IMAP, or Internet Message Access Protocol, is a standard email protocol that allows users to access and manage their email on a remote server. Understanding what is IMAP server is crucial for efficient email communication. An IMAP server stores email messages on a mail server and enables multiple devices to access the same mailbox, ensuring that changes made from any device are synchronized.
What is IMAP server for Gmail, and what is imap server address? Gmail uses an IMAP server to allow seamless access to emails from various devices. Similarly, understanding what is IMAP server for iCloud helps iCloud users keep their emails synchronized across Apple devices. For general email users, knowing what is IMAP server for email is important for setting up their email clients correctly.
When configuring email on different platforms, it's useful to know what is IMAP server example settings, such as those required for popular services like Gmail and Outlook. Specifically, what is IMAP server for Outlook entails using Microsoft's IMAP settings to access emails from Outlook servers.
On mobile devices, figuring out what is IMAP server on iPhone ensures that emails are properly synced on Apple devices. Understanding what is IMAP server mean in IT is vital for IT professionals to manage and troubleshoot email systems effectively. Overall, knowing what is IMAP server enhances email management across various platforms and devices.
what is imap server?
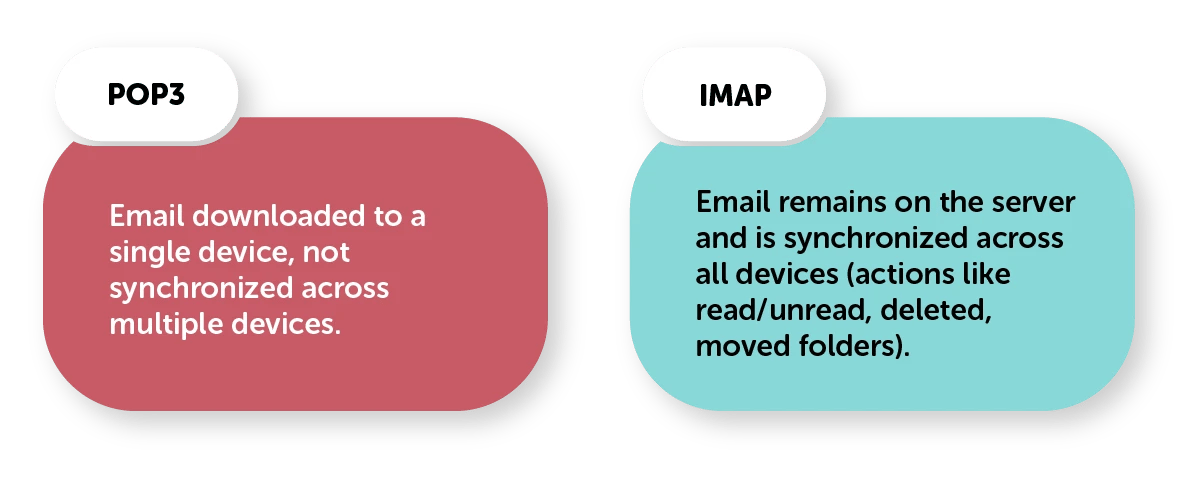
Understanding "what is my IMAP server", and IMAP vs POP3 is crucial for managing your email effectively across multiple devices. An IMAP server, or Internet Message Access Protocol server, stores your emails on a central server, allowing you to access and synchronize your email from any device. When setting up your email client, you often need to know specific details about what is IMAP server.
Firstly, knowing what is IMAP server password is essential as it is required to authenticate and access your email account on the server. For users who access their email through a web interface, understanding what is IMAP server for webmail helps in configuring their email settings correctly to ensure proper synchronization.
The next critical piece of information is what is IMAP server address, which is the specific server address used to connect your email client to the mail server. For instance, knowing what is Gmail IMAP server address is necessary to set up your Gmail account on various devices and email clients.
Apple users often need to understand what is IMAP server Apple to configure their Apple Mail or other Apple devices. Additionally, identifying what is IMAP server directory helps in setting the correct path for storing and managing email folders.
Finally, comprehending what is IMAP server name,What is my IMAP server is vital for correctly configuring your email client. This, combined with understanding what is IMAP server address, completes the setup process. Whether you are using a desktop client or a mobile device, knowing these details ensures that your email experience is seamless and efficient.For information about different servers, you can refer to the article Different types of servers.
