In the digital age, where connectivity is king, knowing Mbps meaning, bitrate mbps meaning, and mbps meaning wifii is essential for navigating the online world. Mbps, or megabits per second, is a fundamental measure of internet speed. It dictates how quickly data can be transmitted from one point to another, shaping our online experiences in profound ways. Whether you're streaming videos, downloading files, or gaming online, Mbps meaning plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and seamless connection.
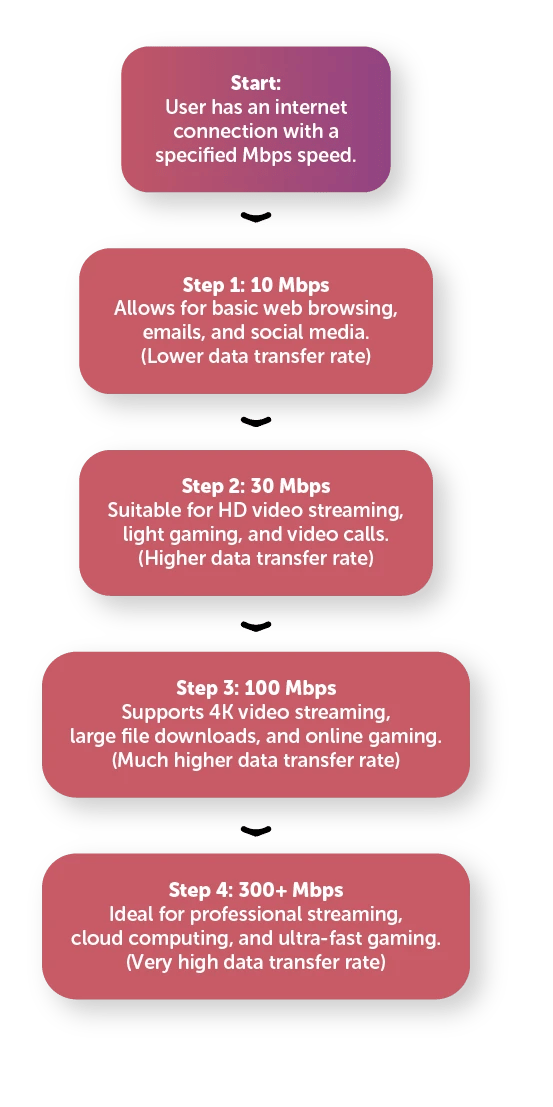
Let's start with the basics: 10 Mbps, 1 mbps meaning meaning you have a decent internet speed that allows for smooth web browsing and basic streaming. It's a good starting point for most households, but as your internet usage grows, you may find yourself needing more speed.
Upgrading to 30 Mbps meaning you can enjoy faster downloads, smoother streaming, and better overall performance. This speed is ideal for households with multiple users or devices, ensuring everyone can stay connected without experiencing any slowdowns.
When it comes to code rate Mbps meaning you're optimizing your data transfer, ensuring that your information is transmitted quickly and accurately. This is particularly important for activities that require a high level of precision, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
If you're lucky enough to have 300 Mbps meaning you have lightning-fast internet speeds that can handle anything you throw at it. Whether you're streaming in 4K, downloading large files, or gaming online, this speed ensures you can do it all without any buffering or lag.
Upload Mbps meaning is often overlooked but is just as important as download speed. With 50 Mbps meaning you can quickly and easily share files, upload videos, and video chat with friends and family without any issues.
For those looking for a balance, 10 mbps meaning/100 Mbps meaning you have the flexibility to choose between two different speeds depending on your needs. This can be particularly useful for households with varying internet usage patterns.
At the higher end of the spectrum, 100 Mbps meaning you have a mbps meaning internetconnection that can handle even the most demanding online activities. Whether you're a hardcore gamer, a video editing enthusiast, or a small business owner, this speed ensures you can stay connected and productive.
But what exactly does mbps meaning of computer? Mbps meaning is the speed at which data is transmitted between devices, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Whether you're transferring files between your computer and a server or streaming content from the internet, Mbps meaning is crucial for ensuring a seamless experience.
