Virtualization technology has revolutionized the way operating systems and applications are managed, allowing users to create multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. This advancement has been particularly significant in the Linux ecosystem, offering a range of open-source and free virtualization solutions tailored for various needs. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the best virtualization software for Linux users, exploring their features, benefits, and suitability for different distributions.
Understanding Virtualization and Its Importance in Linux
Before talking about the best virtualization software for Linux, let’s see what are the virtualization software first. Virtualization in Linux involves creating virtual instances of hardware, operating systems, networks, or storage resources. This technology enables users to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single physical server, optimizing resource utilization and enhancing flexibility.
In the Linux ecosystem, virtualization plays a pivotal role by facilitating the creation and managemTop Virtualization Hardware for Maximum Efficiency
ent of virtual machines (VMs) that operate independently of the underlying hardware. It allows for the isolation of software environments, efficient resource allocation, and the ability to experiment with different operating systems and applications.
For more information about what is virtualization, check our article on this topic.
Key Considerations When Choosing Best Virtualization Software for Linux:
Before deciding what is the best virtualization software for Linux, several essential factors warrant consideration:
Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with your Linux distribution (e.g., Kali Linux, Arch Linux, Linux Mint) to guarantee seamless integration and functionality.
Feature Set: Evaluate features such as hardware support, performance, ease of use, and management capabilities offered by the software.
Security Features: Assess the security measures provided by the software to protect both the virtual machines and the underlying infrastructure.
Community Support: Consider software that enjoys active community-driven development and frequent updates for stability, bug fixes, and feature enhancements. This ensures ongoing support and improvement of the virtualization tool.
Top 5 Virtualization Software for Linux
1. Oracle VirtualBox
Oracle VirtualBox stands as one of the most popular and versatile open-source virtualization software available for Linux distributions, including Kali Linux, Arch Linux, and various others. Since its inception in 2007 by Oracle Corporation, VirtualBox has garnered widespread acclaim owing to its extensive compatibility and robust feature set.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- Cross-Platform Support: VirtualBox offers seamless compatibility across multiple host platforms, including Mac, Windows, Solaris, and Linux, enhancing its usability and versatility.
- User-Friendly Interface: Known for its intuitive user interface, VirtualBox simplifies the process of creating and managing virtual machines, making it accessible to both novice users and seasoned professionals.
- Diverse OS Support: If you’re looking for the best virtualization software for arch Linux, VirtualBox supports a wide array of guest operating systems, including various versions of Windows, Linux (2.4, 2.6, 3.x, 4.x), DOS, OpenBSD, Solaris, OpenSolaris, and OS/2.
- Advanced Functionality: VirtualBox comes packed with features like drag-and-drop functionality, shared folders, seamless mode, and support for SMP (Symmetric Multi-Processing) to enhance user experience and productivity.
- API Control: Offering a public API for controlling VM configuration and execution through programming languages like Python, XPCOM, SOAP, and Java, VirtualBox ensures flexibility and extensibility.
- Regular Updates and Community Support: Constantly updated by a vibrant community and Oracle, VirtualBox receives frequent releases, bug fixes, and feature enhancements, maintaining its reliability and stability.
Installing Oracle VirtualBox on Linux:
For users operating on Ubuntu, the installation process involves executing terminal commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install virtualbox
Additionally, users can install the VirtualBox Extension Pack to access additional functionalities:
sudo apt-get install virtualbox-ext-pack
Oracle VirtualBox's adaptability, comprehensive feature set, and continual development make it an ideal choice for users seeking a powerful and user-friendly virtualization solution within the Linux environment.
For a deeper understanding of virtualization frameworks, explore the different types of virtualization to see how each method shapes performance and resource management within Linux environments.
2. Linux KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine):
.png)
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) stands out as a robust virtualization solution integrated directly into the Linux kernel. Developed by the Linux Kernel Community and merged into the kernel since Linux version 2.6.20, KVM has evolved into a fundamental component of many Linux distributions, offering exceptional performance and security features.
For a deeper understanding of how KVM compares to other virtualization options, explore our detailed comparison in KVM vs LXC, where we break down the advantages and unique features of each technology.
Key Features and Advantages:
- Secure Virtualization: KVM ensures enhanced security through technologies like SELinux and sVirt, enabling robust security isolation for guest VMs. It facilitates mandatory Access Control (MAC), fortifying the security of the virtualized environments.