The types of IMAP servers
Understanding the types of IMAP servers is crucial for managing your email efficiently across different platforms and devices. But first, what is IMAP server? An IMAP server, or Internet Message Access Protocol server, stores your emails on a central server, enabling you to access and synchronize your messages from any device. Let's explore the various types of IMAP servers and their specific uses.
Public IMAP Servers
Public IMAP servers are provided by popular email services like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook. Knowing what is IMAP server for these public providers helps users configure their email clients correctly. For instance, understanding what is IMAP server for Gmail involves knowing the specific server address (imap.gmail.com) and port settings required to access Gmail through an email client. Public IMAP servers are widely used due to their ease of setup and integration with various email applications.
Private IMAP Servers
Private IMAP servers are typically used by businesses and organizations to host their email services on private networks. These servers are managed internally and offer enhanced security and control. Understanding what is IMAP server in a private context involves configuring server settings unique to the organization. This setup ensures secure and efficient email communication, tailored to the specific needs of the business.
Cloud-Based IMAP Servers
Cloud-based IMAP servers are hosted on cloud platforms, providing scalability and flexibility. Knowing what is IMAP server in a cloud environment helps in setting up and maintaining email access across various devices and locations. These servers offer the advantage of reduced infrastructure costs and increased accessibility, making them ideal for businesses with distributed teams or remote workforces.
Specialized IMAP Servers
Specialized IMAP servers cater to specific industries or applications. For example, educational institutions might use specialized IMAP servers to manage student and faculty emails. Understanding what is IMAP server settings tailored to these environments ensures that the unique requirements of the industry are met, providing reliable and efficient email communication.
Apple-Specific IMAP Servers
For users of Apple products, understanding what is IMAP server Apple involves using Apple-specific settings to ensure seamless synchronization across all Apple devices. Apple’s iCloud email service, for instance, requires specific IMAP server settings (imap.mail.me.com) to configure correctly. This ensures that emails, contacts, and calendars are synchronized across all Apple devices, providing a unified experience.
In summary, knowing what is IMAP server and the different types available—public, private, cloud-based, specialized, and Apple-specific—helps in setting up and managing email effectively. Whether for personal use, business, or specific applications, understanding these distinctions ensures a smooth and efficient email experience.
IMAP ports
Understanding IMAP ports is essential for configuring your email client correctly and ensuring smooth communication with your email server. But first, what is IMAP server? An IMAP server, or Internet Message Access Protocol server, stores your emails on a central server, allowing you to access and synchronize your messages from any device. Let's delve into the different IMAP ports and their significance.
Standard IMAP Ports
IMAP servers typically use two main ports: port 143 and port 993. Knowing what is IMAP server and its associated ports is crucial for setting up your email client.
-
Port 143: This is the default port for IMAP without encryption. When connecting to an IMAP server via port 143, the communication is typically unencrypted, making it suitable for internal networks where security is not a major concern. However, for most users, especially those accessing email over the internet, encrypted connections are preferred.
-
Port 993: This port is used for IMAP over SSL/TLS, providing encrypted communication between your email client and the IMAP server. Understanding what is IMAP server and the importance of port 993 ensures that your email data is transmitted securely, protecting it from potential eavesdropping and interception.
Configuring IMAP Ports
When setting up an email client, knowing what is IMAP server port configuration involves specifying the correct port numbers to ensure proper connectivity and security.
-
For public email services: Services like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook have specific port settings. For instance, knowing what is IMAP server port for Gmail means using port 993 for a secure connection.
-
For private and cloud-based IMAP servers: Organizations might have different configurations. It’s essential to check with your IT department or service provider to understand what is IMAP server port settings for your specific setup.
How does IMAP work?
Understanding how IMAP works is essential for efficient email management across multiple devices. But first, what is IMAP server? An IMAP server, or Internet Message Access Protocol server, stores your emails on a central server, allowing you to access and synchronize your messages from any device. Let's explore how IMAP functions and why it's a critical component of modern email systems.
Connecting to the IMAP Server
When you set up an email client, the first step is connecting to the IMAP server. Understanding what is IMAP server in this context means recognizing it as the central repository where your emails are stored.
-
Authentication: Your email client uses your credentials (username and password) to authenticate with the IMAP server. This step ensures that only authorized users can access the email account.
-
Server Settings: Knowing what is IMAP server settings, including the server address and port numbers, is crucial for establishing this connection.
