In the realm of modern networking, a fundamental question often arises: what is RADIUS server? This inquiry is pivotal for understanding how secure and efficient user authentication is managed across diverse systems. To dive deeper into what is RADIUS server, we need to explore its role in networking, its mechanisms, and its applications.
So, what is RADIUS server? RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service. It is a networking protocol that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management for users who connect and use a network service. Essentially, when we ask, "what is RADIUS server?" we are delving into a system that ensures users are who they claim to be, are allowed to access specific resources, and can be tracked for usage and billing purposes.
When considering what is RADIUS server used for, the primary purpose is to authenticate users before they gain access to a network. This is particularly important in large organizations where maintaining security and access control is critical. A RADIUS server verifies user credentials against a centralized database, ensuring that only authorized users can connect. This leads us to the question: what is RADIUS server authentication? It is the process where the server checks the credentials (like username and password) provided by a user against its database and grants or denies access based on this verification.
To fully grasp what is RADIUS server and how it works, imagine an employee trying to access a company's internal network. When they input their login details, the RADIUS server checks these credentials against its records. If the information matches, the user is granted access; if not, access is denied. This is a streamlined method to manage user access across multiple platforms without the need for redundant credential databases.
In networking terms, what is RADIUS server in networking? It is a crucial component that integrates with network devices such as routers, switches, and VPN concentrators to enforce security policies consistently across the network. When we talk about what is RADIUS server IP, this refers to the specific IP address assigned to the RADIUS server, which network devices use to communicate with it.
For network administrators, understanding what is RADIUS server configuration is essential. This involves setting up the server with necessary protocols, policies, and user data to ensure it operates effectively. Also, knowing what is RADIUS server IP address is crucial for troubleshooting and network management.
In today's wireless age, a common query is what is RADIUS server for WiFi? It is a vital tool for securing wireless networks by ensuring only authorized users can connect to the WiFi network. Additionally, what is RADIUS accounting server? It tracks the usage of network resources by authenticated users, which is useful for monitoring and billing purposes.
Lastly, questions like what is RADIUS server group name attribute arise, where specific user groups can be assigned different access rights and policies based on their group membership. Ultimately, understanding what is RADIUS server used for can significantly enhance network security and management efficiency.
What is RADIUS Server
What is RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service)? This essential question opens the door to understanding a cornerstone of modern network security and management. A RADIUS server, short for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, plays a pivotal role in verifying the identity of users attempting to access a network, ensuring that only authorized individuals gain entry. But what is RADIUS server exactly, and why is it so critical in today’s interconnected world?
To begin with, what is RADIUS server in networking? A RADIUS server is a centralized system that performs three crucial functions: Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA). This means it checks if users are who they say they are (Authentication), determines what resources they can access (Authorization), and tracks their activities on the network (Accounting). This comprehensive approach enhances security by centralizing user management, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
When exploring what is RADIUS server and how it works, imagine a corporate employee attempting to log into the company’s internal network from a remote location. The RADIUS server receives the login request, verifies the user’s credentials against its database, and if the credentials match, grants access. This process happens swiftly and seamlessly, ensuring security without hindering user experience.
What is RADIUS server example? A practical example is seen in educational institutions. Universities often deploy RADIUS servers to manage student access to campus WiFi. Each student’s login credentials are verified by the RADIUS server before they can connect to the internet, ensuring that only enrolled students utilize the network.
In the realm of operating systems, RADIUS server Windows refers to the implementation of a RADIUS server on a Windows-based system. Microsoft provides a built-in solution called Network Policy Server (NPS), which acts as a RADIUS server, enabling organizations to leverage their existing Windows infrastructure for user authentication and network access control.
What is Use RADIUS protocol? The RADIUS protocol is a networking protocol that facilitates communication between the RADIUS server and various network devices like routers, switches, and access points. It ensures that authentication requests are handled efficiently and securely.
