Setting up a private Git server on a VPS is a powerful way to maintain control over your code repositories while leveraging the flexibility and scalability of a virtual private server. This guide will walk you through how to set up a private Git server on VPS efficiently and securely, covering every essential step. Whether you’re a developer or a team leader, learning how to set up a Git server ensures complete privacy and customization. By following these steps to set up a private Git server on VPS, you can host your repositories, control access, and optimize performance. We'll explore how to install Git on VPS and configure it for seamless version control. If you're wondering about the best practices to setup a private Git server, this guide will provide detailed instructions and tips, ensuring you master how to set up a Git server with ease. If You need VPS, visit 1Gbits VPS Hosting.
How to Set Up a Private Git Server on VPS

Create the SSH Key Pair
One of the foundational steps in how to set up a private Git server on VPS is creating an SSH key pair. SSH keys ensure secure authentication between your local machine and the VPS, enabling seamless repository management. This step is crucial whether you're on Windows, Linux, or Mac. In this guide, we’ll focus on how to create the SSH key pair as part of how to set up a private Git server on VPS Mac. َAlso Read What Is VPS Hosting, 10 things you can do with VPS, and Applications You Can Run on Your VPS.
Why Use SSH for Your Git Server?
When you setup a private Git server, using SSH keys enhances security by eliminating the need for password-based authentication. It’s particularly important for a self-hosted Git server, where security is entirely in your hands. With SSH keys, you can ensure that only authorized devices have access, and this approach integrates perfectly when you’re working to install Git on VPS.
Steps to Create an SSH Key Pair
-
Generate the SSH Key Pair Locally
Start by opening your terminal on your local machine. On Mac, this is easily accessible from the Applications folder or Spotlight Search. Run the following command to generate an SSH key:
· ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
This command creates a 4096-bit RSA key, which is robust and secure for setting up a self-hosted Git server. Replace "your_email@example.com" with your email address to identify the key.
-
Specify the Key Location
The terminal will prompt you to save the file. By default, it saves to ~/.ssh/id_rsa. You can press Enter to confirm or specify a different path. This file will contain your private key. -
Secure Your Private Key
Next, you'll be prompted to create a passphrase. This adds another layer of security to your SSH key. If you prefer, you can leave this blank, but using a strong passphrase is highly recommended when working on tasks like how to set up automatic deployment with Git with a VPS. -
Locate Your Public Key
After completing the steps, your key pair is ready. The private key resides in the specified location, and the public key is saved as id_rsa.pub in the same directory. You’ll need the public key to grant access to the VPS.
Adding Your SSH Key to the VPS
After generating your key pair, the next step in how to set up a private Git server on VPS is transferring your public key to the server. This process ensures secure communication between your local machine and the VPS for actions like Git pull on VPS.
-
Copy the Public Key to VPS
Use the ssh-copy-id command to copy the key to your server. Replace user and host with your VPS credentials:
· ssh-copy-id user@host
Alternatively, you can manually append the contents of id_rsa.pub to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on the VPS.
-
Test the SSH Connection
Once the public key is on the VPS, test the connection:
· ssh user@host
If successful, no password will be required. This confirms that the SSH key authentication is working, which is essential for managing a self-hosted Git server securely.
Configuring Git on the VPS
With SSH in place, the next phase in how to set up a private Git server on VPS Mac is to install Git on VPS. Use the following commands to ensure Git is installed and ready:
· sudo apt update
· sudo apt install git
For CentOS or Fedora, use yum install git, and for Mac environments, Homebrew is the go-to tool.
Automating Deployments and Repository Management
Once SSH and Git are configured, you can explore advanced features like how to set up automatic deployment with Git with a VPS. By combining Git hooks with SSH, you can trigger deployment scripts automatically whenever changes are pushed to your repositories. This feature is especially useful for maintaining a self-hosted Git server.
You can also choose a VPS in a strategic location to optimize performance and reduce latency. Learn more about selecting the best VPS location for your needs.