Synchronizing Emails
One of the main advantages of IMAP is its ability to synchronize emails across multiple devices. Understanding what is IMAP server synchronization helps you appreciate how changes made on one device are reflected on others.
-
Fetching Emails: When you open your email client, it fetches a list of your emails from the IMAP server. This list includes email headers, such as the sender, subject, and timestamp.
-
Downloading Content: The full content of an email is downloaded only when you open it. This approach saves bandwidth and storage space on your device.
Managing Folders and Messages
IMAP allows you to organize your emails into folders directly on the server. Understanding what is IMAP server folder management is essential for keeping your inbox organized.
-
Creating and Deleting Folders: You can create, rename, or delete folders on the IMAP server, and these changes are synchronized across all devices.
-
Moving Messages: When you move an email from one folder to another, the change is updated on the server, ensuring consistency across devices.
IMAP Commands
IMAP operates using a set of commands that facilitate various email operations. Knowing what is IMAP server command set is important for understanding how different actions are executed.
-
FETCH: Retrieves specific email data from the server.
-
STORE: Updates the flags of a message (e.g., marking an email as read).
-
COPY: Copies a message to another folder.
-
SEARCH: Searches for messages matching specified criteria.
Security and Encryption
IMAP supports secure communication to protect your email data. Understanding what is IMAP server security involves recognizing the importance of encryption protocols.
-
SSL/TLS Encryption: IMAP over SSL/TLS (usually on port 993) encrypts the connection between your email client and the server, safeguarding your data from eavesdropping.
-
Authentication Mechanisms: Secure authentication methods, such as OAuth, further protect your email account from unauthorized access.
Offline Access and Synchronization
IMAP provides flexibility in how emails are accessed and stored. Understanding what is IMAP server offline access helps in managing emails when not connected to the internet.
-
Cached Data: Email clients can cache data locally, allowing you to read and compose emails offline. These changes are synchronized with the IMAP server once you reconnect.
-
Selective Synchronization: Users can choose which folders or emails to synchronize, optimizing storage use and performance.
Understanding what is IMAP server and how IMAP works provides a comprehensive view of this crucial email protocol. From initial connection and synchronization to folder management and security, IMAP ensures a seamless and efficient email experience across all your devices. By mastering these aspects, you can optimize your email setup for better performance and reliability.
Advantages and limitations of IMAP
IMAP, or Internet Message Access Protocol, offers numerous advantages for managing email across multiple devices. Let's explore some of the key benefits:
Seamless Synchronization
-
Real-time Updates: IMAP ensures that changes made to emails, folders, and actions on one device are instantly synchronized across all devices.
-
Consistency: Users experience a consistent email environment regardless of the device they are using, ensuring a seamless and streamlined email management experience.
Accessibility from Anywhere
-
Remote Access: With IMAP, emails are stored on a remote server, allowing users to access their email accounts from any location with an internet connection.
-
Device Independence: Users can access their emails from computers, smartphones, tablets, or any other device, providing unparalleled flexibility and accessibility.
Advanced Organization Features
-
Folder Management: IMAP supports the creation of folders, subfolders, and labels, enabling users to organize their emails efficiently.
-
Server-Side Filtering: Users can set up rules and filters on the server to automatically sort incoming emails into specific folders based on predefined criteria.
Reduced Storage Requirements
-
Selective Downloading: IMAP only downloads email headers initially, retrieving the full email content only when needed. This minimizes storage usage on devices and ensures efficient use of available space.
-
No Local Storage: Because emails are stored on a remote server, users do not need to worry about managing local storage for their email data.
Enhanced Collaboration
-
Multi-User Access: IMAP allows multiple users to access and manage the same email account simultaneously.
-
Improved Communication: Enhanced collaboration features foster teamwork, improve communication, and streamline workflows, making IMAP an ideal choice for businesses and teams.
Limitations of IMAP
While IMAP offers many advantages, it also has some limitations that users should be aware of:
Dependency on Internet Connection
-
Offline Access: IMAP requires an internet connection to access emails stored on the remote server. Users may experience limitations in accessing emails when offline or in areas with poor connectivity.
Server Reliability
-
Dependence on Server Uptime: IMAP relies on the availability and reliability of the email server. Any downtime or server issues can impact users' ability to access their emails and may result in disruptions to email communication.
