Today, using a VPN has become very common for maintaining online security and privacy. You may have come across VPN services offering various protocols such as OpenVPN, L2TP/IPSec, and dozens of others, but in this article, we will compare two long-standing giants in this field: OpenVPN and L2TP/IPSec. This comparison will help you understand which protocol is better suited to your needs and why choosing the wrong one could put both your security and your valuable bandwidth at risk. So join us at 1Gbits as we explore OpenVPN vs. L2TP/IPSec.
What Is openvpn vs. l2tp/ipsec?
Before comparing performance, it’s important to understand the underlying architecture of these two protocols, because their differences in security and speed come directly from these foundational designs.
How OpenVPN Works
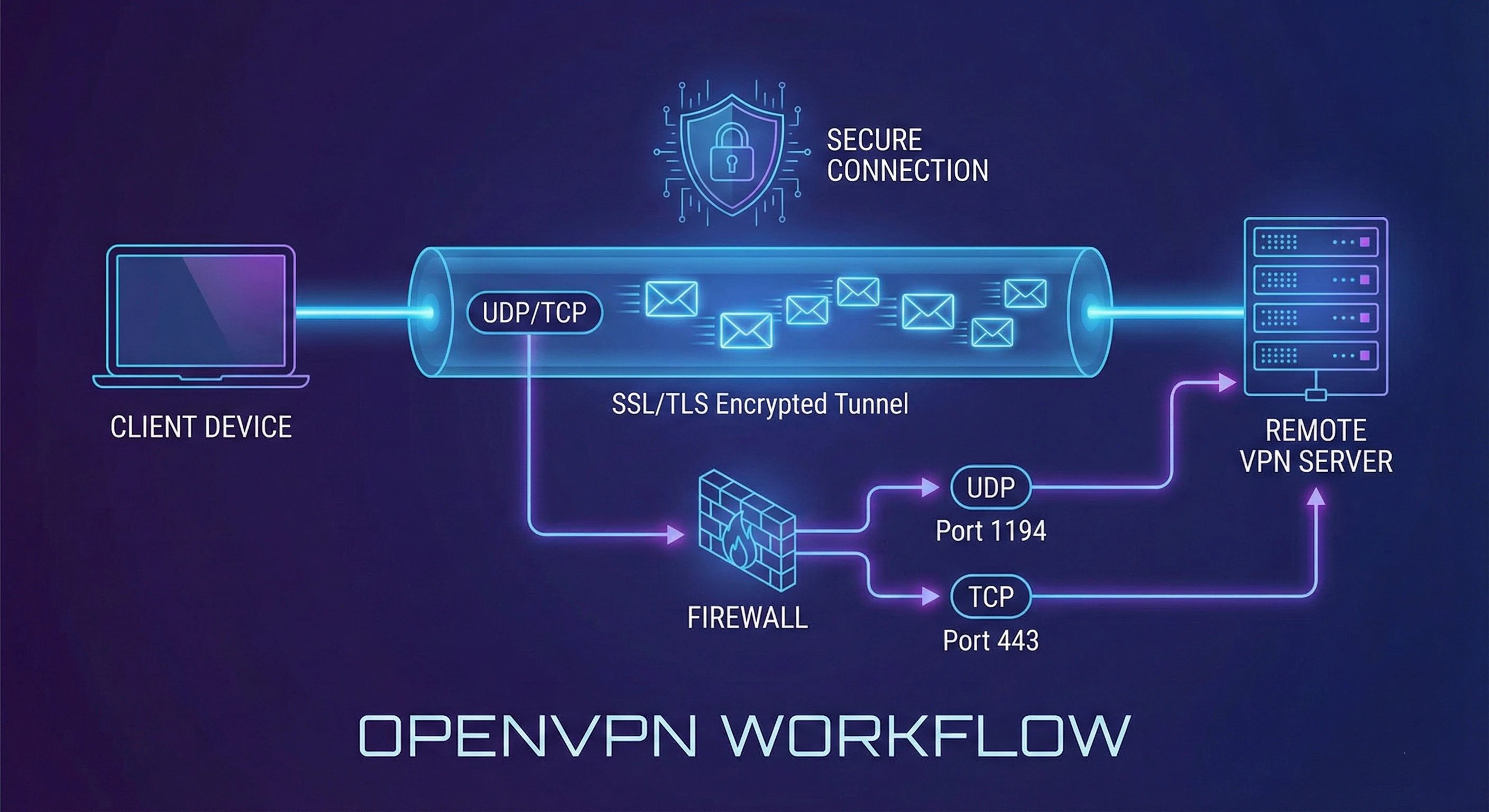
OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol built on SSL and TLS, widely considered the industry’s gold standard. It uses the OpenSSL library for both encryption and key exchange. A major strength of OpenVPN is its flexibility at the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model. It can run over UDP, which offers higher speed with minimal overhead, or over TCP, which provides better stability by retransmitting lost packets but generally performs more slowly.
OpenVPN uses UDP port 1194 by default, yet it can also run on port 443 with either TCP or UDP. This allows its traffic to blend with regular HTTPS, making it far easier to bypass strict corporate or governmental firewalls.
