, and related services, check out:
Conclusion
Windows Server Group Policy is a powerful tool for administrators, enabling centralized management, security enforcement, and automation across both user and computer objects. By understanding how Group Policy works, creating and linking GPOs, and following best practices, organizations can achieve consistent, secure, and efficient IT operations.
If you’re looking to implement or manage Windows Server Group Policy in a reliable hosting environment, 1Gbits offers robust solutions:
-
Windows VPS and Dedicated Servers with instant setup
-
24/7 support and global data centers
-
Affordable pricing without compromising performance
By leveraging 1Gbits services, you can ensure your Windows Server environment is not only configured correctly with Group Policy but also hosted in a high-performance, secure, and reliable infrastructure.





![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)