When it comes to wireless networks, the question of what is RADIUS server for WiFi arises. A RADIUS server is integral to securing WiFi networks by ensuring that only users with valid credentials can connect. This prevents unauthorized access and protects sensitive data transmitted over the wireless network.
FreeRADIUS is another term that often comes up in discussions about what is RADIUS in networking. FreeRADIUS is an open-source implementation of the RADIUS protocol, widely used for its flexibility and robustness. It allows organizations of all sizes to deploy a RADIUS server without the costs associated with commercial solutions, providing a powerful tool for managing network access.
In summary, what is RADIUS server? It’s a vital component of network security, ensuring that only authorized users can access network resources while tracking their activity for better management and accountability. Whether it’s in a corporate environment, educational institution, or public WiFi, a RADIUS server plays a crucial role in safeguarding network integrity and user data.
How does RADIUS Server Authentication work?
A crucial component in network security and management is understanding what is RADIUS server. RADIUS, or Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, is a centralized system that handles user authentication, authorization, and accounting. By managing these processes from a single point, a RADIUS server ensures that only authorized users can access network resources, maintaining the integrity and security of the network.
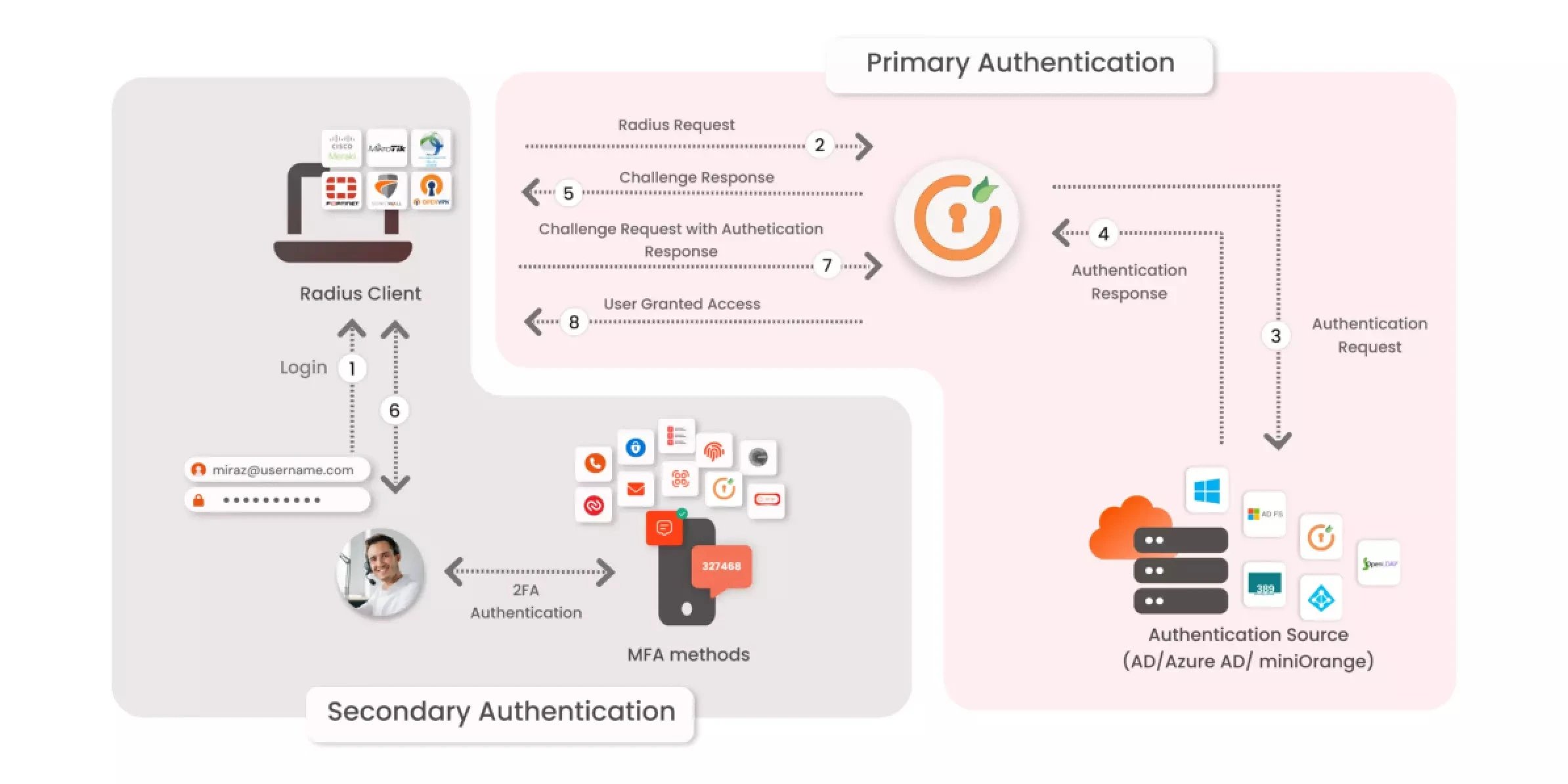
Initial Connection
To comprehend how RADIUS server authentication works, let's start with the initial connection. When a user tries to connect to a network—whether through a wired or wireless connection—their device sends a connection request to a network access server (NAS). This NAS could be a router, switch, or WiFi access point. The NAS acts as the intermediary between the user and the RADIUS server.
Credential Submission