How L2TP/IPSec Works
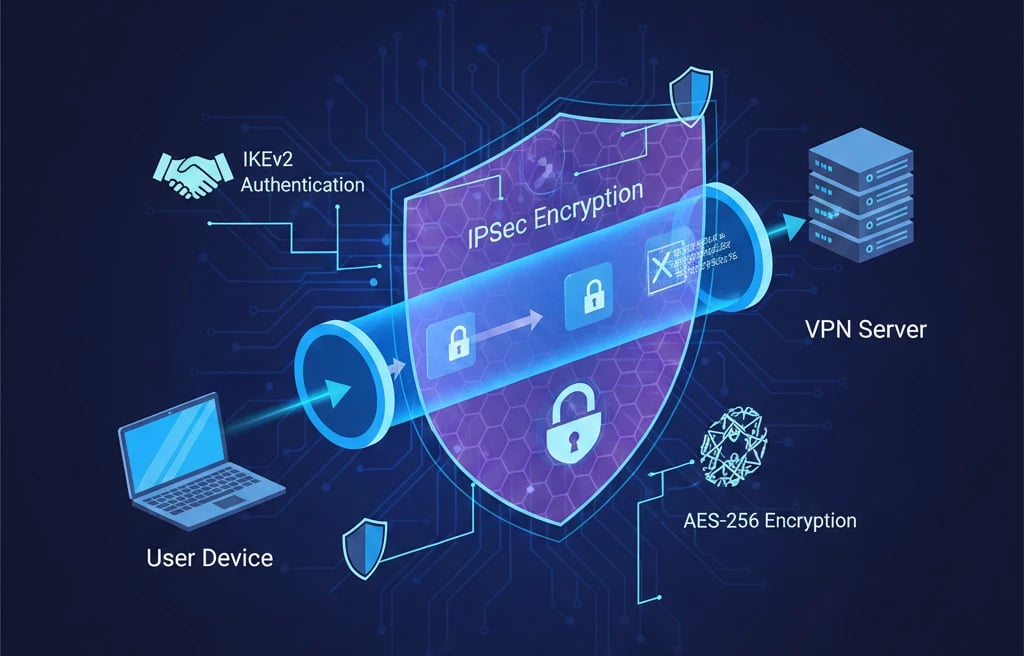
L2TP, or Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol, is essentially a tunneling method rather than a security solution. Operating at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2), its role is to establish a tunnel between the user and the VPN server. Since L2TP does not provide encryption or authentication by itself, it must be paired with IPsec to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and user verification. The resulting combination, known as L2TP over IPsec, joins L2TP’s tunneling capability with IPsec’s strong cryptographic features. IPsec often uses protocols such as IKEv2 for authentication and relies on AES-256 for data encryption.
In short, OpenVPN offers a unified and integrated design, while L2TP/IPsec depends on a two-layer structure, which leads to the clear differences you will see in the comparison sections ahead.
OpenVPN vs L2TP/IPSec: Core Differences
Structural differences between these two protocols create tangible effects on how they are used and perform in real-world scenarios.
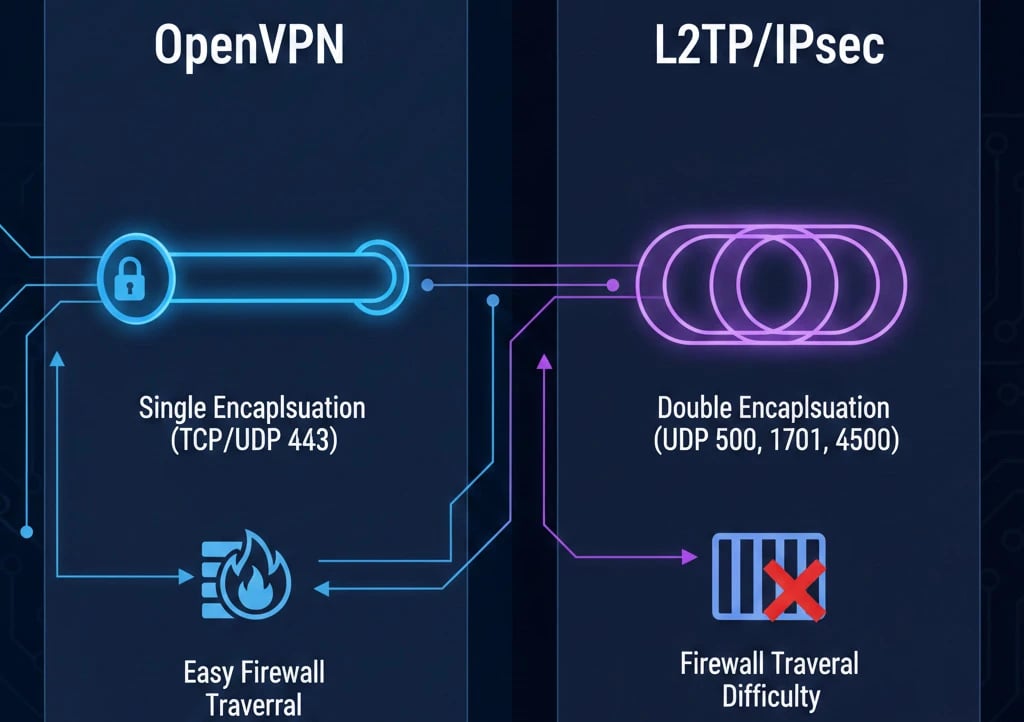
Double Encapsulation vs Single Encapsulation
As mentioned earlier, L2TP/IPSec introduces significantly more overhead than OpenVPN because it encapsulates data twice, once with L2TP for tunneling and once with IPsec for encryption. This double encapsulation directly results in lower throughput. OpenVPN, on the other hand, encapsulates and encrypts data only once, making it more efficient in terms of resource usage and bandwidth.