When it comes to broadband Mbps meaning is all about maximizing your bandwidth for faster, more reliable internet access. By understanding Mbps meaning, you can ensure you're getting the most out of your internet connection, whether you're browsing the web, streaming videos, or gaming online.
In conclusion, Mbps meaning is a crucial metric for understanding and optimizing your internet speed. Whether you're a casual internet user or a power user, Mbps meaning plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and seamless online experience. So, the next time you're wondering what Mbps means, remember, it's more than just a number – it's the key to unlocking a world of possibilities online.
What are mbps meaning?
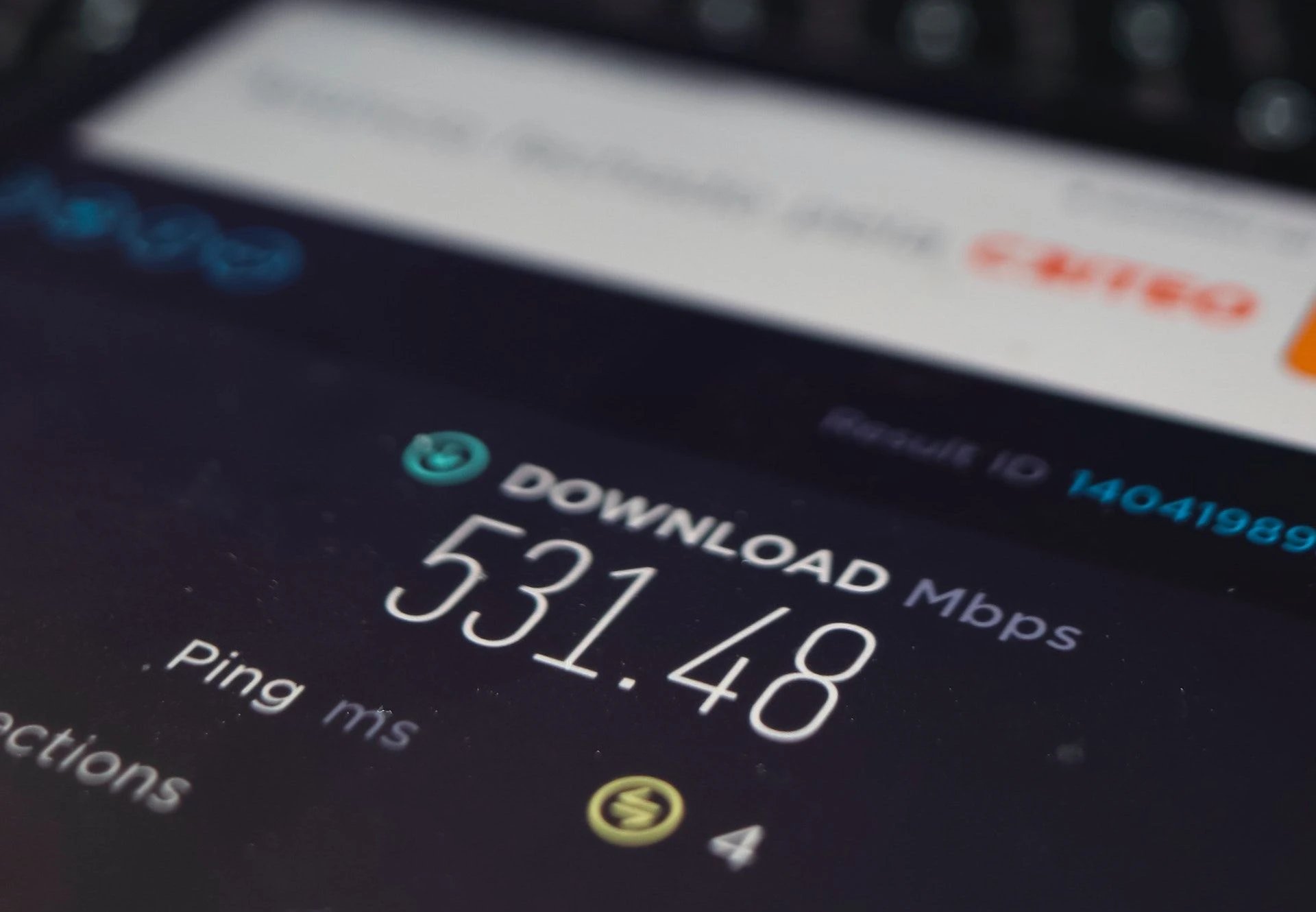
In the realm of internet connectivity, the term "Mbps" reigns supreme, serving as a beacon that guides us through the digital landscape. Mbps, an acronym for megabits per second, is a fundamental unit of measurement that defines the speed at which data travels across the vast network of cyberspace. It is a metric that holds the key to unlocking the true potential of our online experiences.