Security Concerns
-
Data Privacy: Emails stored on a remote server may be vulnerable to security breaches or unauthorized access.
-
Encryption: While many IMAP servers support encryption protocols to protect data in transit, users should ensure that their email provider offers adequate security measures to safeguard sensitive information.
Storage Space Limitations
-
Server Storage Limits: Some IMAP email providers impose storage limits on users' email accounts. Users may need to periodically manage their email storage or upgrade to a higher storage plan to avoid reaching storage limits.
Complexity for Novice Users
-
Configuration Complexity: Configuring IMAP settings and managing advanced features such as server-side filtering may be challenging for novice users.
-
Learning Curve: Users transitioning from POP3 or other email protocols may require time to adapt to the features and functionality of IMAP.
|
Feature |
IMAP |
POP3 |
|
Email Storage |
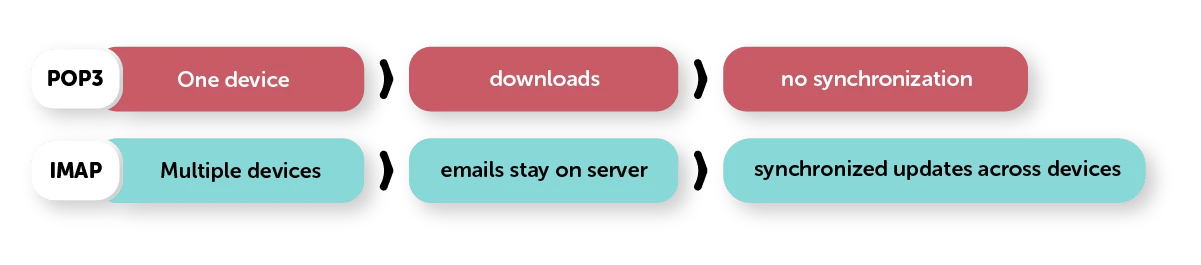
Emails are stored on the server and synchronized across devices. |
Emails are downloaded to the device and usually removed from the server. |
|
Multi-Device Access |
Yes, changes are reflected across all devices. |
No, changes apply only to the device that downloaded the emails. |
|
Server Storage Use |
Requires more server storage space. |
Uses less server storage space. |
|
Offline Access |
Requires an internet connection to access emails (unless cached). |
Downloaded emails are accessible without an internet connection. |
What is imap server used for?
The IMAP server plays a crucial role in modern email communication, offering a range of functionalities that enhance the user experience. Let's explore what the IMAP server is used for and how it revolutionizes email management.
Email Synchronization
The primary purpose of an IMAP server is to synchronize emails across multiple devices seamlessly. With an IMAP server, users can access their emails from anywhere, ensuring that changes made on one device are reflected instantly on all others. This synchronization ensures that users have access to the latest emails, folders, and actions, providing a consistent email experience across devices.
Remote Access
An IMAP server enables remote access to email accounts stored on the server. Users can log in to their email accounts from any device with an internet connection, whether it's a computer, smartphone, or tablet. This remote access ensures that users can stay connected and productive even when they are away from their primary device.
Advanced Organization
IMAP servers support advanced organization features that allow users to manage their emails efficiently. Users can create folders, subfolders, and labels to categorize and prioritize their emails. Additionally, IMAP servers often support server-side filtering and rules, enabling users to automatically sort incoming emails into specific folders based on predefined criteria.
Collaboration
IMAP servers facilitate collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and manage the same email account simultaneously. This collaborative functionality is particularly useful for businesses and teams, as it enables seamless communication and collaboration on email correspondence and projects.
Backup and Recovery
IMAP servers often include backup and recovery features that protect users' email data from loss or corruption. Emails stored on the server are regularly backed up, ensuring that users can recover their data in the event of accidental deletion or system failure. This backup and recovery capability provide users with peace of mind knowing that their email data is secure and protected.
Integration with Email Clients
IMAP servers integrate seamlessly with a wide range of email clients, including desktop clients like Microsoft Outlook, Apple Mail, and Mozilla Thunderbird, as well as mobile apps like Gmail and Outlook Mobile. This compatibility ensures that users can access their emails using their preferred email client, regardless of the device or platform they are using.
In conclusion, the IMAP server serves a variety of purposes that revolutionize email management. From seamless email synchronization and remote access to advanced organization features and collaboration capabilities, the IMAP server enhances the user experience and productivity. Whether it's for personal use, business communication, or team collaboration, the IMAP server plays a critical role in modern email communication.