Port Dependence and Firewall Traversal
One of the most important factors to consider when setting up a VPN on a VPS is its ability to connect in restricted networks. L2TP/IPSec relies on fixed UDP ports for operation:
-
UDP 500 for initial key exchange (IKE)
-
UDP 1701 for L2TP configuration
-
UDP 4500 to facilitate NAT traversal
This dependence on fixed ports makes L2TP/IPSec easier to block by network administrators or ISPs. In contrast, OpenVPN is highly flexible. It can run on TCP port 443 and effectively disguise VPN traffic as standard encrypted HTTPS web traffic. This traffic obfuscation gives OpenVPN a clear advantage in connection reliability in restricted environments.
Native Support vs Third-Party Software
L2TP/IPSec has a major advantage in initial setup due to its built-in support on almost all major operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS. Users can define an L2TP/IPSec connection directly in their network settings without installing any additional software.
OpenVPN, while highly compatible across platforms, usually requires a third-party client application such as OpenVPN Connect to function. This makes initial setup slightly more complex than L2TP/IPSec, especially for non-technical users.
These fundamental architectural differences also clearly impact performance, which will be discussed in the next section.
l2tp/ipsec vs openvpn speed Comparison

Although the WireGuard protocol offers the highest speed, there are still significant performance differences when comparing OpenVPN and L2TP/IPsec, which are caused by protocol overhead.
The destructive impact of double encapsulation in L2TP/IPSec
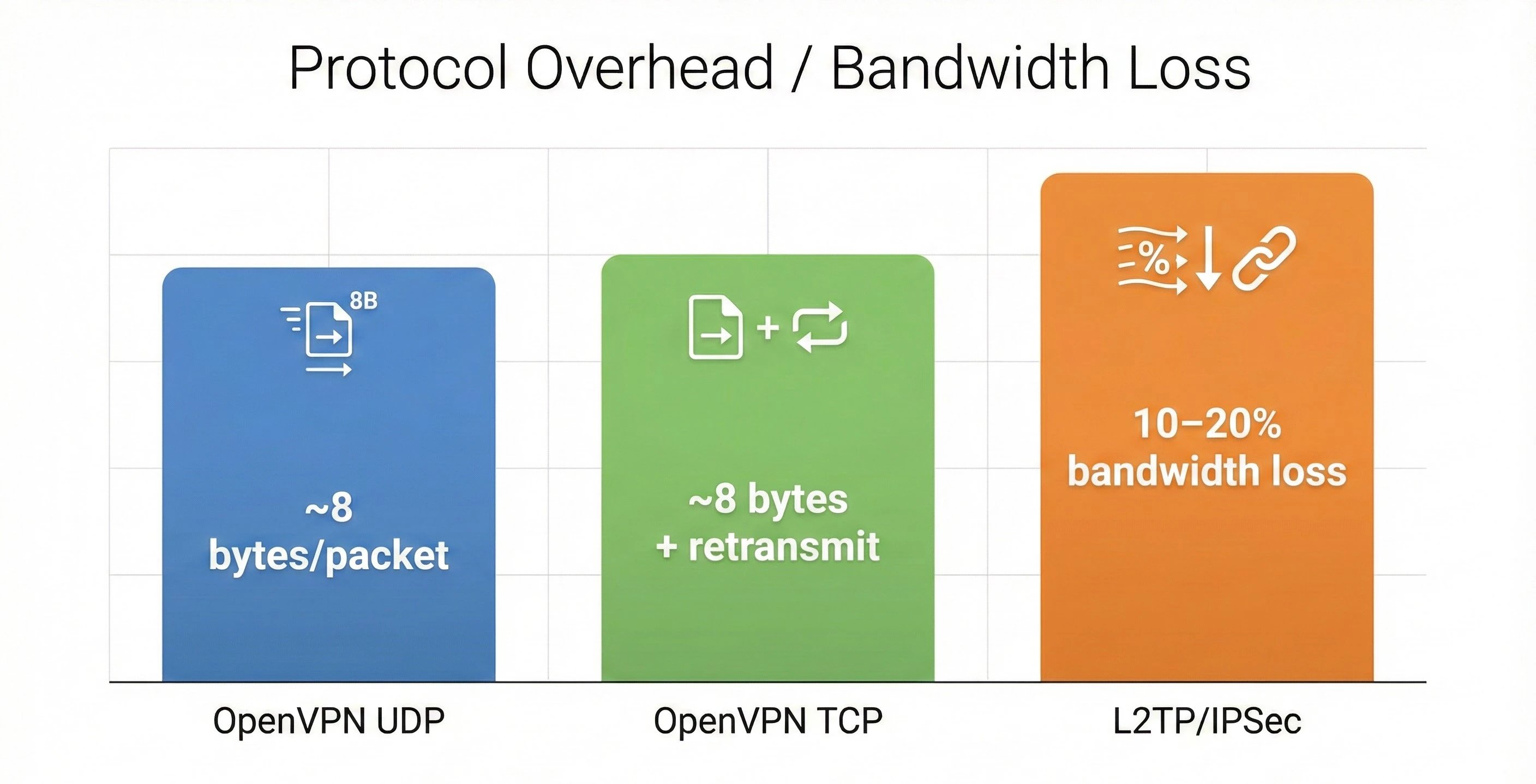
L2TP/IPSec is inherently a slower protocol. The extra overhead from its two-step process, tunneling with L2TP and encryption with IPsec, creates significant protocol overhead. Analyses indicate that L2TP/IPSec can have protocol overhead in the range of 10 to 20 percent. In some independent tests, this overhead resulted in the loss of nearly half of the available bandwidth.