At its core, Mbps meaning is straightforward yet profound. It represents the rate at which data can be transmitted, indicating the number of megabits (millions of bits) that can be transferred in a single second. When you encounter internet plans offering speeds of 10 Mbps, 30 Mbps, or even 300 Mbps, you are witnessing the promise of swift and seamless connectivity.
But Mbps meaning extends beyond just speed; it embodies efficiency and capability. Consider the concept of a code rate Mbps meaning – it signifies the efficiency of data transmission, ensuring that every bit of information is conveyed accurately and promptly. This efficiency is crucial for activities that require precision, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
In the realm of computing, Mbps meaning is equally significant. It defines the speed at which data is transmitted within a computer system, playing a crucial role in its performance. A computer equipped with a 100 Mbps network interface card (NIC) can transfer data at speeds up to 100 Mbps, provided the network infrastructure supports it.
So, what does.mbps mean for your internet experience? Mbps meaning dictates how quickly you can stream videos, download files, browse the web, and engage in various online activities. A higher Mbps translates to faster and more efficient performance, while a lower Mbps may result in slower load times and buffering.
When discussing internet speeds, the terms "upload Mbps meaning" and "download Mbps meaning" often come into play. Upload Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can send data from your device to the internet, while download Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can receive data from the internet to your device.
Bandwidth Mbps meaning is another crucial concept to understand. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time. A higher Mbps signifies a wider bandwidth, allowing for more data to be transmitted simultaneously.
In comparison, kbps (kilobits per second) is another unit of measurement often juxtaposed with Mbps. While Mbps refers to millions of bits per second, kbps refers to thousands of bits per second. For instance, 1 Mbps is equivalent to 1,000 kbps.
In essence, Mbps meaning is a cornerstone of modern connectivity. It defines the speed at which we navigate the digital landscape, influencing our interactions, entertainment, and productivity. Understanding Mbps is not just about knowing a technical term; it's about unlocking the full potential of the internet and embracing a world of seamless connectivity.
Meaning of bandwidth mbps

In this part we discuss about meaning of bandwidth mbps. Bandwidth Mbps stands as a beacon in the realm of internet connectivity, illuminating the path to seamless and efficient data transmission. It is a term that encapsulates the essence of speed and efficiency, dictating the rate at which data can be transmitted over a network. Understanding bandwidth Mbps is crucial for optimizing your internet experience and ensuring a smooth digital journey.
At its core, Mbps stands for megabits per second, a unit of measurement that defines the speed at which data travels across a network. It represents the number of megabits (millions of bits) that can be transferred in a single second. When you encounter internet plans offering speeds of 10 Mbps, 30 Mbps, or even 300 Mbps, you are witnessing the promise of swift and seamless connectivity.
Bandwidth Mbps plays a pivotal role in shaping your internet experience. It determines how quickly you can stream videos, download files, browse the web, and engage in various online activities. A higher bandwidth Mbps translates to faster and more efficient performance, while a lower bandwidth Mbps may result in slower load times and buffering.
But bandwidth Mbps is not just about speed; it is also about capacity. It represents the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time. A higher bandwidth Mbps signifies a wider pipeline, allowing for more data to be transmitted simultaneously.
When discussing internet speeds, the terms "upload Mbps meaning" and "download Mbps meaning" often come into play. Upload Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can send data from your device to the internet, while download Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can receive data from the internet to your device.
In comparison, kbps (kilobits per second) is another unit of measurement often juxtaposed with Mbps. While Mbps refers to millions of bits per second, kbps refers to thousands of bits per second. For instance, 1 Mbps is equivalent to 1,000 kbps.
In essence, bandwidth Mbps is the lifeblood of modern connectivity. It defines the speed and capacity of your internet connection, shaping your online experiences in profound ways. Understanding bandwidth Mbps is essential for optimizing your internet usage and ensuring a seamless digital journey. So, the next time you encounter the term Mbps, remember, it's not just a number; it's the key to unlocking the full potential of the internet.
Broadband mbps meaning
Broadband Mbps stands at the forefront of modern connectivity, heralding a new era of high-speed internet access. It is a term that encapsulates the essence of speed and efficiency, dictating the rate at which data can be transmitted over a network. Understanding broadband Mbps is essential for harnessing the full potential of your internet connection and embracing a world of seamless digital experiences.
At its core, Mbps stands for megabits per second, a unit of measurement that defines the speed at which data travels across a network. It represents the number of megabits (millions of bits) that can be transferred in a single second. When you encounter internet plans offering speeds of 10 Mbps, 30 Mbps, or even 300 Mbps, you are witnessing the promise of swift and seamless connectivity.
Broadband Mbps plays a pivotal role in shaping your internet experience. It determines how quickly you can stream videos, download files, browse the web, and engage in various online activities. A higher broadband Mbps translates to faster and more efficient performance, while a lower broadband Mbps may result in slower load times and buffering.
But broadband Mbps is not just about speed; it is also about capacity. It represents the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time. A higher broadband Mbps signifies a wider pipeline, allowing for more data to be transmitted simultaneously.
When discussing internet speeds, the terms "upload Mbps meaning" and "download Mbps meaning" often come into play. Upload Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can send data from your device to the internet, while download Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can receive data from the internet to your device.
In comparison, kbps (kilobits per second) is another unit of measurement often juxtaposed with Mbps. While Mbps refers to millions of bits per second, kbps refers to thousands of bits per second. For instance, 1 Mbps is equivalent to 1,000 kbps.
In essence, broadband Mbps is the cornerstone of modern connectivity. It defines the speed and capacity of your internet connection, shaping your online experiences in profound ways. Understanding broadband Mbps is essential for optimizing your internet usage and ensuring a seamless digital journey. So, the next time you encounter the term Mbps, remember, it's not just a number; it's the key to unlocking the full potential of the internet.
Megabits per second vs. megabytes per second: What's the difference?
Mbps stands for megabits per second, a unit used to measure data transfer speed. It represents the rate at which data can be transmitted over a network. When you see an internet plan advertised as 10 Mbps, 30 Mbps, or even 300 Mbps, it's referring to the speed at which you can download or upload data.
In the realm of computer technology, Mbps meaning plays a crucial role in defining the capabilities of your hardware. For example, a computer with a 100 Mbps network interface card (NIC) can transfer data at speeds up to 100 Mbps, provided the network infrastructure supports it.
What Does Mbps Mean for Internet Speeds?
what do mbps speeds mean؟ Mbps meaning dictates how fast you can stream videos, download files, browse the web, and perform other online activities. A higher Mbps means you can do these things faster and more efficiently, while a lower Mbps may result in slower load times and buffering.
Mbps Up and Down Meaning
In this part we talk about mbps up and down meaning. When it comes to internet speeds, the terms "upload Mbps meaning" and "download Mbps meaning" often come up. Upload Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can send data from your device to the internet, while download Mbps meaning refers to the speed at which you can receive data from the internet to your device.
In this part we talk mbps and kbps meaning. Mbps and kbps (kilobits per second) are both units of measurement used to quantify data transfer speeds. While Mbps refers to millions of bits per second, kbps refers to thousands of bits per second. For example, 1 Mbps is equal to 1,000 kbps.
mbps means and full form is "megabits per second." Full form of mbps and meaningis a standard unit of measurement used to quantify data transfer speeds. Mbps is used to describe the speed of internet connections, network interfaces, and other data transfer technologies.
Mbps and Its Importance in Bandwidth
Bandwidth Mbps refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time. It is a measure of the capacity of a network to carry data. A higher bandwidth Mbps means that more data can be transmitted at once, leading to faster internet speeds.
Understanding the Difference Between Mbps and MBps
|
Unit |
Conversion |
|
1 Mbps |
0.125 MBps |
|
8 Mbps |
1 MBps |
|
100 Mbps |
12.5 MBps |
|
300 Mbps |
37.5 MBps |
It's important to note the difference between Mbps and MBps. Mbps (megabits per second) is a measure of data transfer speed, while MBps (megabytes per second) is a measure of data storage capacity. There are 8 megabits in a megabyte, so 1 MBps is equal to 8 Mbps.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between mbps and mbps meaning is essential for making informed decisions about internet speeds and data transfer rates. Mbps meaning is crucial for determining the speed and efficiency of your internet connection, while MBps is used to measure data storage capacity. By understanding these concepts, you can ensure that you are getting the most out of your internet connection and data transfer technologies.
Megabits vs. megabytes: Why it matters

In the vast digital realm, understanding the difference between Megabits (Mb) and Megabytes (MB) is akin to deciphering a secret code. Let's embark on a journey to unravel this mystery, exploring why it matters and delving into the enigmatic world of Mbps.
Firstly, what is an Mbps? Mbps stands for Megabits per second, a unit used to measure data transfer speed. It indicates how many bits (not bytes) of data can be transmitted in one second. It's crucial to note the distinction: 1 byte is composed of 8 bits.
Why It Matters
Understanding the difference between Megabits and Megabytes matters immensely in the digital landscape, especially when dealing with internet speed. Internet service providers (ISPs) often advertise internet speeds in Mbps. For instance, you might see a plan offering speeds of "100 Mbps." This means that the internet connection can theoretically transfer 100 million bits of data per second.
The Real-world Implications
To put this into perspective, let's consider downloading a file. If you have a 100 Mbps internet connection, theoretically, you could download a 1,000 Megabit (125 Megabyte) file in 10 seconds. However, due to various factors such as network congestion and overhead, the actual download time might be slightly longer.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
One common misconception is that internet speeds are measured in Megabytes per second (MBps). This is incorrect. Internet speeds are typically measured in Megabits per second (Mbps). Therefore, when you see an internet speed advertised as "100 Mbps," it means 100 Megabits per second, not Megabytes.
Practical Examples
Let's consider another scenario: streaming video. Video streaming services often require a minimum internet speed for smooth playback. For instance, streaming a high-definition video might require speeds of at least 5 Mbps, while streaming in 4K could require upwards of 25 Mbps.
Understanding Bitrate
Bitrate, often expressed in Mbps, is the amount of data processed in a given amount of time, typically used in the context of audio or video encoding. Higher bitrates generally result in better quality but require faster internet speeds for smooth playback.
In conclusion, the distinction between Megabits and Megabytes is crucial in understanding and navigating the digital world, particularly when it comes to internet speed and data transfer. Mbps, though often misunderstood, plays a pivotal role in determining how fast data can be transmitted, impacting everything from file downloads to video streaming. So, the next time you see an internet speed advertised in Mbps, remember, it's all about those bits, not bytes.
Bits vs. bytes: What is the difference?

In the digital realm, bits and bytes are the fundamental units of information. A bit is the smallest unit of data in computing, representing a binary digit of either 0 or 1. On the other hand, a byte is a group of 8 bits, forming the basic building block of data in most computer systems.
Why It Matters in Mbps
When it comes to measuring data transfer speed, understanding the difference between bits and bytes is crucial. Internet speeds, often measured in Mbps (Megabits per second), indicate the rate at which data is transmitted. For example, a 100 Mbps internet connection can theoretically transfer 100 million bits of data per second.
Real-world Applications
Consider downloading a file that is 100 Megabits (Mb) in size. With a 100 Mbps connection, you could theoretically download this file in 1 second. However, in reality, factors such as network congestion and latency can affect the actual download time.
Misunderstandings and Clarifications
It's important to note that internet speeds are typically advertised in Mbps, not Megabytes per second (MBps). This distinction is crucial, as it can impact your expectations regarding download speeds and the time it takes to transfer data.
Practical Examples
Streaming services often require a minimum internet speed for smooth playback. For example, streaming a high-definition video may require speeds of at least 5 Mbps, while streaming in 4K may require upwards of 25 Mbps to ensure a seamless viewing experience.
Understanding Bitrate
Bitrate, often measured in Mbps, is the rate at which bits are processed during data transmission. In the context of audio and video encoding, a higher bitrate typically results in better quality, but it also requires faster internet speeds for smooth playback.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between bits and bytes is essential in navigating the digital world, particularly when it comes to internet speed and data transfer. Mbps, as a measurement of data transfer speed, plays a crucial role in determining how quickly data can be transmitted, impacting various aspects of digital communication and entertainmen
What are bits and bytes used for?
In the realm of computing, bits and bytes are the foundational units of information. A bit, the smallest unit, represents a binary digit, either a 0 or 1. A byte, consisting of 8 bits, is a fundamental unit used to store and transmit data in computer systems.
The Role of Mbps
Mbps, or Megabits per second, is a measurement of data transfer speed. It indicates how many millions of bits can be transmitted in one second. Understanding Mbps is crucial for assessing the speed and efficiency of data transmission in various digital applications.
Data Storage and Transmission
Bytes are used for storing and transmitting data in computers. They are used to represent characters, numbers, and other types of information. For example, a single byte can represent a letter of the alphabet or a number from 0 to 255.
Internet Speeds
Mbps is commonly used to measure internet speeds. When you see an internet plan advertised as "100 Mbps," it means that the connection can theoretically transfer 100 million bits of data per second. This measurement is important for activities like streaming videos, online gaming, and downloading files.
Understanding Bitrate
Bitrate, often expressed in Mbps, refers to the rate at which bits are processed during data transmission. In the context of audio and video streaming, a higher bitrate generally results in better quality but requires faster internet speeds to maintain smooth playback.
Networking and Communication
In computer networks, bits and bytes are used to transmit data between devices. Networking protocols define how data is formatted, transmitted, and received. Mbps is used to measure the speed of data transmission in networks, ensuring efficient communication between devices.
Storage Capacity
Bytes are also used to measure storage capacity. For example, a gigabyte (GB) is equivalent to 1 billion bytes. Storage devices such as hard drives and solid-state drives use bytes to store data, with larger capacities measured in terabytes (TB) or petabytes (PB).
In conclusion, bits and bytes are fundamental units of information used in computing for data storage, transmission, and communication. Mbps, as a measurement of data transfer speed, plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and performance of digital systems and networks. Understanding these concepts is essential for navigating the digital world effectively.
How do I mbps test?
Before we delve into testing Mbps, let's clarify what Mbps means. Mbps stands for Megabits per second, which is a measurement of data transfer speed. It indicates how many millions of bits can be transmitted in one second. This measurement is crucial for assessing the speed and efficiency of data transmission in various digital applications.
What You'll Need
To test your Mbps, you'll need a device (such as a computer or smartphone) connected to the internet and a reliable internet connection. It's also helpful to have a web browser installed on your device.
Choosing a Testing Method
There are several ways to test your Mbps. One popular method is to use an online speed test tool. These tools measure your internet speed by downloading and uploading a small amount of data to and from your device.
Using an Online Speed Test Tool
To use an online speed test tool, follow these steps:
-
Open a web browser on your device.
-
Navigate to a reputable speed test website. Examples include Speedtest by Ookla, Fast.com by Netflix, and Google's Internet Speed Test.
-
Click on the "Go" or "Start" button to begin the speed test.
-
Wait for the test to complete. The tool will measure your download and upload speeds in Mbps.
Interpreting the Results
Once the speed test is complete, you'll see your download and upload speeds displayed in Mbps. Download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device, while upload speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from your device to the internet.
Understanding Bitrate
Bitrate, often measured in Mbps, refers to the rate at which bits are processed during data transmission. In the context of internet speed testing, a higher bitrate indicates faster data transfer speeds.
Factors Affecting Mbps
Several factors can affect your Mbps test results, including the quality of your internet connection, network congestion, and the capabilities of your device. It's important to consider these factors when interpreting your speed test results.
Testing your Mbps is a simple yet effective way to assess the speed and performance of your internet connection. By understanding what Mbps means and how it relates to data transfer speed, you can better evaluate your internet service and make informed decisions about your digital activities.
How many Mbps do I need for internet and network?
Mbps, short for Megabits per second, is a unit used to measure data transfer speed. It indicates how many millions of bits can be transmitted in one second. When evaluating how many Mbps you need for your internet and network, several factors come into play.
Internet Usage
Your internet usage habits play a significant role in determining the Mbps you need. For basic web browsing and email, a lower Mbps connection may suffice. However, for activities like streaming high-definition videos, online gaming, or video conferencing, a higher Mbps connection is recommended for smoother performance.
Number of Users
The number of users on your network can impact the Mbps you need. A household with multiple users simultaneously streaming videos, playing online games, or video conferencing will require a higher Mbps connection to accommodate the increased data demands.
Types of Devices
Different devices have varying data requirements. For example, streaming 4K video on a smart TV requires more Mbps than browsing the web on a smartphone. Consider the types of devices connected to your network and their data needs when determining your Mbps requirements.
Streaming Services
Streaming services often recommend minimum Mbps requirements for smooth playback. For example, streaming Netflix in standard definition typically requires at least 3 Mbps, while streaming in 4K Ultra HD may require upwards of 25 Mbps.
Online Gaming
Online gaming typically requires a stable internet connection with low latency. While the Mbps requirements for gaming are relatively low, a higher Mbps connection can help reduce lag and improve gameplay, especially in multiplayer games.
Video Conferencing
Video conferencing applications like Zoom or Microsoft Teams require a certain Mbps for smooth video and audio quality. Higher Mbps connections can help ensure a seamless video conferencing experience with minimal disruptions.
Upload vs. Download Speeds
When considering Mbps requirements, it's essential to differentiate between upload and download speeds. Download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device, while upload speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from your device to the internet. Depending on your usage, you may need to prioritize one over the other.
conclusion, determining how many Mbps you need for your internet and network depends on various factors, including your internet usage habits, the number of users on your network, the types of devices you use, and the specific online activities you engage in. By understanding these factors and their impact on Mbps requirements, you can choose an internet plan that meets your needs and provides a seamless online experience.
How are broadband speeds measured?
Mbps, or Megabits per second, is a metric used to measure the speed of broadband internet connections. It indicates the rate at which data is transmitted over a network, with higher Mbps values corresponding to faster internet speeds.
Types of Broadband Connections
Broadband speeds can vary depending on the type of connection. Common types of broadband connections include DSL, cable, fiber-optic, and satellite. Each type of connection has its own maximum Mbps speeds, with fiber-optic typically offering the fastest speeds.
Download vs. Upload Speeds
Broadband speeds are often categorized into download and upload speeds. Download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device, while upload speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from your device to the internet. Mbps is used to measure both download and upload speeds.
How Speeds are Measured
Broadband speeds are measured using specialized equipment that sends and receives data packets over the network. The equipment measures the time it takes for data to travel between two points and calculates the speed based on the amount of data transmitted and the time taken.
Factors Affecting Speeds
Several factors can affect broadband speeds, including network congestion, the quality of the connection, the distance between your device and the network source, and the number of devices connected to the network. These factors can impact the Mbps you experience.
Mbps and Internet Usage
The Mbps you need for optimal internet usage depends on your online activities. For basic web browsing and email, a lower Mbps connection may be sufficient. However, for activities like streaming high-definition videos, online gaming, or video conferencing, a higher Mbps connection is recommended for smoother performance.
Choosing the Right Plan
When selecting a broadband plan, it's essential to consider your internet usage habits and the Mbps offered by the provider. Look for plans that offer enough Mbps to support your online activities without experiencing slowdowns or buffering.
Mbps and Streaming Services
Streaming services often recommend minimum Mbps requirements for smooth playback. For example, streaming Netflix in standard definition typically requires at least 3 Mbps, while streaming in 4K Ultra HD may require upwards of 25 Mbps.
In conclusion, broadband speeds are measured using Mbps, which indicates the rate at which data is transmitted over a network. Understanding Mbps and how it relates to your internet usage can help you choose the right broadband plan to meet your needs for a fast and reliable internet connection.
Mbps in video bit rate
Mbps, or Megabits per second, is a unit used to measure data transfer speed. In the context of video bitrate, Mbps refers to the rate at which video data is transmitted or processed. It plays a crucial role in determining the quality and smoothness of video playback.
What is Video Bitrate?
