In the world of virtualization, choosing the right solution is crucial for maximizing performance and efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the comparison of KVM vs Proxmox, two popular virtualization technologies. KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is renowned for its robust performance and integration with Linux, while Proxmox is celebrated for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive feature set. We'll explore various aspects, including linux kvm vs proxmox, oracle kvm vs proxmox, and kvm vs proxmox vs vmware, to help you make an informed decision.
Additionally, we'll examine kvm vs proxmox ve, comparing the enterprise-ready features and scalability options of each platform. Performance is a critical factor, so we'll analyze proxmox vs kvm performance to highlight which solution delivers superior results. The comparison will also cover proxmox vs qemu kvm, shedding light on the differences and similarities between these technologies.
For those using specific Linux distributions, we will look at ubuntu kvm vs proxmox and debian kvm vs proxmox to understand how each virtualization solution integrates with these popular operating systems. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of kvm vs proxmox, helping you choose the best virtualization technology for your needs.
What is Proxmox?

Proxmox is a powerful and flexible open-source server virtualization management platform that combines the capabilities of two core technologies: Proxmox Virtual Environment (VE) and Proxmox Backup Server. Proxmox VE is designed to manage and deploy virtualized environments using KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) and LXC (Linux Containers), while Proxmox Backup Server focuses on efficient and secure data backups. Together, they provide a comprehensive solution for enterprise virtualization and disaster recovery. If you want to read the comparison of VMware and Proxmox, read the article Comparing VMware and Proxmox.
One of the standout features of Proxmox is its seamless integration with KVM, an open-source virtualization technology that is built directly into the Linux kernel. KVM allows Proxmox to deliver high performance and efficiency in virtual machine management. When considering Proxmox KVM virtualization, users benefit from a robust and scalable infrastructure that can handle various workloads and applications.
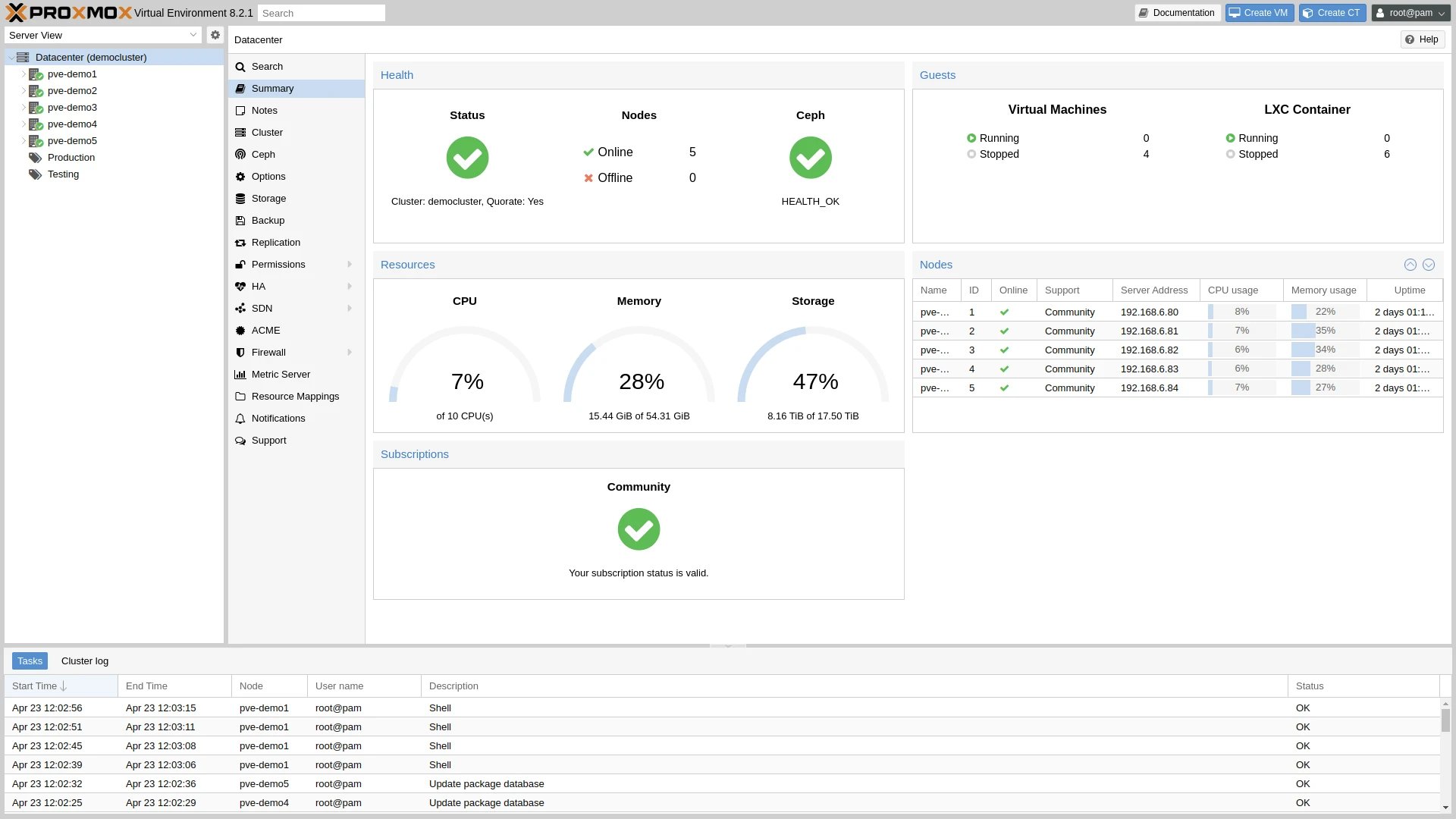
Performance is a critical factor when evaluating virtualization platforms. In the context of Proxmox vs KVM performance, Proxmox leverages KVM’s native performance benefits while enhancing them with additional features and optimizations. Proxmox’s architecture is designed to ensure minimal overhead, allowing virtual machines to run at near-native speeds. Additionally, Proxmox includes features like live migration, storage replication, and network management, which contribute to overall system performance and reliability.