OpenVPN: Speed with UDP, Stability with TCP
On the other hand, OpenVPN allows users to choose between speed and stability:
-
OpenVPN UDP (Speed): UDP offers the fastest performance for OpenVPN because it does not require packet acknowledgment. Protocol overhead is minimal, around 8 bytes per packet. This mode is ideal for high-bandwidth activities such as streaming or transferring large files.
-
OpenVPN TCP (Stability): In networks where packets may be lost or strict firewalls are present, TCP resends lost packets. Tunneling TCP over TCP causes both the VPN layer and the underlying network to resend packets, leading to significant slowdowns or even connection drops.
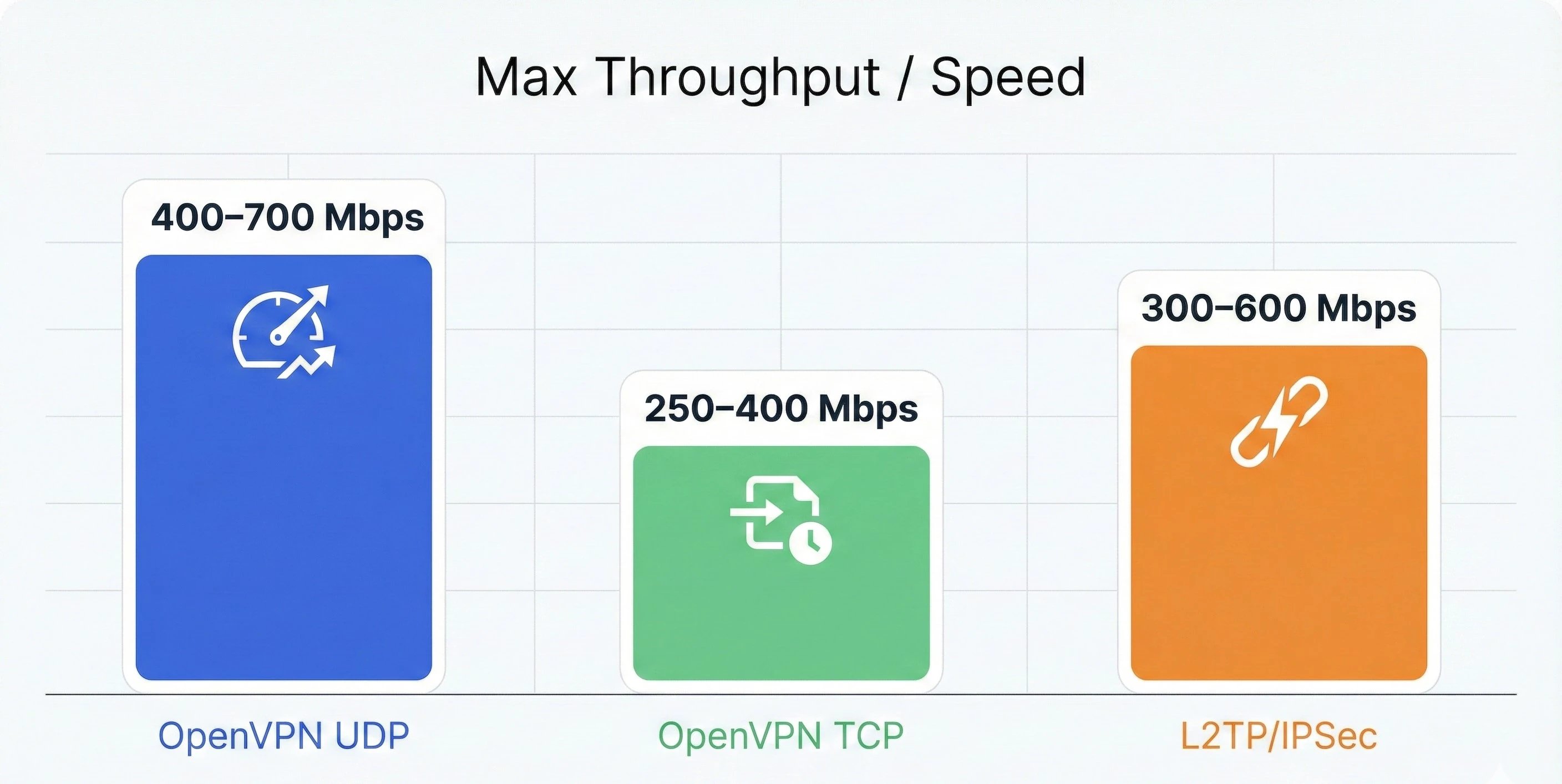
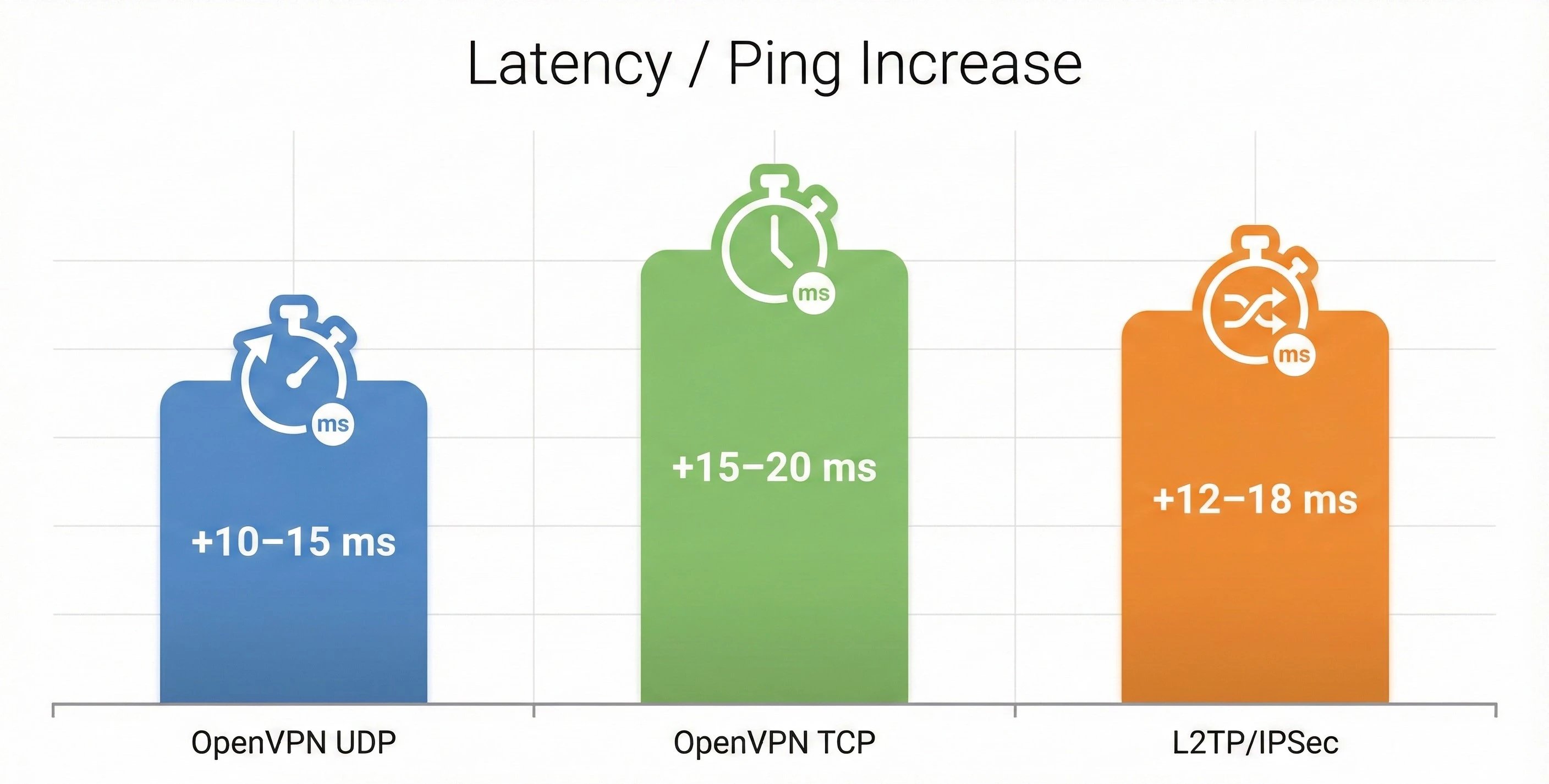
As a technical rule, L2TP/IPSec cannot be relied on for optimal performance and high speed. While OpenVPN UDP can reach speeds of up to around 400 Mbps, L2TP/IPSec is typically much slower due to its high overhead.