Best Practices for Security
-
Regularly update your SSH key pairs.
-
Restrict access to the ~/.ssh directory on both local and server machines.
-
Disable root login on your VPS to minimize vulnerabilities.
Managing Repositories and Git Commands
After setting up the SSH key, you can use commands like git clone, git push, and Git pull on VPS to manage repositories. These commands leverage SSH for secure communication, making your setup private Git server efficient and robust.
In conclusion, creating an SSH key pair is a pivotal step in how to set up a private Git server on VPS. It provides secure authentication, paving the way for repository management and features like how to set up automatic deployment with Git with a VPS. By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth, secure, and efficient workflow with your self-hosted Git server.
Setup a Git User and Install Git on your VPS

When learning how to set up a private Git server on VPS, setting up a dedicated Git user and installing Git are critical steps. These tasks lay the groundwork for securely hosting and managing repositories. This guide explains how to create a Git user, install Git on VPS, and configure the environment to ensure smooth version control. Whether you're using Ubuntu, CentOS, or Debian, the process is similar, with minor differences in package management.
Why Create a Dedicated Git User?
A dedicated Git user ensures secure access to your repositories and minimizes risks. By isolating Git processes under a specific user, you create a controlled environment. This step is a best practice when building a self-hosted Git server and aligns with secure repository management principles in how to set up a private Git server on VPS.
Additionally, if you're considering hosting your Git server on a dedicated machine, you may want to explore the benefits of renting a VPS. Renting a VPS provides flexibility, scalability, and improved control over your server environment, making it an ideal choice for hosting a private Git server securely.
Steps to Create a Git User
-
Log in to Your VPS
Start by logging into your VPS using SSH:
· ssh root@your-vps-ip
Replace your-vps-ip with the actual IP address of your VPS.
-
Create the Git User
Use the adduser command to create a new user dedicated to Git operations. For instance:
· sudo adduser git
You’ll be prompted to set a password and enter user details. Complete the process to ensure the new user is added to the system.
-
Grant SSH Access to the Git User
Copy your public SSH key to the Git user’s home directory:
· sudo mkdir /home/git/.ssh
· sudo cp ~/.ssh/authorized_keys /home/git/.ssh/
· sudo chown -R git:git /home/git/.ssh
· sudo chmod 700 /home/git/.ssh
· sudo chmod 600 /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
This step ensures the Git user has the necessary permissions for secure SSH access.
-
Restrict Shell Access (Optional)
If the Git user is only for repository management, you can restrict shell access:
· sudo usermod -s /usr/bin/git-shell git
This limits the user’s ability to execute non-Git commands, enhancing security for your self-hosted Git server.
Installing Git on VPS
After setting up the Git user, the next step in how to set up a private Git server on VPS is to install Git. This process varies slightly depending on your VPS operating system.
-
Update the Package Manager
Begin by updating your system to ensure you’re downloading the latest software versions:
· sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
For CentOS:
· sudo yum update -y
-
Install Git on VPS
Use the appropriate command to install Git: -
On Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo apt install git -y
-
On CentOS/Fedora:
sudo yum install git -y
-
On Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S git
-
Verify Git Installation
Once the installation is complete, verify it by checking the version:
git --version
You should see the installed Git version in the output, confirming that Git is ready for use in your self-hosted Git server setup.
Configuring Git for Your VPS
To finalize the installation, configure global Git settings for the Git user.
-
Switch to the Git User
Log in as the Git user:
su - git
-
Set Up Global Git Configurations
Configure the Git username and email to identify commits:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "your_email@example.com"
These settings apply to all repositories managed by this Git user, which is crucial for maintaining clarity and accountability in version control.