How to set up IMAP in Gmail
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) allows seamless access to your Gmail account from various devices. Here's how to set it up:
Step 1: Enable IMAP Access in Gmail Settings
-
Open Gmail and click on the gear icon in the top right corner.
-
Select "See all settings" and navigate to the "Forwarding and POP/IMAP" tab.
-
Enable IMAP access by selecting "Enable IMAP" and then click "Save Changes."
Step 2: Configure Your Email Client with IMAP Settings
-
Open your preferred email client, such as Microsoft Outlook.
-
Navigate to the account settings and select "Add Account."
-
Enter your Gmail address and password.
-
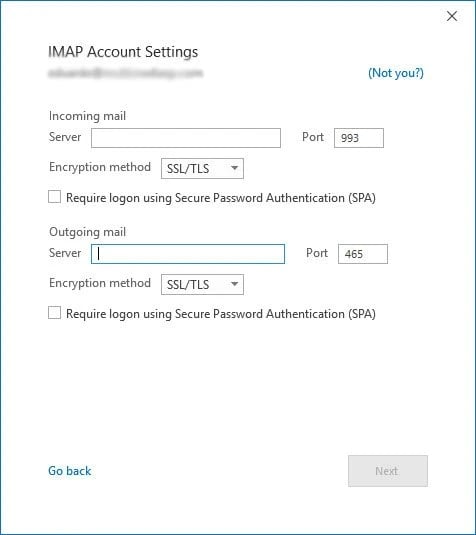
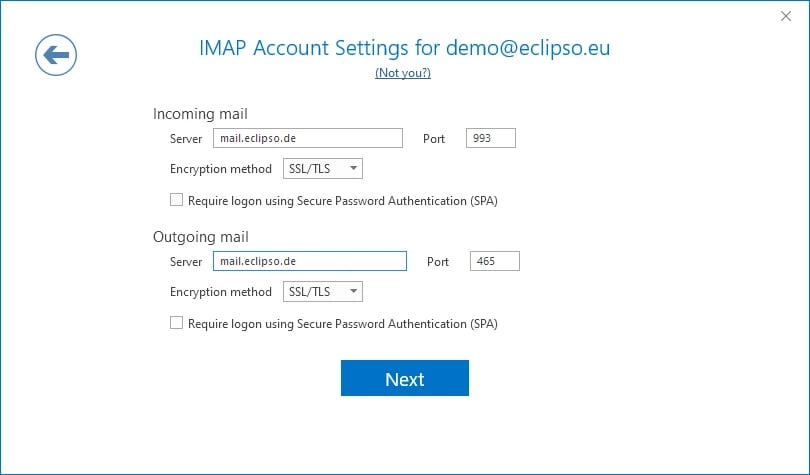
Choose "IMAP" as the account type and enter the following IMAP server settings:
-
Incoming Mail (IMAP) Server: imap.gmail.com
-
Port: 993
-
Security: SSL/TLS
-
Outgoing Mail (SMTP) Server: smtp.gmail.com
-
Port: 587
-
Security: STARTTLS
Step 3: Complete the Setup and Sync Your Emails
-
Follow the prompts to complete the setup process.
-
Once configured, your email client will sync with the Gmail IMAP server, allowing you to access your emails, folders, and actions seamlessly across devices.
In this setup, Gmail serves as the IMAP server example, providing reliable email access through the IMAP protocol. Similarly, Outlook users can configure their accounts to use the IMAP server for seamless synchronization across devices. With IMAP, Outlook users can access their emails, folders, and actions consistently, ensuring a streamlined email experience across platforms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the IMAP server serves as a vital component in modern email communication, offering unparalleled flexibility and convenience to users. With IMAP, users can access their emails, folders, and actions seamlessly across multiple devices, ensuring consistency and productivity. The IMAP server enables real-time synchronization of email data, allowing changes made on one device to reflect instantly on all others connected to the same IMAP server. This synchronization ensures that users have access to their entire email history regardless of the device they are using. By leveraging the capabilities of the IMAP server, users can enjoy enhanced organization features, collaborative functionalities, and improved access to their email accounts. Whether it's accessing emails from a webmail client, email app, or configuring accounts for Outlook, the IMAP server plays a pivotal role in facilitating efficient and reliable email communication.