Upon receiving the connection request, the NAS prompts the user for their login credentials, typically a username and password. These credentials are then encapsulated and securely transmitted to the RADIUS server using the RADIUS protocol. This protocol ensures that the data is encrypted and protected during transmission, maintaining the security of sensitive information.
Authentication Process
At this stage, what is RADIUS server doing? The server receives the user’s credentials and checks them against its database of authorized users. This database might be an internal directory or an external one like Active Directory or LDAP. The RADIUS server's job is to verify that the credentials provided match those stored in the database.
Response to NAS
Based on the authentication result, the RADIUS server responds to the NAS with one of three messages:
-
Access-Accept: If the credentials are valid, the server sends an Access-Accept message, granting the user access to the network.
-
Access-Reject: If the credentials are invalid, the server sends an Access-Reject message, denying network access.
-
Access-Challenge: In some cases, the server may send an Access-Challenge message requesting additional information, such as a second factor of authentication.
User Access and Accounting
Once the NAS receives an Access-Accept message, it allows the user to access the network. The RADIUS server also performs accounting functions, tracking user activity, session duration, and data usage. This information is vital for both security monitoring and billing purposes.
WiFi and Beyond
What is RADIUS server for WiFi? In wireless networks, a RADIUS server is indispensable for securing access points. It ensures that only users with valid credentials can connect, protecting the network from unauthorized access. This application is common in corporate environments, educational institutions, and public hotspots.
Centralized Security
In summary, what is RADIUS server? It is a central hub for managing user authentication, authorization, and accounting. By leveraging the RADIUS protocol, it ensures secure communication and centralized control, enhancing network security and efficiency. Whether in securing WiFi networks or managing access in complex corporate environments, a RADIUS server is essential for maintaining robust network security.
What is AAA?