Proxmox KVM virtualization stands out due to its ease of use and comprehensive feature set. The Proxmox web interface provides a user-friendly experience, enabling administrators to easily create, manage, and monitor virtual machines and containers. This contrasts with a more manual setup process when using standalone KVM, which often requires extensive command-line interaction and additional configuration efforts.
Moreover, Proxmox supports a wide range of storage options, including local storage, shared storage (NFS, iSCSI, Ceph), and advanced storage replication, which ensures data integrity and availability. The integrated backup and restore functionalities are particularly valuable for enterprise environments, ensuring that critical data is protected and can be quickly recovered in case of failures.
Additionally, Proxmox supports a wide range of guest operating systems, from various Linux distributions to Windows, BSD, and more, making it a versatile choice for diverse IT environments. The support for containers (LXC) alongside traditional virtual machines (KVM) allows for optimized resource utilization and flexibility.
In conclusion, when comparing KVM vs Proxmox, it’s clear that Proxmox extends the capabilities of KVM with a comprehensive set of tools and features designed to simplify and enhance virtualization management. Proxmox KVM virtualization offers a robust, high-performance, and user-friendly platform ideal for both small businesses and large enterprises. The combination of Proxmox’s management interface, high availability, integrated backup, and advanced storage options positions it as a superior choice for those seeking a reliable and efficient virtualization solution.
What is kvm?

KVM, or Kernel-based Virtual Machine, is an open-source virtualization technology integrated into the Linux kernel. It transforms a Linux system into a powerful hypervisor capable of running multiple virtual machines (VMs) simultaneously. Each VM has its own virtualized hardware, including CPU, memory, storage, and network interfaces, making KVM an efficient and flexible solution for server virtualization. If you want to read the comparison of VMware and Proxmox, read the article Comparing VMware and Proxmox.
KVM stands out due to its simplicity and performance. Being part of the Linux kernel, it benefits from the stability, security, and performance optimizations inherent to Linux. KVM supports a wide range of guest operating systems, including various Linux distributions, Windows, BSD, and more, providing versatile deployment options for different use cases.
When discussing KVM vs Proxmox, it's crucial to understand that Proxmox leverages KVM as its core virtualization technology. While KVM on its own offers robust virtualization capabilities, Proxmox extends these functionalities with a comprehensive suite of management tools, enhancing the overall virtualization experience.