openvpn vs l2tp performance (2025 Benchmarks)
To get a better understanding of the speed and performance of these two protocols, let’s review some key benchmarks:
Max Throughput / Speed
Latency / Ping Increase
Protocol Overhead
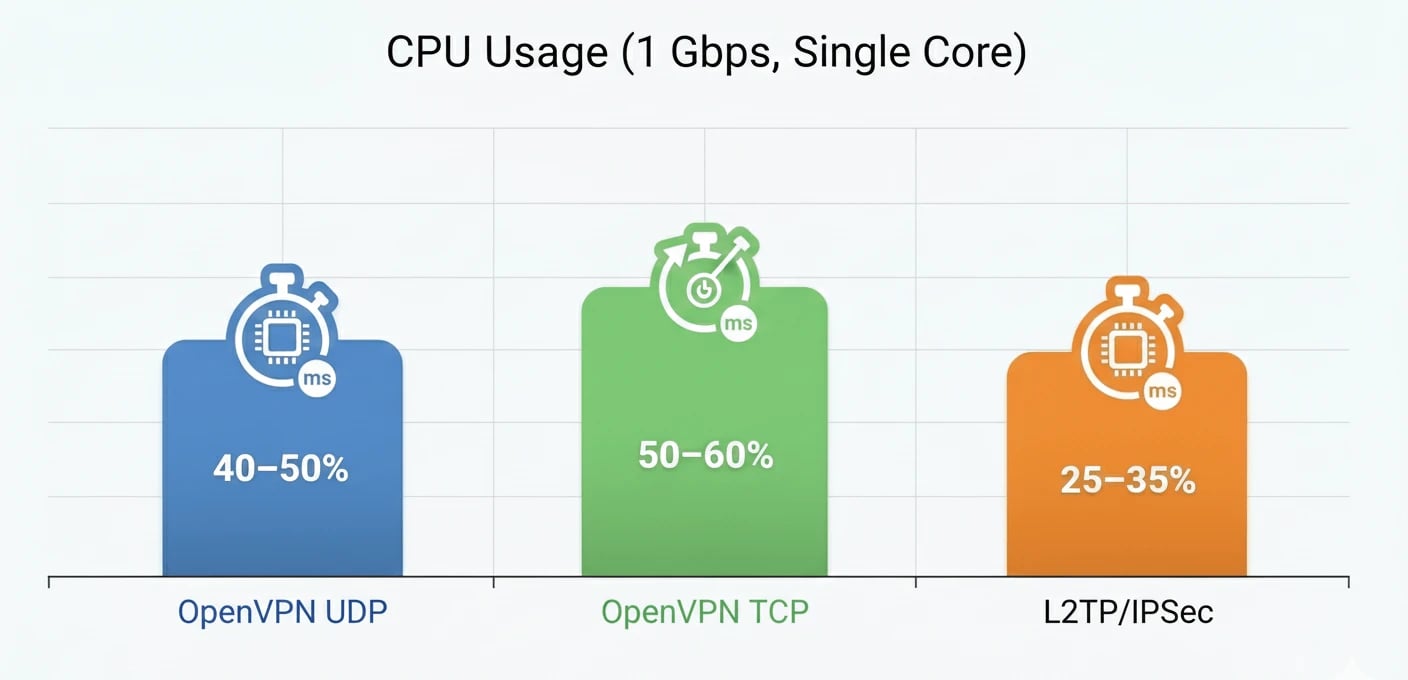
CPU Usage (1 Gbps, Single Core)
CPU Usage (AES-NI Hardware Acceleration)
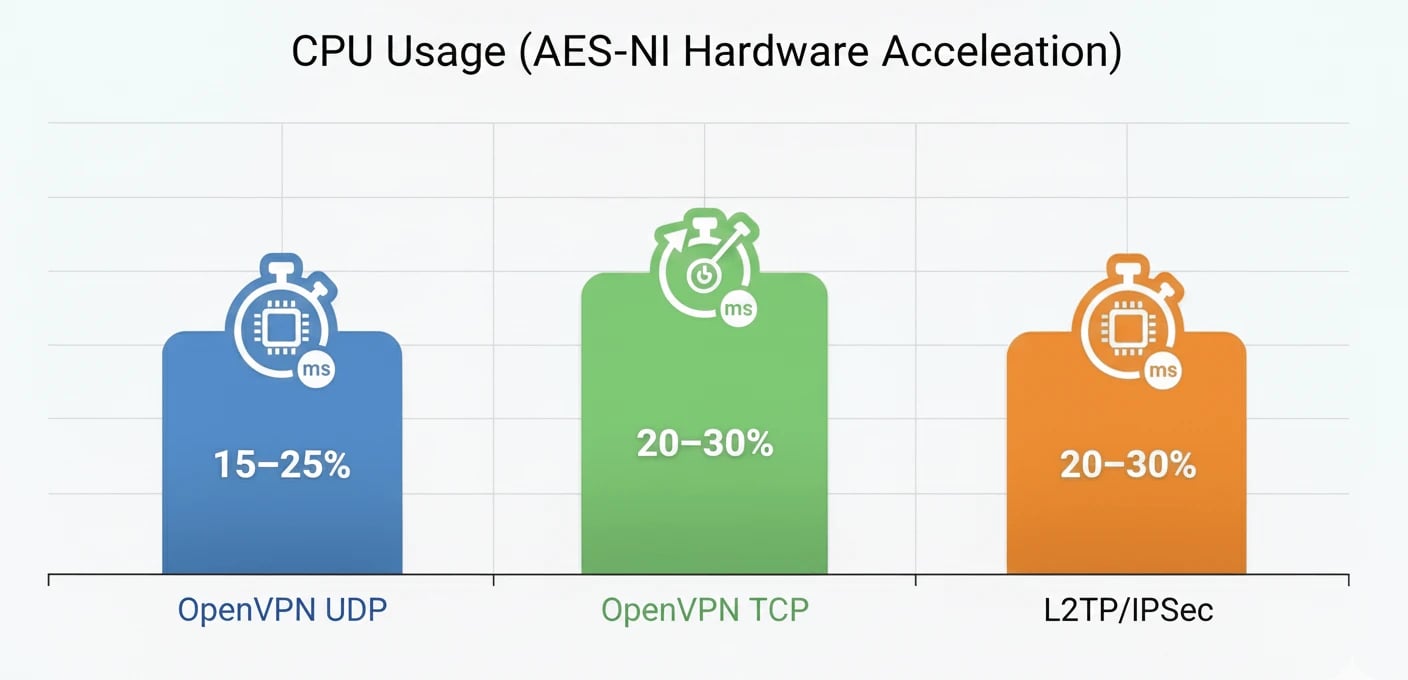
In simple terms, OpenVPN UDP offers the best balance between speed and stability, making it an excellent choice for streaming, online gaming, and everyday home use. In contrast, L2TP/IPSec performs very well in enterprise networks with strong multi-core hardware, but due to higher overhead, it can be slightly slower on home networks or weaker internet connections.