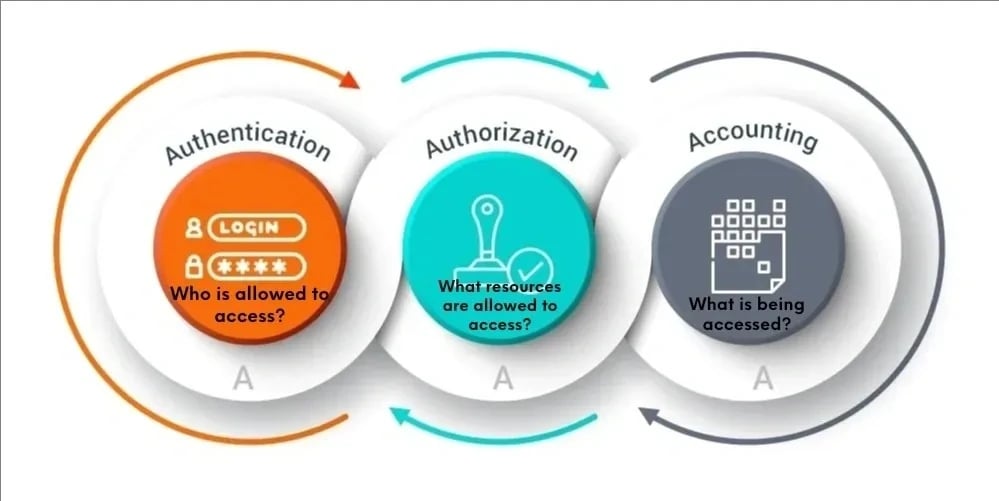
In the world of network security, the term AAA stands for Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting. These three components are critical for managing and securing access to network resources. But what is AAA exactly, and how does it function in practice? At the heart of AAA systems, we often find the RADIUS server, a pivotal element that helps implement these processes efficiently. To understand AAA fully, it's essential to explore each component and how a RADIUS server facilitates their operation.
Authentication
Authentication is the first pillar of AAA. It involves verifying the identity of users trying to access a network. So, what is RADIUS server's role in authentication? When a user attempts to log in, their credentials are sent to the RADIUS server using the RADIUS protocol. The server checks these credentials against a central database. If the information matches, the user is authenticated and granted access. This process ensures that only legitimate users can access the network, thereby enhancing security.
Authorization
Once a user is authenticated, the next step is authorization. This process determines what resources and services the authenticated user is permitted to access. Here, what is RADIUS server's role? The RADIUS server uses predefined policies and rules to grant or restrict access to various network resources. For instance, an employee might have access to certain internal databases but not to others. The server ensures that users only access resources appropriate to their roles, maintaining the integrity and security of sensitive information.
Accounting
The final component of AAA is accounting, which involves tracking user activities on the network. What is RADIUS server's function in accounting? It keeps detailed logs of user sessions, including login and logout times, data accessed, and the amount of data transferred. This information is crucial for various purposes, such as monitoring network usage, generating usage reports, and identifying potential security breaches. Accounting ensures that every action within the network is recorded, providing transparency and accountability.
The RADIUS Protocol
What is RADIUS protocol, and why is it vital for AAA? The RADIUS protocol standardizes communication between the RADIUS server and network devices like routers and switches. It ensures secure transmission of authentication, authorization, and accounting data, maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of this information. The protocol's reliability and security make it a preferred choice for implementing AAA in many organizations.
Real-World Applications
What is RADIUS server in real-world applications? Consider a university where students and staff need access to the campus WiFi. The RADIUS server authenticates users, authorizes access to specific resources, and tracks usage for security and billing purposes. Similarly, in a corporate setting, a RADIUS server manages employee access to internal networks, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
In summary, AAA—Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting—is crucial for network security and management. What is RADIUS server's role in AAA? It serves as the backbone, efficiently implementing these processes through the reliable RADIUS protocol. By understanding AAA and the function of RADIUS servers, organizations can better secure their networks and ensure proper access control and accountability.
RADIUS Server Authentication methods
Network security is paramount in today's digital landscape, and understanding RADIUS server authentication methods is key to maintaining robust security. So, what is RADIUS server, and how does it ensure secure network access?
A RADIUS server, or Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, is a centralized system that manages user authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA). But how does it authenticate users, and what methods are employed? Let's delve into the authentication methods used by a RADIUS server.
1. Password-Based Authentication
The most common method of RADIUS server authentication is password-based authentication. When a user attempts to connect to a network, they provide their username and password. What is RADIUS server doing at this point? It receives these credentials via the RADIUS protocol and verifies them against a stored database. If the credentials match, access is granted. This method is straightforward but relies heavily on strong password policies to ensure security.
2. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
To enhance security, many organizations implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA). What is RADIUS server's role in 2FA? After the initial password verification, the RADIUS server prompts the user for a second factor, typically a temporary code sent to their mobile device or generated by an authenticator app. This added layer of security ensures that even if passwords are compromised, unauthorized access is still prevented.
3. Certificate-Based Authentication
For higher security needs, certificate-based authentication is employed. In this method, users or devices authenticate themselves using digital certificates issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). What is RADIUS server doing here? It verifies the presented certificate against its trusted CA database. This method is highly secure as it mitigates risks associated with password-based authentication.
4. EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol)
What is RADIUS protocol, and how does EAP fit in? The RADIUS protocol supports multiple authentication methods through EAP, allowing for flexible and secure user authentication. EAP is an authentication framework that supports various authentication mechanisms, including token cards, smart cards, and biometric methods. When using EAP, the RADIUS server acts as a broker, facilitating the authentication process between the user and the network.
5. LDAP Integration
Many organizations integrate their RADIUS servers with LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) directories. What is RADIUS server's function in this integration? It acts as an intermediary, verifying user credentials against the LDAP directory. This method streamlines user management by leveraging existing directory services.
In summary, what is RADIUS server? It is the backbone of network security, employing various authentication methods to ensure only authorized users gain access. By understanding these methods and the role of the RADIUS protocol, organizations can implement effective and secure authentication strategies. Whether using password-based authentication, 2FA, certificate-based methods, or EAP, a RADIUS server provides the flexibility and security needed to protect network resources effectively.
What is aradius server used for?

In the realm of network security, understanding what is RADIUS server is crucial for managing and protecting access to network resources. So, what is RADIUS server used for, and why is it so vital in today’s digital environment?
A RADIUS server, or Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, is primarily used for Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management. This centralized system ensures that only authenticated users can access network resources, thereby enhancing security.
Authentication
One of the primary uses of a RADIUS server is to authenticate users attempting to access a network. When a user tries to log in, their credentials are sent to the RADIUS server using the RADIUS protocol. The server checks these credentials against a database and, if they match, grants the user access. This process ensures that only legitimate users can access the network.
Authorization
What is RADIUS server’s role in authorization? After authentication, the server determines what resources the user is allowed to access. It ensures that each user has appropriate permissions based on their role within the organization. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information and resources.
Accounting
Accounting is another critical function of a RADIUS server. It tracks user activities, such as login and logout times, data usage, and accessed resources. This information is vital for monitoring network usage, generating reports, and identifying potential security breaches.
Practical Applications
What is RADIUS server used for in practical terms? In a corporate environment, it manages employee access to internal networks, ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive data. In educational institutions, it controls student and staff access to campus WiFi, providing secure internet connectivity.
The Backbone of Network Security
In summary, what is RADIUS server? It is a vital component of network security, used for authenticating users, authorizing their access to resources, and accounting for their activities. By utilizing the RADIUS protocol, it ensures secure and efficient management of network access, protecting both the network and its users.
Concluison
In conclusion, understanding what is RADIUS server is essential for anyone involved in network security and management. So, what is RADIUS server? It is a critical component that ensures the secure authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) of users within a network. By verifying credentials and enforcing access policies, a RADIUS server safeguards network resources against unauthorized access.
What is RADIUS server's impact on organizational security? It centralizes user management, making it easier to enforce security policies consistently across the entire network. Whether in corporate environments, educational institutions, or public WiFi networks, the role of a RADIUS server is indispensable for maintaining robust security.
Furthermore, what is RADIUS server’s contribution to user accountability? By tracking user activities and generating detailed usage reports, it provides invaluable insights into network usage patterns and potential security threats.
In summary, what is RADIUS server? It is the backbone of secure network access, ensuring that only authorized users can connect and that their activities are monitored for safety and compliance. Understanding and implementing RADIUS servers is fundamental to protecting and efficiently managing modern network infrastructures.





![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)