Proxmox KVM virtualization builds on the solid foundation of KVM, offering a user-friendly interface and additional features that simplify the management of virtual environments. For instance, Proxmox provides an intuitive web-based GUI, enabling administrators to easily create, manage, and monitor VMs and containers. This ease of use is a significant advantage when comparing KVM vs Proxmox, as standalone KVM requires more manual configuration and command-line proficiency.
Performance is a critical consideration in virtualization. In terms of Proxmox vs KVM performance, Proxmox enhances the inherent performance benefits of KVM with advanced features like high availability, live migration, and integrated backup solutions. These features ensure minimal downtime and data integrity, crucial for enterprise environments. While KVM alone offers excellent performance, Proxmox's additional capabilities provide a more comprehensive and resilient solution.
Moreover, Proxmox supports clustering, allowing multiple Proxmox servers to be managed as a single entity. This feature is particularly beneficial for scaling and load balancing, ensuring optimal resource utilization across the virtualized infrastructure. In contrast, KVM lacks built-in clustering capabilities, making Proxmox KVM a more attractive option for larger, dynamic environments.
Another notable feature of Proxmox KVM virtualization is the support for both KVM and LXC (Linux Containers), offering a hybrid approach to virtualization. This flexibility allows administrators to choose the best-suited technology for their specific needs, optimizing resource allocation and performance.
In conclusion, while KVM provides a robust and efficient virtualization foundation, Proxmox builds on this by offering a comprehensive management platform that simplifies and enhances virtualization tasks. When evaluating KVM vs Proxmox, the additional features and user-friendly interface of Proxmox make it a superior choice for those seeking a complete and efficient virtualization solution. The combination of Proxmox KVM ensures high performance, scalability, and ease of management, making it ideal for both small and large-scale deployments.
Why use Proxmox?
Proxmox has become a popular choice in the virtualization world, offering a robust and user-friendly platform for managing virtual machines (VMs) and containers. Let’s explore the key reasons why Proxmox stands out and why it might be the ideal solution for your virtualization needs.
Comprehensive Management Interface
One of the primary reasons to use Proxmox is its comprehensive web-based management interface. Unlike KVM, which typically requires extensive command-line interaction, Proxmox provides an intuitive GUI that simplifies the creation, deployment, and monitoring of VMs. This ease of use is a significant advantage in the KVM vs Proxmox comparison, making Proxmox accessible even to those with limited technical expertise.
Enhanced Performance and Scalability
When considering Proxmox vs KVM performance, Proxmox enhances KVM’s native capabilities with additional features that boost overall efficiency. Proxmox supports high availability (HA) clustering, allowing VMs to automatically migrate to another node in the event of a hardware failure. This ensures minimal downtime and continuous service availability, which is particularly beneficial for enterprise environments.
Integrated Backup Solutions
Proxmox includes integrated backup and restore functionalities, ensuring that your data is protected and can be quickly recovered in case of failures. This contrasts with KVM, where setting up backups requires additional tools and configurations. The built-in backup solutions in Proxmox simplify the process, making it a more attractive option in the KVM vs Proxmox debate.
Hybrid Virtualization with KVM and LXC
Proxmox supports both KVM for full virtualization and LXC for container-based virtualization. This hybrid approach allows users to choose the most appropriate technology for their workloads, optimizing resource utilization. In the Proxmox KVM virtualization setup, administrators can run both VMs and containers side-by-side, providing greater flexibility and efficiency compared to a standalone KVM setup.
Advanced Networking and Storage Options
Proxmox offers advanced networking and storage options that are crucial for modern IT environments. It supports a wide range of storage types, including local storage, shared storage (NFS, iSCSI, Ceph), and advanced storage replication. Additionally, Proxmox includes robust network management features, such as software-defined networking (SDN) and VLAN support, which are essential for complex and scalable infrastructures. These advanced capabilities give Proxmox an edge in the KVM vs Proxmox comparison.
Cost-Effective Solution
Proxmox is an open-source solution, which means it can be implemented without the hefty licensing fees associated with many other virtualization platforms. This cost-effectiveness, combined with its rich feature set, makes Proxmox an excellent choice for organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises.
Community and Support
Proxmox has a vibrant and active community, providing a wealth of resources, forums, and documentation. This community support, combined with professional support options, ensures that users can get help and advice when needed. In contrast, while KVM also has a strong community, the additional features and integrations provided by Proxmox make it easier to find targeted support for specific use cases.