Security Comparison: OpenVPN vs L2TP/IPSec
OpenVPN, being open-source, significantly reduces the risk of hidden backdoors or vulnerabilities and strengthens its resistance to attacks. It uses the OpenSSL library and supports various encryption algorithms, including AES-256-GCM, which provides strong encryption while combining authentication and encryption for better performance and security than AES-256-CBC.
L2TP/IPSec also uses strong AES-256 encryption, but many implementations rely on a pre-shared key (PSK) for authentication. If the PSK is weak or exposed, the entire tunnel’s security collapses, giving attackers access to encrypted data. The table below outlines the major security differences between the two protocols.
|
Technical Feature |
OpenVPN |
L2TP/IPSec |
Final Security Assessment |
|
Base Protocol |
SSL/TLS (Layer 4) |
L2TP/IPSec (Layer 2/3) |
OpenVPN’s single-layer architecture offers higher flexibility. |
|
Authentication Method |
Digital certificates, Username/Password |
PSK, Digital Certificates |
PSK in L2TP/IPSec is a configuration weakness and increases the risk of spoofing¹⁸ |
|
Code Transparency |
Open-source and auditable (High Trust) |
Industry Standard (Trust Concerns) |
OpenVPN is preferred for higher security² |
|
Encryption Capability |
AES-256, Blowfish (Highly flexible)¹⁷ |
AES-256 (Standard and strong)¹⁵ |
OpenVPN offers more flexibility to use the latest ciphers. |
In one sentence, the transparency and integrated architecture of OpenVPN make it a more secure choice, while L2TP/IPSec comes with significant and noteworthy security concerns.
OpenVPN vs L2TP/IPSec for Streaming, Gaming & Privacy
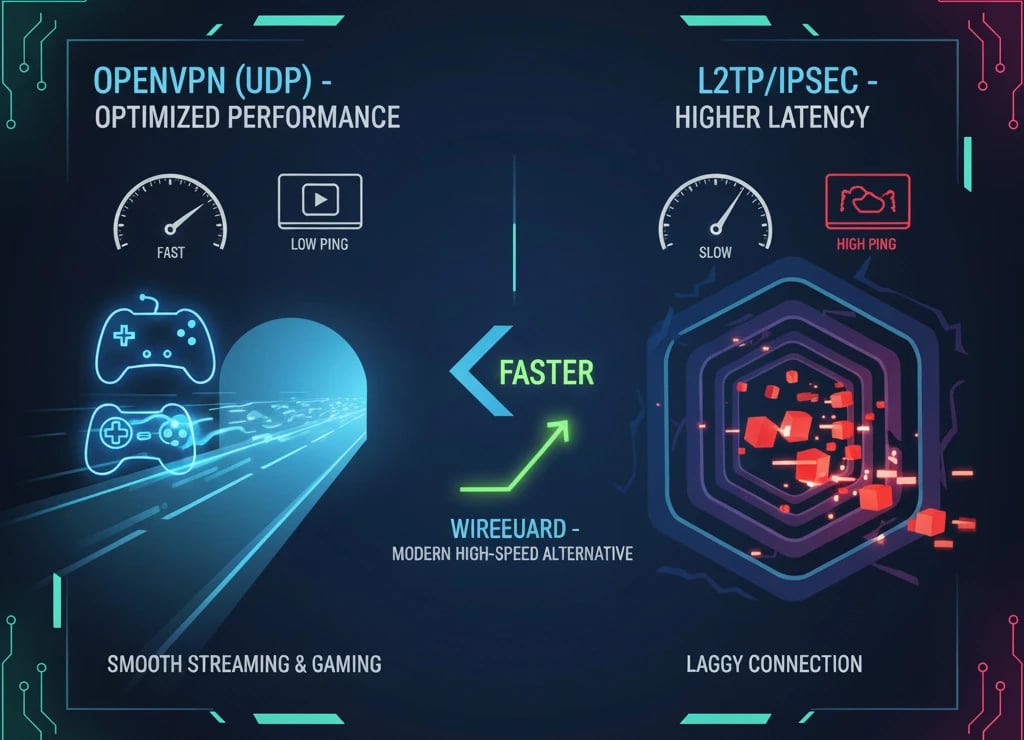
Activities such as streaming and gaming require low latency and high throughput. OpenVPN (UDP), with its lower overhead and more efficient packet handling, delivers better performance compared to L2TP/IPSec. L2TP/IPSec, due to its double encapsulation, introduces higher latency, which can disrupt smooth gaming or streaming experiences.
On the other hand, OpenVPN, thanks to its open-source architecture and use of OpenSSL, remains the preferred choice. It is worth noting that L2TP/IPSec also uses UDP, but its double encryption can result in slightly higher ping. For this reason, many gamers prefer OpenVPN, which combines security with lower latency. Newer protocols like WireGuard are specifically designed for these purposes and are often the first choice for gamers.
Device & OS Compatibility Comparison
Now, let's take a closer look at the device and OS compatibility of both OpenVPN and L2TP/IPSec, comparing their support across desktop systems, mobile devices, and network infrastructure.
|
Criteria |
OpenVPN |
L2TP/IPSec |
|
Support for Desktop OS |
Supported on Windows, macOS, and Linux with official clients. Can run on other platforms via third-party clients. |
Supported natively on Windows, macOS, and most Linux distros. |
|
Router & Network Device Support |
Widely supported on routers (e.g., DD-WRT, OpenWrt, pfSense). |
Supported on some routers but often needs manual configuration and NAT setup. |
|
Mobile Support |
Requires a third-party client app (e.g., OpenVPN app) on Android and iOS. |
Native support on Android and iOS |
|
Android & iOS Behavior |
May need a client app but supports features like port 443 for bypassing restrictions. |
Easier to set up due to built-in OS support, OpenVPN can be more complex for non-tech users. |
|
Ease of Setup on Mobile |
Needs third-party apps, which may be tricky for non-technical users. |
Simple setup, no extra apps needed. |
|
Best for Routers/Network Infrastructure |
Easier to configure and more flexible, with wide router support (DD-WRT, OpenWrt). |
Harder to configure, requires manual NAT adjustments. |
This comparison highlights how both OpenVPN and L2TP/IPSec stack up in terms of device compatibility, mobile behavior, and router support. Depending on your needs, one may be better suited for your setup.
Use Cases: When Should You Choose Each Protocol?
To help you make a clearer decision, we break down these two protocols based on real-world scenarios and the needs you’re most likely to face:
Choose OpenVPN if…
- Your priority is maximum security and privacy, making it ideal for handling confidential files or accessing sensitive corporate systems. Its strong AES-256-GCM encryption and open-source audits ensure reliable protection.
- You need to bypass strict firewalls when connecting from places with heavy filtering such as certain countries, universities, or hotels. Running on TCP port 443 helps OpenVPN blend in with regular HTTPS traffic.
- You require high configuration flexibility to adjust encryption, key sizes, or transport protocols.
This is especially useful for IT environments that need fine-tuned performance or security levels.
Choose L2TP/IPsec if…
- You value simple setup and native support for quick, app-free connections on mobile or desktop devices. It’s suitable when you only need a basic security layer for every day, non-sensitive use.
- You are using older devices that don’t support modern protocols.
Legacy routers and older operating systems often have built-in L2TP/IPsec as their only option.
Overall, the right choice depends on whether you need top-tier security or just a lightweight, easily supported connection.
openvpn vs pptp vs l2tp ipsec vs wireguard
Here’s a quick comparison of the key factors for WireGuard, L2TP/IPSec, OpenVPN, and PPTP to help you decide which VPN protocol best fits your needs.
|
Comparison Criteria |
WireGuard |
L2TP/IPSec |
OpenVPN |
PPTP |
|
Speed Ranking (Fastest → Slowest) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Very Fast (Over 85% of bandwidth retained) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐ Moderate (50–60% bandwidth retention) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐Moderate (UDP better than TCP – 60–70% bandwidth) |
⭐⭐ Fairly Fast but Insecure |
|
Security Ranking (Strongest → Weakest) |
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Very Strong – Modern, simple, up-to-date encryption |
⭐⭐⭐ Good Security but Older |
⭐⭐⭐⭐ Very Secure – Strong encryption and customizable |
⭐ Very Weak – Easily compromised with outdated encryption |
|
Connection Stability |
Stable with minimal issues |
Relatively Stable |
Very Stable, good for unstable networks |
Weak |
|
Firewall/NAT Traversal |
Good |
Weak – Fixed ports often blocked |
Excellent – Especially with TCP/443 |
Moderate |
|
CPU and Resource Consumption |
Very Low – Minimalistic design |
Moderate |
Relatively High (Heavy encryption) |
Low |
|
Ease of Configuration |
Moderate to Difficult for Beginners |
Difficult – Requires IPSec knowledge |
Moderate |
Very Easy |
|
Device Compatibility |
Moderate but improving |
Very Good (Supports almost all devices) |
Excellent – Wide support |
Very Good |
|
Best for Streaming and Gaming |
Excellent |
Moderate |
Good (OpenVPN UDP) |
Good (But Insecure) |
This comparison should help you understand which protocol suits your needs based on speed, security, and stability.
Get Your VPN VPS Now
In this article, we saw that each VPN protocol has its own advantages and limitations, so the best choice ultimately depends on your specific needs. If you’re looking to set up your VPN with high speed and strong security, our services at 1Gbits are an excellent option. By purchasing an OpenVPN VPS or VPS for VPN, you can get a powerful virtual server with instant setup and 24/7 support. Our global 1Gbits data centers also ensure that you can connect to your server with minimal latency from anywhere in the world. With these features, you can build a fast, secure, and reliable private network and enjoy all the benefits of a fully trusted VPN.





![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)