Integrating Git with Your VPS
Once Git is installed and configured, you can integrate it with your workflow. For instance:
-
Create Bare Repositories: Use bare repositories for pushing and pulling changes.
mkdir -p /home/git/myrepo.git
cd /home/git/myrepo.git
git init --bare
-
Clone the Repository: Clone it to your local machine using SSH:
git clone git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/myrepo.git
-
Push and Pull Changes: Seamlessly push and pull changes between your local machine and the VPS, ensuring smooth version control in your self-hosted Git server.
Automating Git Server Management
To take your server to the next level, explore automation options like hooks for deployment. Combining these tools enhances the flexibility and efficiency of your self-hosted Git server, making how to set up a private Git server on VPS even more powerful.
Setting up a dedicated Git user and installing Git on VPS are indispensable steps in how to set up a private Git server on VPS. By following this guide, you can securely manage repositories, streamline development workflows, and maintain complete control over your version control environment.Bottom of Form
Add your SSH Key to the Access List
One of the most important steps in how to set up a private Git server on VPS is configuring secure access through SSH keys. Adding your SSH key to the access list ensures that only authorized users can interact with your repositories. This process leverages the secure shell (SSH) protocol to authenticate users without requiring passwords, making it a preferred method for securing a self-hosted Git server.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to generate an SSH key, add it to your Git server’s access list, and verify access. These steps are essential in mastering how to set up a private Git server on VPS while ensuring security and functionality. If you're looking to try this out without commitment, consider exploring a free trial VPS to get started with no upfront costs.
Why Use SSH Keys for Git Access?
SSH keys provide a robust authentication method that eliminates the need for password management. Using SSH keys:
-
Prevents unauthorized access to your self-hosted Git server.
-
Enhances security through encryption.
-
Streamlines operations like pulling, pushing, or automating deployment workflows.
Adding SSH keys is vital when setting up Git operations, especially in configurations like how to set up a private Git server on VPS for mac users or for Linux-based systems.
Generating an SSH Key
-
Check for an Existing Key
Before creating a new SSH key, ensure you don’t already have one. Run the following command on your local machine:
ls ~/.ssh
If you see files like id_rsa and id_rsa.pub, you already have a key. Otherwise, proceed to create a new one.
-
Generate a New SSH Key
Use the ssh-keygen command to create an SSH key pair:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
-
The -t rsa specifies the type of key to generate.
-
The -b 4096 flag ensures the key is 4096 bits long for enhanced security.
Press Enter to save the key in the default location (~/.ssh/id_rsa) and set a passphrase if desired.
Copying the SSH Key
Once your key is generated, you need to add the public key to your VPS.
-
Display the Public Key
View the content of your public key using:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Copy the output, as this is the key you’ll add to your Git server.
-
Log In to Your VPS
Use SSH to connect to your VPS:
ssh root@your-vps-ip
-
Add the Key to the Git User
Append the public key to the authorized_keys file for your Git user:
echo "your-public-key" >> /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
Replace your-public-key with the output of the cat command above.
-
Set Permissions
Ensure proper permissions for the .ssh directory and the authorized_keys file:
chmod 700 /home/git/.ssh
chmod 600 /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
chown -R git:git /home/git/.ssh
These steps prevent unauthorized modifications and ensure secure access.
Verifying SSH Access
After adding the key, test your connection to the self-hosted Git server.
-
Test the Connection
From your local machine, run:
ssh git@your-vps-ip
If everything is configured correctly, you should be logged in as the Git user.
-
Clone a Repository Using SSH
Test repository access by cloning a Git repository:
git clone git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/myrepo.git
This confirms that your SSH key is working and that you’ve successfully implemented secure access as part of how to set up a private Git server on VPS.
Enhancing Access Security
For advanced setups, consider these options:
-
Restrict User Commands: Limit the Git user’s access to Git-specific actions using git-shell.
-
Monitor Access Logs: Regularly review SSH access logs to ensure there are no unauthorized attempts.
These practices are especially important for automation setups, such as how to set up automatic deployment with git with a VPS.
Troubleshooting SSH Issues
If you encounter issues:
-
Check Key Permissions: Ensure the .ssh directory and authorized_keys file have the correct permissions.