Video bitrate, measured in Mbps, is the amount of data processed in a given amount of time during video playback. A higher bitrate generally results in better video quality but also requires a faster internet connection for smooth streaming.
Importance of Mbps in Video Streaming
Mbps is essential in video streaming as it determines the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to your device per second. A higher Mbps connection ensures that the video can be streamed in higher resolutions without buffering or lag.
Impact of Mbps on Video Quality
The Mbps of a video stream directly impacts its quality. Higher Mbps streams can support higher resolutions, such as 1080p or 4K, which require more data to maintain image clarity and detail.
Choosing the Right Mbps for Streaming
When selecting a video streaming service or plan, consider your internet speed in Mbps. For example, streaming services like Netflix recommend different Mbps speeds for various resolutions, such as 3 Mbps for SD, 5 Mbps for HD, and 25 Mbps for 4K Ultra HD.
Mbps and Video Encoding
Video encoding processes like compression and decompression affect the Mbps of a video stream. Efficient encoding techniques can reduce the required Mbps without sacrificing video quality.
Mbps and Video Editing
When editing videos, the Mbps of the video files can impact the editing process. Higher Mbps files may require more processing power and storage space but can result in higher-quality final videos.
Mbps and Video Conferencing
In video conferencing, Mbps determines the quality and smoothness of video and audio transmission. A higher Mbps connection ensures a clearer and more stable video conferencing experience.
Mbps and Live Streaming
For live streaming, Mbps is crucial for maintaining a stable connection and transmitting video data in real-time. Higher Mbps connections are recommended for higher-quality live streams.
In conclusion, Mbps plays a vital role in video bitrate, impacting video quality, streaming smoothness, and overall viewing experience. Understanding Mbps in video bitrate can help you make informed decisions when streaming, editing, or hosting video content.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital communication and technology, understanding the meaning and significance of Mbps, or Megabits per second, is paramount. Mbps serves as a fundamental metric for measuring data transfer speeds, playing a crucial role in various aspects of our digital lives, from internet connectivity to video streaming and beyond.
At its core, Mbps represents the rate at which data is transmitted over a network. This measurement is instrumental in determining how quickly information can be sent and received, impacting the efficiency and performance of digital systems and services. Whether you're browsing the web, streaming videos, or engaging in online gaming, Mbps plays a pivotal role in ensuring a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
One of the key areas where Mbps is of utmost importance is in internet connectivity. When choosing an internet plan, the Mbps offered by the provider can significantly impact your online experience. Higher Mbps connections allow for faster downloads, smoother video streaming, and more responsive online gaming. Understanding your Mbps requirements based on your internet usage habits can help you select the right plan to meet your needs.
Moreover, Mbps is integral to video bitrate, which determines the quality and smoothness of video playback. Higher Mbps streams support higher resolutions, such as 1080p or 4K, delivering crisp, detailed images. Whether you're watching movies, TV shows, or live streams, Mbps ensures that you can enjoy high-quality video content without buffering or lag.
In addition to video streaming, Mbps also plays a crucial role in video editing and conferencing. Higher Mbps connections provide the necessary bandwidth for seamless video editing, allowing for faster file transfers and smoother playback. Similarly, in video conferencing, Mbps ensures clear and stable video and audio transmission, facilitating effective communication and collaboration.
Furthermore, Mbps is essential for live streaming, enabling content creators to deliver high-quality video content in real-time. Whether you're broadcasting a live event, webinar, or gaming session, Mbps ensures that your audience receives a smooth and immersive viewing experience.
In conclusion, Mbps is a fundamental metric that underpins the speed and efficiency of data transfer in the digital world. Whether you're browsing the web, streaming videos, or engaging in online communication, Mbps plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless and enjoyable user experience. By understanding the meaning and significance of Mbps, you can make informed decisions when it comes to selecting internet plans, streaming services, and digital tools, ultimately enhancing your digital experience.






![What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide] What Is Cold Data Storage? ❄️ [2026 Guide]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-cold-data-storage-750xAuto.webp)
![What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained] What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? 🖥️ [VDI Explained]](https://1gbits.com/cdn-cgi/image//https://s3.1gbits.com/blog/2026/02/what-is-virtual-desktop-infrastructure-vdi-750xAuto.webp)