- Direct Hardware Access: As one of the options for the best virtualization software for Linux, KVM leverages a loadable kernel module (KVM.ko) to transform the Linux kernel into a hypervisor. This allows VMs direct access to underlying hardware resources, resulting in efficient performance and resource utilization.
- Diverse Storage Support: It offers compatibility with various storage Linux virtualization options supported by Linux, such as local disks and network-attached storage (NAS), enhancing storage flexibility for VMs.
- Live Migration and Dynamic Memory Management: KVM supports live migration, enabling seamless movement of running VMs between physical hosts without service interruption. Dynamic memory management optimizes memory allocation and usage across VMs.
- Flexible CPU Allocation: As one of the best virtualization software for Linux, KVM facilitates hotplug vCPUs, enabling users to add or remove virtual CPUs on-the-fly without disrupting the VM's operation. This flexibility enhances VM performance and scalability.
- Linux Process Integration: KVM treats each VM as a Linux process managed by the kernel, utilizing control groups, scheduler, real-time extensions, and network namespaces for efficient management and resource allocation. These feature make KVM the best virtualization software for Kali Linux.
Installing KVM on Ubuntu:
To install KVM on Ubuntu, users can execute the following commands in the terminal:
sudo apt-get install qemu-system libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon-system
For a minimal setup without graphical packages:
sudo apt-get install --no-install-recommends qemu-system libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon-system
3. GNOME Boxes
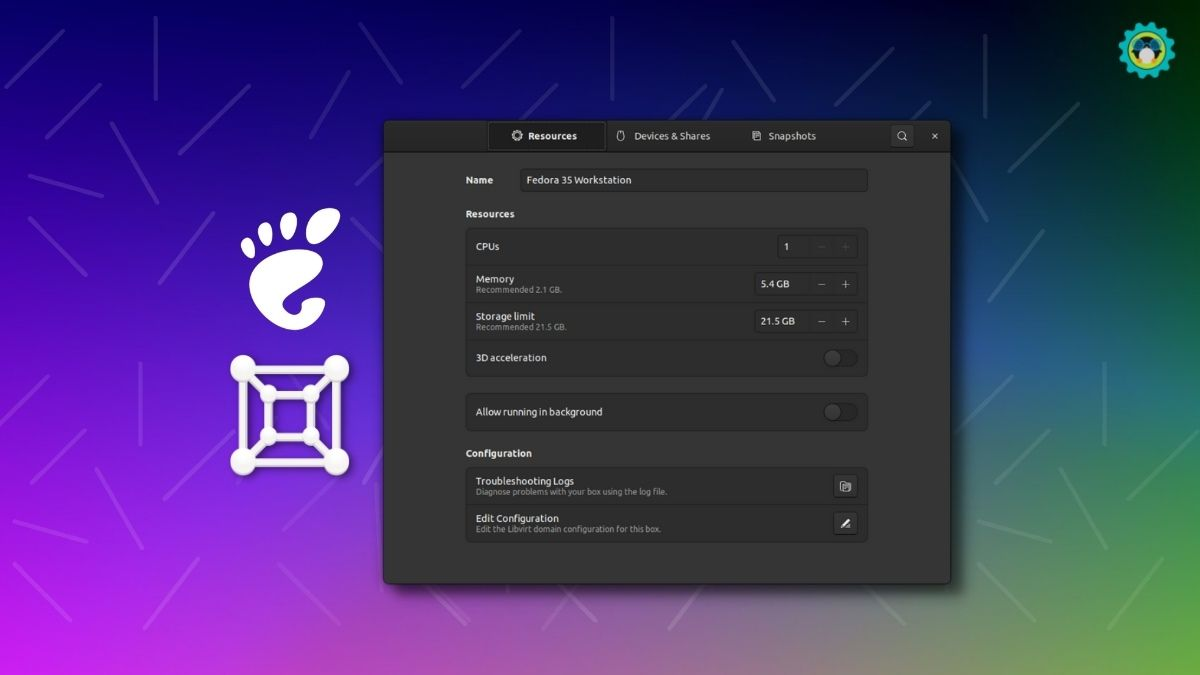
GNOME Boxes serves as a simple yet effective virtualization application designed primarily for Linux environments. As the default virtual machine software in many Linux distributions, including Fedora, GNOME Boxes offers an intuitive and hassle-free virtualization experience suitable for various users, including beginners and seasoned Linux enthusiasts.