-
Verify SSH Agent: Add your private key to the SSH agent:
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
-
Firewall Configuration: Ensure your VPS firewall allows SSH traffic on port 22.
Adding your SSH key to the access list is a fundamental step in how to set up a private Git server on VPS. By securing access and ensuring proper configuration, you can maintain a robust self-hosted Git server for seamless collaboration and development.
Setup a Local Repository
When learning how to set up a private Git server on VPS, setting up a local repository is a critical step. This allows developers to create, manage, and synchronize code between their local machines and the private Git server. Setting up a local repository involves initializing a Git repository, connecting it to the private Git server, and managing files and commits for version control.
In this guide, we will explain the steps to set up a local repository and connect it to a private Git server, ensuring smooth collaboration and secure synchronization. Whether you’re working on a self-hosted solution or experimenting with how to set up a private Git server on VPS mac, these steps apply universally.
You can also consider hosting your private Git server on a reliable VPS for better performance and security. For cost-effective options, check out our guide on cheap VPS, where you'll find affordable and reliable solutions for hosting your private Git server.
1. Initialize a Local Git Repository
The first step in setting up a local repository is to initialize Git in your project directory.
-
Install Git on Your Local Machine
If Git isn’t already installed, download and install it: -
For macOS: Use brew install git.
-
For Linux: Use sudo apt install git or sudo yum install git.
-
For Windows: Download Git from the official Git website.
-
Navigate to Your Project Directory
Use the terminal to navigate to your project folder:
· cd /path/to/your/project
-
Initialize the Repository
Run the following command to create a new Git repository:
· git init
This creates a .git directory that tracks all changes to your project.
-
Verify the Initialization
Use ls -a to confirm the presence of the .git folder. This indicates that Git is tracking your project.
2. Create a Repository on the Private Git Server
Before connecting your local repository, you need a repository on your VPS.
Log In to Your VPS
Connect to your VPS using SSH:
· ssh git@your-vps-ip
-
Navigate to the Git Directory
Create or navigate to the directory where you want to host your repository:
· cd /home/git
· mkdir myrepo.git
· cd myrepo.git
· git init --bare
The --bare flag creates a repository for remote access, as bare repositories don’t have a working directory.
Set Permissions
Ensure the Git user owns the repository:
· chown -R git:git /home/git/myrepo.git
This step prepares your VPS for use as a self-hosted Git server, a key element in how to set up a private Git server on VPS.
3. Connect the Local Repository to the Git Server
Once the local and remote repositories are ready, the next step is connecting them.
Add the Remote Repository
In your local repository, run the following command:
· git remote add origin git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/myrepo.git
Replace your-vps-ip with your VPS’s IP address or domain name.
-
Verify the Remote Repository
Use the git remote -v command to confirm the connection:
· origin git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/myrepo.git (fetch)
· origin git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/myrepo.git (push)
4. Commit and Push Changes
With the connection established, you can now commit changes and push them to the server.
Stage Changes
Add files to the staging area:
· git add
The adds all changes in the project directory.
Commit Changes
Commit the staged changes with a message:
git commit -m "Initial commit"
Push Changes to the Server
Push the changes to the remote repository:
· git push -u origin main
If your branch is named differently (e.g., master), replace main with your branch name.
Testing the Setup
Verify the connection by performing a Git pull from another machine or directory:
Clone the Repository
Clone the repository from your VPS:
· git clone git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/myrepo.git
Check Remote Access
Navigate into the cloned repository and run git pull origin main to ensure the setup works.
These steps ensure that your local repository integrates seamlessly with your private Git server, fulfilling the requirements of how to set up a private Git server on VPS.
Advanced Configurations
For advanced users:
-
Enable Automatic Deployment: Learn how to set up automatic deployment with git with a VPS to streamline updates.
-
Optimize Workflow for Teams: Use branch permissions and hooks to manage collaborations effectively.
Using your Git Server from your Local Computer
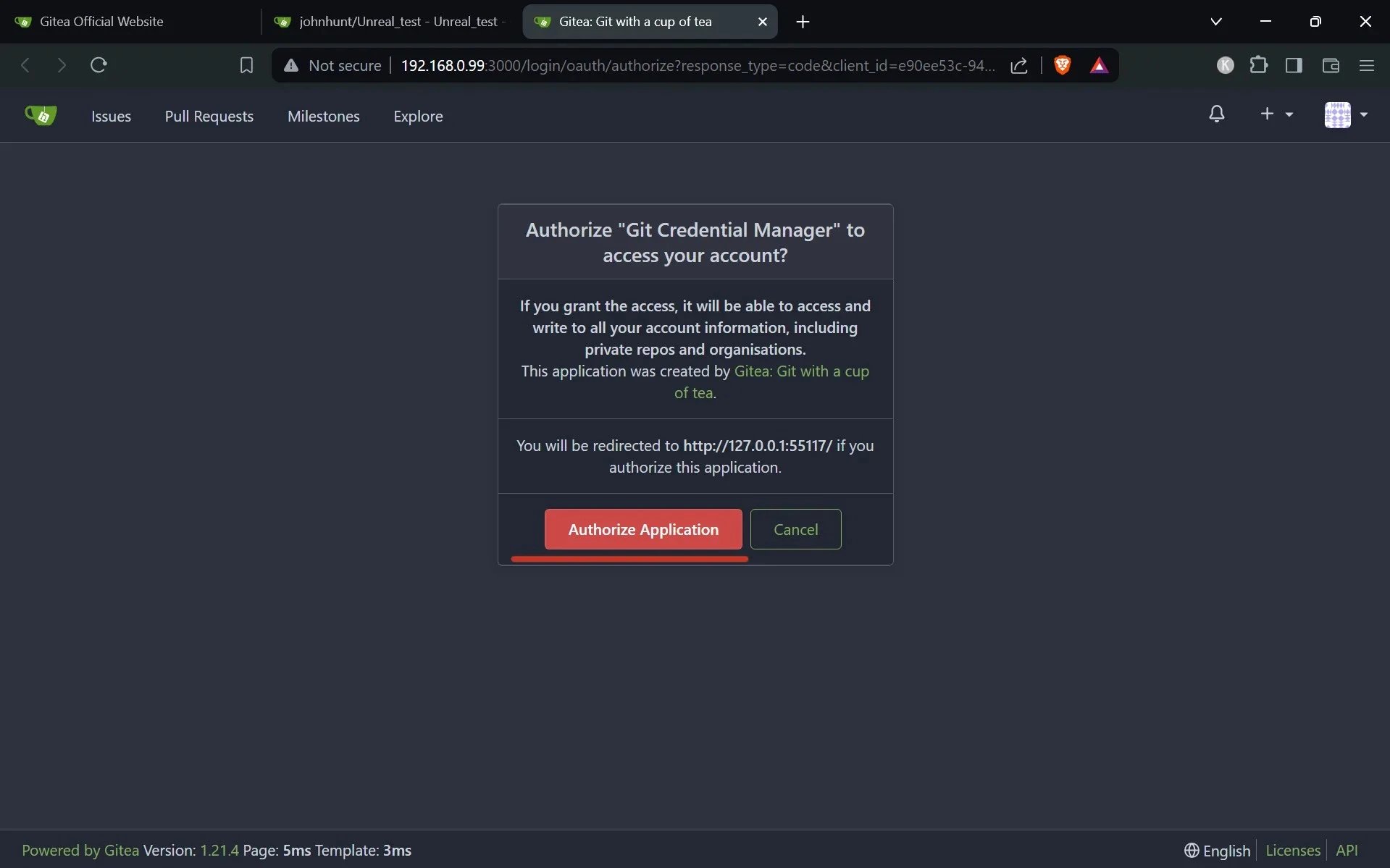
When learning how to set up a private Git server on VPS, one of the most important aspects is understanding how to use the Git server from your local computer. This step allows developers to push, pull, and manage code directly with the server. By establishing a smooth connection between your local machine and your Git server, you enable seamless version control and collaboration.