In conclusion, when comparing KVM vs Proxmox, Proxmox offers a more comprehensive and user-friendly virtualization solution. Its advanced features, such as high availability, integrated backups, hybrid virtualization, and advanced networking, enhance the native capabilities of KVM, making it a superior choice for managing and scaling virtualized environments. Proxmox’s cost-effectiveness and strong community support further solidify its position as an ideal virtualization platform for both small-scale and enterprise deployments.
Why use kvm?
Proxmox is a robust and user-friendly virtualization platform that offers a range of powerful features, making it an excellent choice for managing virtual machines (VMs) and containers. Here’s a detailed look at why Proxmox might be the ideal solution for your virtualization needs.
Simplified Management Interface
One of the standout benefits of using Proxmox is its intuitive web-based management interface. Unlike KVM, which often requires extensive command-line expertise, Proxmox provides a comprehensive GUI that simplifies the creation, deployment, and monitoring of VMs. This user-friendly interface is a significant advantage in the KVM vs Proxmox comparison, making Proxmox accessible to both novice and experienced users.
Superior Performance and Scalability
When evaluating Proxmox vs KVM performance, Proxmox enhances KVM’s inherent capabilities with additional features that boost overall efficiency. Proxmox supports high availability (HA) clustering, allowing VMs to automatically migrate to another node in case of hardware failure. This feature ensures minimal downtime and continuous service availability, which is critical for enterprise environments. The ability to manage clusters effectively gives Proxmox an edge in performance and scalability over standalone KVM setups.
Integrated Backup Solutions
Data protection is a critical aspect of any virtualization platform. Proxmox includes integrated backup and restore functionalities, ensuring that your data is secure and can be quickly recovered in case of failures. In contrast, KVM requires additional tools and configurations for backups. This built-in backup solution in Proxmox simplifies the process, providing a more streamlined approach to data protection in the KVM vs Proxmox debate.
Hybrid Virtualization with KVM and LXC
Proxmox supports both KVM for full virtualization and LXC for container-based virtualization. This hybrid approach allows users to choose the most suitable technology for their specific workloads, optimizing resource utilization. The flexibility of running both VMs and containers side-by-side in a Proxmox KVM virtualization setup provides greater efficiency and versatility compared to using KVM alone.
Advanced Networking and Storage Options
Proxmox offers advanced networking and storage options that are crucial for modern IT environments. It supports a variety of storage types, including local storage, shared storage (NFS, iSCSI, Ceph), and advanced storage replication. Additionally, Proxmox includes robust network management features, such as software-defined networking (SDN) and VLAN support. These advanced capabilities make Proxmox a more comprehensive solution in the KVM vs Proxmox comparison.
Cost-Effective Solution
Proxmox is an open-source platform, which means it can be implemented without the high licensing fees associated with many other virtualization solutions. This cost-effectiveness, combined with its rich feature set, makes Proxmox an excellent choice for organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises. The financial advantage of Proxmox is another key point in the KVM vs Proxmox evaluation.
Strong Community and Support
Proxmox boasts a vibrant and active community, providing a wealth of resources, forums, and documentation. This community support, coupled with available professional support options, ensures that users can get help and advice when needed. While KVM also has a strong community, the additional features and integrations offered by Proxmox make it easier to find targeted support for specific use cases.
In summary, when comparing KVM vs Proxmox, Proxmox emerges as a more comprehensive and user-friendly virtualization platform. Its advanced features, such as high availability, integrated backups, hybrid virtualization, and advanced networking, enhance the native capabilities of KVM, making Proxmox a superior choice for managing and scaling virtualized environments. The cost-effectiveness and strong community support further solidify Proxmox as an ideal virtualization solution for both small-scale and enterprise deployments.
Comparing kvm vs proxmox

KVM, or Kernel-based Virtual Machine, is a powerful and efficient virtualization solution integrated into the Linux kernel. It offers robust performance and flexibility, making it a preferred choice for many organizations. Here’s a detailed look at why you should consider using KVM for your virtualization needs.
|
Feature |
KVM |
Proxmox VE |
|
User Interface |
Requires command-line usage |
Web-based interface for easy management |
|
Container Support |
Limited support or requires extra tools |
Native support for LXC container-based virtualization |
|
Backup Features |
Requires manual configuration & tools |
Built-in backup server with advanced features |
|
Network Management |
Requires manual and complex setup |
Integrated network management tools for simplified configuration |
Native Integration and Performance
KVM is built directly into the Linux kernel, which means it benefits from the stability, security, and performance optimizations of Linux. This native integration ensures minimal overhead, allowing VMs to run at near-native speeds. In the KVM vs Proxmox debate, while Proxmox builds on KVM's capabilities, KVM alone provides a lean and highly efficient virtualization layer without additional complexities.