Key Highlights and Features:
- Effortless Setup: GNOME Boxes streamlines the virtual machine setup process by employing a straightforward interface and a quick setup wizard. It ensures that even users new to Linux can easily deploy VMs without encountering complex configurations.
- Direct OS Loading: If you’re looking for the best free virtualization software for Linux, this software allows loading an operating system (OS) image directly from a URL, automatically detecting the OS and allocating sufficient resources like RAM and disk space for smooth operation.
- Cloning Feature: As one of the options for the best virtualization software for Linux free, GNOME Boxes features a clone function that enables users to create instant copies of existing virtual machines, facilitating swift deployment of multiple similar VMs.
- Command-Line Interface (CLI) Support: For advanced users familiar with command-line interfaces, GNOME Boxes offers a robust CLI, allowing greater control and customization.
- Basic Appearance with Competitive Functions: Although its appearance might seem basic, GNOME Boxes competently handles a variety of virtualization tasks and is on par with other more visually advanced virtualization solutions.
While GNOME Boxes may lack some advanced functionalities present in other Linux best virtualization software, its simplicity and ease of use make it an attractive option for Linux users seeking quick and best virtual machine for Linux on Windows 10 deployments. However, users might occasionally encounter minor performance issues, such as delays in accessing disk images or mouse release delays when switching back to the host OS.
For a deeper understanding of how virtualization compares to containerization and to decide which solution best suits your needs, check out our detailed comparison in Virtualization vs Containerization.
4. oVirt:
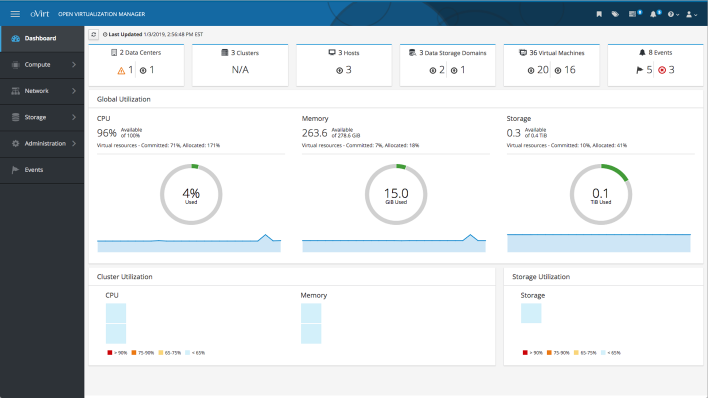
oVirt, a robust open-source virtualization management platform, emerges as a powerful tool designed for enterprises and communities seeking an advanced and feature-rich solution within the Linux environment. Founded by Red Hat as a community project, oVirt facilitates centralized management of Linux virtual machines (VMs), storage, compute, and networking resources through a user-friendly web interface.
Key Features and Capabilities:
- KVM Integration: Built upon Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM), oVirt leverages KVM's capabilities for x86-64 and PowerPC64 architectures, ensuring a stable and secure virtualization environment.
- Advanced Network Management: You might be wondering about how to enable virtualization in Linux. Offering comprehensive network management options, oVirt enables configuration of interfaces, gateways, subnet masks, and supports various storage backends such as NFS, FC, SCSI, and POSIX-compliant file systems.
- High Availability and Disaster Recovery: With features like live migration, live snapshots, and VM cloning, oVirt ensures high availability and disaster recovery readiness. It allows users to move running VMs between physical hosts seamlessly and restore systems in case of failure.
- Centralized Management Engine: As one of the options for the best virtualization software for Linux, The oVirt engine provides a centralized management interface equipped with programming interfaces and a graphical administration console, simplifying the deployment and administration of virtualized environments.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Integrating security features such as SELinux and sVirt, oVirt ensures enhanced security, access control, and isolation within the virtualized infrastructure.
Continuously evolving, the oVirt project aims to expand its support, promising future development for ARM architectures. It also introduces the oVirt Node, a lightweight hypervisor based on CentOS, serving as an advanced management interface with API support.