Step 1: Verify the Git Server Connection
To use your Git server from your local computer, ensure that your local machine can communicate with the server.
-
Test SSH Connection
If you’ve already added your SSH key to the server, verify the connection by running:
· ssh git@your-vps-ip
Replace your-vps-ip with your VPS’s IP address or domain name. You should see a successful login message, confirming that the SSH connection works.
-
Troubleshoot Connection Issues
If the connection fails, recheck: -
Your server’s firewall settings.
-
The correct placement of your SSH public key in the server’s authorized keys.
-
Network restrictions that might block SSH traffic.
Step 2: Clone a Repository from the Git Server
Cloning a repository allows you to download its contents to your local machine for development.
-
Get the Repository URL
The repository URL typically looks like this:
· git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/repo-name.git
-
Clone the Repository
Run the following command:
· git clone git@your-vps-ip:/home/git/repo-name.git
This will create a directory named repo-name in your current folder, containing the repository files.
-
Verify Cloning Success
Navigate into the cloned repository and check its status:
· cd repo-name
· git status
If successful, this means you’ve correctly connected your local computer to your Git server as part of how to set up a private Git server on VPS.
Step 3: Push Changes to the Git Server
After making changes to your local repository, you can push them to the server.
-
Stage Your Changes
Add files to the staging area:
· git add .
-
Commit Your Changes
Create a commit message that summarizes your updates:
· git commit -m "Your commit message here"
-
Push Changes
Push your changes to the server:
· git push origin main
Replace main with your branch name if it’s different.
Step 4: Pull Updates from the Git Server
Regularly pulling updates ensures your local repository stays synchronized with the server.
-
Pull the Latest Changes
Use the following command to fetch and merge changes:
· git pull origin main
This command ensures your local copy reflects the latest commits on the server.
-
Resolve Merge Conflicts
If conflicts arise during the pull, resolve them manually by editing the affected files, then stage and commit the resolved changes.
Step 5: Configure Advanced Workflows
Using your Git server effectively involves advanced configurations and workflows.
-
Set Up Automatic Deployment
Explore how to set up automatic deployment with git with a VPS by configuring post-receive hooks on the server. This ensures that changes pushed to the repository automatically deploy to production or staging environments. -
Branch Management
Work with multiple branches for better project organization. For instance, you can create a new feature branch locally:
· git checkout -b feature-branch
· git push origin feature-branch
-
Self-Hosted CI/CD
Enhance your self-hosted Git server by integrating tools like Jenkins for continuous integration and deployment.
Step 6: Troubleshoot Common Issues
When using a self-hosted Git server, you might encounter issues like authentication errors or network timeouts.
-
Authentication Errors
-
Ensure the SSH private key on your local machine matches the public key on the server.
-
Use ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa to add your private key to the SSH agent.
-
Slow Performance
-
Optimize server resources on your VPS to handle multiple connections.
-
Use Git commands like git gc to clean up unnecessary files and optimize repository performance.Top of Form
Conclusion
Setting up a private Git server on a VPS empowers you with control, security, and flexibility for managing your projects. From creating SSH key pairs and setting up a Git user to configuring repositories and using the server from your local machine, the process ensures a self-hosted version control system tailored to your needs. By learning how to set up a private Git server on VPS, you gain the ability to streamline collaboration and enhance development workflows. Whether for personal or team projects, this setup provides a secure, reliable, and efficient solution for managing your codebase. Start building today!






![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![How to Change VPS Password 🔑 [Windows & Linux] How to Change VPS Password 🔑 [Windows & Linux]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2025/12/how-to-change-your-vps-password-750xAuto.webp)