Flexibility and Customization
KVM offers a high degree of flexibility and customization, allowing administrators to tailor their virtualization environment to specific needs. This can be particularly beneficial for advanced users who prefer to have granular control over their system configurations. Compared to Proxmox KVM virtualization, which includes a user-friendly interface and additional features, KVM’s straightforward and minimalist approach can be ideal for those who favor a more hands-on, customizable setup.
Wide Range of Supported Systems
KVM supports a vast array of guest operating systems, including various Linux distributions, Windows, BSD, and more. This broad compatibility ensures that you can run almost any software environment within a KVM virtual machine. In the KVM vs Proxmox comparison, while Proxmox also supports multiple OS types, KVM’s direct integration into the Linux kernel makes it an inherently versatile and adaptable solution.
Cost-Effective and Open Source
KVM is an open-source technology, making it a cost-effective choice for virtualization. There are no licensing fees, and it benefits from continuous improvements and support from the open-source community. In terms of KVM vs Proxmox cost-effectiveness, while Proxmox is also open source, KVM’s direct use without additional layers or interfaces can reduce complexity and potential costs related to management overhead.
Security and Isolation
KVM provides robust security features, including strong isolation between virtual machines. Each VM operates as a separate process, leveraging Linux's security features to ensure a secure environment. In the Proxmox vs KVM performance comparison, KVM’s security and isolation features stand out, particularly for users who require stringent security measures.
Resource Efficiency
KVM is known for its efficient use of resources. It supports advanced features such as CPU and memory overcommitment, allowing for optimal utilization of physical hardware. When comparing KVM vs Proxmox, while Proxmox adds additional management layers and features, KVM’s resource efficiency ensures that maximum performance is extracted from the available hardware.
Community and Support
KVM has a strong and active open-source community, providing extensive documentation, forums, and user-contributed resources. This community support ensures that users can find solutions and share knowledge easily. While Proxmox KVM also benefits from a robust community, the direct involvement of KVM in the Linux ecosystem means it often receives updates and support from a broader range of contributors.
In summary, when evaluating KVM vs Proxmox, KVM offers a highly efficient, flexible, and secure virtualization solution with minimal overhead. Its native integration with the Linux kernel ensures superior performance and stability. While Proxmox enhances KVM with additional features and a user-friendly interface, KVM’s direct, customizable approach makes it an excellent choice for those who prefer a lean, powerful, and cost-effective virtualization environment.
Conclusion
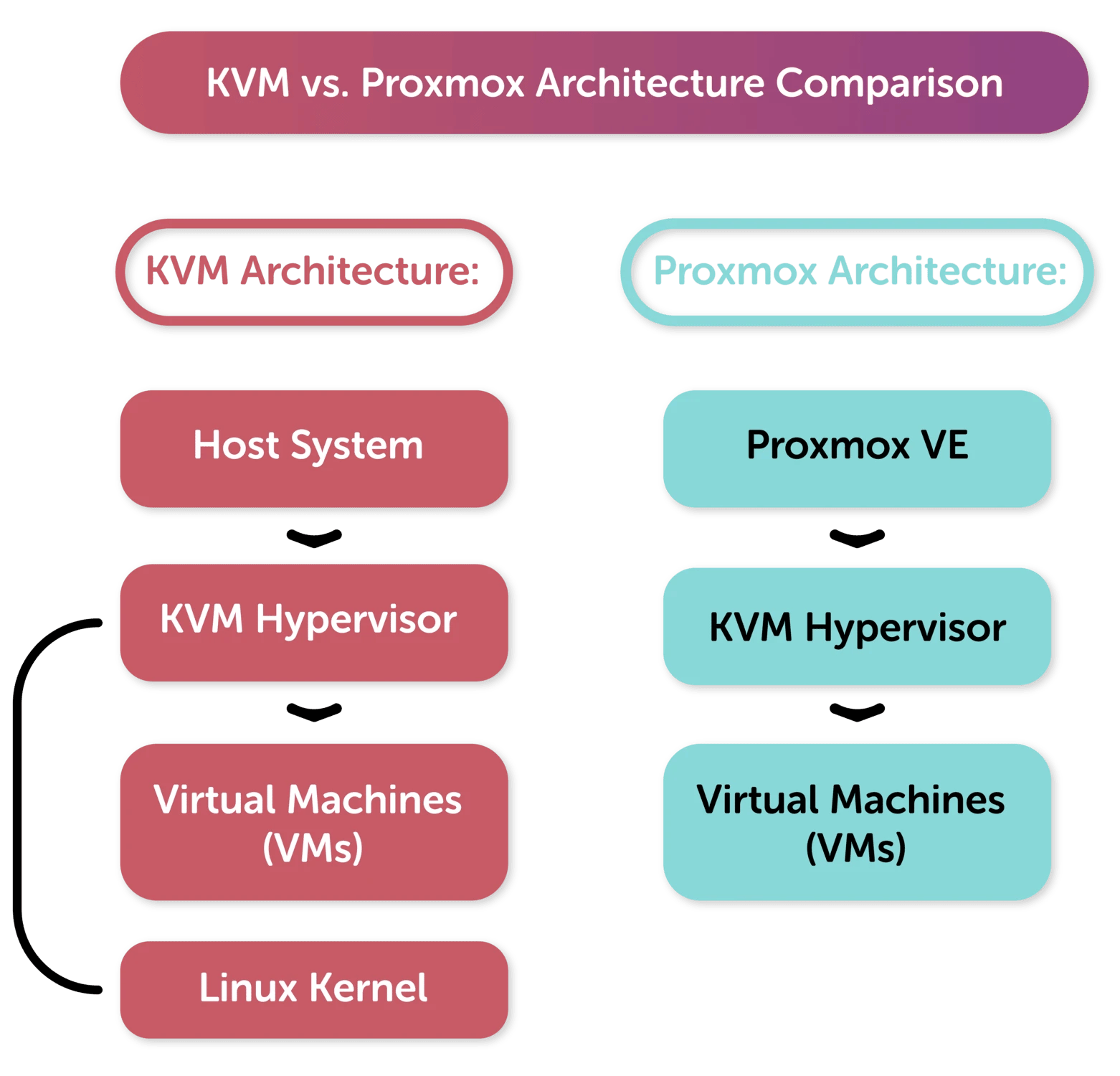
In conclusion, the choice between KVM and Proxmox hinges significantly on your specific needs and technical expertise. KVM stands out as a robust hypervisor integrated deeply into the Linux kernel, offering powerful virtualization capabilities at the foundational level. Its direct integration with Linux makes it highly efficient for environments where performance and scalability are paramount. Administrators familiar with Linux ecosystems will find KVM's command-line interface and flexibility appealing, allowing for fine-grained control over virtualized environments.
On the other hand, Proxmox presents a comprehensive virtualization platform that incorporates KVM alongside LXC containers, providing a unified management interface through its web-based GUI. This makes it exceptionally user-friendly for those looking to manage virtual machines and containers within a single environment without delving deeply into command-line operations. Proxmox's added features like live migration, high availability clustering, and backup solutions further enhance its appeal for enterprise environments seeking robust virtualization with simplified management.
For enterprises weighing KVM vs Proxmox, performance benchmarks often highlight KVM's edge in raw virtualization power, especially for environments demanding bare-metal performance. Meanwhile, Proxmox's integrated approach appeals to teams looking for an all-in-one solution that balances ease of use with advanced virtualization capabilities. Organizations leaning towards KVM typically prioritize customization and direct kernel integration, whereas those opting for Proxmox value its unified management and broader feature set out of the box.
Ultimately, both KVM and Proxmox excel in different aspects of virtualization, catering to distinct operational needs and preferences. Whether you prioritize performance optimization with KVM or streamlined management with Proxmox, understanding your infrastructure requirements and team expertise will guide you towards the optimal choice for your virtualization environment.
In conclusion, the decision between KVM vs Proxmox rests on aligning technological capabilities with operational objectives, ensuring that your chosen platform not only meets current needs but also scales effectively as your infrastructure grows and evolves.






![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)