5. Proxmox
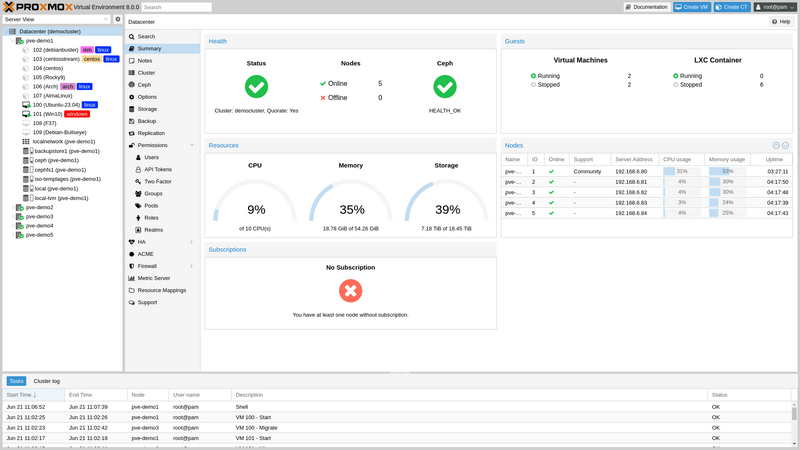
Proxmox, a Debian-based open-source virtualization management solution, offers a comprehensive platform for managing various virtualization technologies, including Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) for virtual machines and Linux Containers (LXC) for lightweight containerization. As one of the best virtualization software for Linux, this solution is designed to provide an efficient and user-friendly interface for managing virtual private servers (VPS) in isolated server environments on a single physical server.
Key Features and Functionalities:
- Support for Advanced Technologies: Proxmox supports Linux OpenVZ and KVM technologies, enabling the management of Virtual Private Servers in isolated environments while utilizing the latest Intel and AMD chipsets.
- Web-Based Interface: Its web interface, based on the ExtJS JavaScript framework, allows users to manage and configure virtual environments easily. Accessible via modern browsers, the interface offers a user-friendly environment for handling various aspects of virtualization.
- Cluster File System (pmxcfs): As one of the options for the best virtualization software for Linux, Proxmox incorporates the Proxmox Cluster File System, which facilitates database-driven file synchronization across clusters, streamlining configuration management.
- Live Migration and High Availability: Proxmox supports live or online migration, enabling the movement of running VMs between cluster nodes without downtime. Additionally, it includes high-availability features to enhance system reliability.
- Flexible Storage Options: Proxmox offers a flexible storage model where VM images can reside on local storage devices or shared storage solutions like SAN and NFS.
- Advanced Networking and Security: The built-in customizable firewall allows complex configurations via GUI or CLI, facilitating firewall rules for individual VMs, containers, or entire clusters. It supports features like firewall macros, security groups, IP sets, and aliases.
Proxmox incorporates a RESTful API using JSON as the primary data format, allowing seamless integration with third-party management tools and custom hosting environments. This integration capability streamlines the utilization of Proxmox in varied infrastructure setups.
For more information, you can check the top opensource virtualization software for Linux article.
Hardware Virtualization vs Software Virtualization
Now that you know about the best virtualization software for Linux, let’s compare hardware and software virtualization. Hardware and software virtualization are distinct approaches to creating virtualized environments, each with unique advantages and uses.
Hardware Virtualization:
- Uses specialized hardware components like processors with virtualization extensions (e.g., Intel VT-x, AMD-V) to manage virtual machines (VMs).
- Directly accesses physical hardware resources for VMs, ensuring robust isolation and efficient performance.
- Commonly applied in enterprise deployments, data centers, and cloud environments due to superior performance and strong isolation.
Software Virtualization:
- Involves software emulation to mimic hardware behavior and create virtual environments.
- Operates within the host OS, offering flexibility in running different OSes regardless of underlying hardware.
- Generally slower due to emulation overhead, suitable for running legacy apps or in scenarios lacking hardware virtualization.
Hardware virtualization excels in performance and isolation, ideal for resource-intensive applications, while software virtualization provides flexibility but may encounter performance overhead due to emulation. For more information, check our article about Top Virtualization Hardware for Maximum Efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing the best virtualization software for Linux depends on specific requirements, compatibility, and desired features. Oracle VirtualBox, Linux KVM, GNOME Boxes, oVirt, and Proxmox are among the top choices catering to diverse Linux distributions and user needs. Whether it's for personal use, enterprise-level deployments, or running Linux on Windows 10, these best virtualization for Linux solutions offer powerful capabilities, ensuring efficient resource utilization and seamless management of virtual environments in the Linux ecosystem. If you're looking to optimize your server's performance, you might want to [buy Linux VPS], which provides dedicated resources and enhanced control over your virtual environment.
People also read: